Daily Current Affairs UPSC- 7th October 2022 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
National Commission for Women
Context
The National Commission for Women (NCW) recently has summoned Congress leader over his “sycophancy” remark