Logarithm: Concepts with Examples | Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Why do we study logarithms ? |

|
| What is a logarithm ? |

|
| The first law of logarithms |

|
| The second law of logarithms |

|
| The third law of logarithms |

|
| Standard bases |

|
Introduction
Introduction
In this unit we are going to be looking at logarithms. However, before we can deal with logarithms. we need to revise indices. This is because logarithms and indices are closely related, and in order to understand logarithms a good knowledge of indices is required.
We know that:16 = 24Here, the number 4 is the power. Sometimes we call it an exponent. Sometimes we call it an index. In the expression 24, the number 2 is called the base.Example
We know that 64 = 82.
In this example 2 is the power, or exponent, or index. The number 8 is the base.
Why do we study logarithms ?
In order to motivate our study of logarithms, consider the following:
we know that: 16 = 24.We also know that 8 = 23Suppose that we wanted to multiply 16 by 8.
One way is to carry out the multiplication directly using long-multiplication and obtain 128. But this could be long and tedious if the numbers were larger than 8 and 16. Can we do this calculation another way using the powers ?
Note that
16 × 8 can be written 24 × 23
This equals = 27
using the rules of indices which tell us to add the powers 4 and 3 to give the new power, 7. What was a multiplication sum has been reduced to an addition sum. Similarly if we wanted to divide 16 by 8:
16 ÷ 8= 24 ÷ 23
This equals = 21 or 2
using the rules of indices which tell us to subtract the powers 4 and 3 to give the new power, 1. If we had a look-up table containing powers of 2, it would be straightforward to look up 27 and obtain 27 = 128 as the result of finding 16 × 8.
Notice that by using the powers, we have changed a multiplication problem into one involving addition (the addition of the powers, 4 and 3). Historically, this observation led John Napier (1550-1617) and Henry Briggs (1561-1630) to develop logarithms as a way of replacing multiplication with addition, and also division with subtraction.
What is a logarithm ?
Consider the expression 16 = 24. Remember that 2 is the base, and 4 is the power. An alternative, yet equivalent, way of writing this expression is log₂16 = 4. This is stated as ‘log to base 2 of 16 equals 4’. We see that the logarithm is the same as the power or index in the original expression. It is the base in the original expression which becomes the base of the logarithm.
The two statements
- 16 = 24
- log2 16 = 4
are equivalent statements. If we write either of them, we are automatically implying the other.
Example
- If we write down that 64 = 82 then the equivalent statement using logarithms is log₈64 = 2.
Example
- If we write down that log₃27 = 3 then the equivalent statement using powers is 33 = 27.
So the two sets of statements, one involving powers and one involving logarithms are equivalent.In the general case we have:
Key Point
if x = an then equivalently loga x = n
loga a = 1
Let us develop this a little more.
Because 10 = 101 we can write the equivalent logarithmic form: log10 10 = 1.Similarly, the logarithmic form of the statement 21 = 2 is log₂2 = 1.
In general, for any base a, a = a1 and so loga a = 1
We can see from the Examples above that indices and logarithms are very closely related. In the same way that we have rules or laws of indices, we have laws of logarithms. These are developed in the following sections.
The first law of logarithms
Suppose
x = an and y = am
then the equivalent logarithmic forms are
loga x = n and loga y = m .....(1)
Using the first rule of indicesxy = an× am = an+m
Now the logarithmic form of the statement xy = an+m is loga xy = n + m. But n = loga x and m = loga y from (1) and so putting these results together we have
loga xy = loga x + loga y
So, if we want to multiply two numbers together and find the logarithm of the result, we can do this by adding together the logarithms of the two numbers. This is the first law.
Key Point
loga xy = loga x + loga y
The second law of logarithms
Suppose x = an, or equivalently loga x = n. Suppose we raise both sides of x = an to the power m:
xm = (an)m
Using the rules of indices we can write this as
xm = anm
Thinking of the quantity xm as a single term, the logarithmic form is
loga xm = nm = mloga x
This is the second law. It states that when finding the logarithm of a power of a number, this can be evaluated by multiplying the logarithm of the number by that power.
Key Pointloga xm = mloga x
The third law of logarithms
As before, suppose
x = an and y = am
with equivalent logarithmic forms
loga x = n and loga y = m ....(2)
Consider x ÷ y.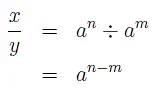 using the rules of indices.In logarithmic form
using the rules of indices.In logarithmic form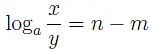 which from (2) can be written
which from (2) can be written This is the third law.
This is the third law.
Key Point
The logarithm of 1
Recall that any number raised to the power zero is 1: a0 = 1. The logarithmic form of this isloga 1 = 0Key Point
loga 1 = 0
The logarithm of 1 in any base is 0.
Logarithmic Formulas Summarized:
- logb(mn) = logb(m) + logb(n)
- logb(m/n) = logb (m) – logb (n)
- logb (xy) = y logb(x)
- m logb(x) + n logb(y) = logb(xmyn)
- logb(m+n) = logb m + logb(1+nm)
- logb(m – n) = logb m + logb (1-n/m)
Examples
Example 1: Suppose we wish to find log2 512.
This is the same as being asked ‘what is 512 expressed as a power of 2 ?’
Now 512 is in fact 29 and so log2 512 = 9.Example2: Suppose we wish to find log8 1/64
This is the same as being asked ‘what is 1/64 expressed as a power of 8 ?’
Now 1/64 can be written 64−1. Noting also that 82 = 64 it follows that using the rules of indices. So log8 = 1/64 = -2Example3: Suppose we wish to find log5 25.
using the rules of indices. So log8 = 1/64 = -2Example3: Suppose we wish to find log5 25.
This is the same as being asked ‘what is 25 expressed as a power of 5 ?’
Now 52 = 25 and so log5 25 = 2.Example4: Suppose we wish to find log25 5.
This is the same as being asked ‘what is 5 expressed as a power of 25 ?’
We know that 5 is a square root of 25, that is 5 = √25. So 25 1/2 = 5 and so log25 5 = 1/2.
Notice from the last two examples that by interchanging the base and the numberThis is true more generally:
Key Point
Example5: Consider log2 8. We are asking ‘what is 8 expressed as a power of 2 ?’ We know that 8 = 23 and so log2 8 = 3.
What about log8 2 ? Now we are asking ‘what is 2 expressed as a power of 8 ?’ Now 23 = 8 and so 2 = ∛8 or 81/3. So log8 2 =1/3.We see again
Standard bases
There are two bases which are used much more commonly than any others and deserve special mention. These are:
base 10 and base eLogarithms to base 10, log10, are often written simply as log without explicitly writing a base down. So if you see an expression like log x you can assume the base is 10. Your calculator will be pre-programmed to evaluate logarithms to base 10. Look for the button marked log.
The second common base is e. The symbol e is called the exponential constant and has a value approximately equal to 2.718. This is a number like π in the sense that it has an infinite decimal expansion. Base e is used because this constant occurs frequently in the mathematical modelling of many physical, biological and economic applications. Logarithms to base e, loge, are often written simply as ln. If you see an expression like ln x you can assume the base is e. Such logarithms are also called Naperian or natural logarithms. Your calculator will be pre-programmed to evaluate logarithms to base e. Look for the button marked ln.
Key Point
Common bases:where e is the exponential constant. Useful results: log 10 = 1, ln e = 1
Using logarithms to solve equations
Using logarithms to solve equations
We can use logarithms to solve equations where the unknown is in the power. Suppose we wish to solve the equation 3x = 5. We can solve this by taking logarithms of both sides. Whilst logarithms to any base can be used, it is common practice to use base 10, as these are readily available on your calculator. So, log 3x = log 5
Now using the laws of logarithms, the left hand side can be re-written to give
x log 3 = log 5
This is more straight forward. The unknown is no longer in the power. Straightaway If we wanted, this value can be found from a calculator.
If we wanted, this value can be found from a calculator.
|
209 videos|443 docs|143 tests
|
FAQs on Logarithm: Concepts with Examples - Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the importance of studying logarithms? |  |
| 2. Can you explain what a logarithm is in simple terms? |  |
| 3. What are the three laws of logarithms and how are they used? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of logarithms with standard bases? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of logarithms in real life? |  |
|
209 videos|443 docs|143 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
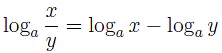
 using the rules of indices. So log8 = 1/64 = -2Example3: Suppose we wish to find log5 25.
using the rules of indices. So log8 = 1/64 = -2Example3: Suppose we wish to find log5 25. This is true more generally:
This is true more generally:
 where e is the exponential constant. Useful results: log 10 = 1, ln e = 1
where e is the exponential constant. Useful results: log 10 = 1, ln e = 1
















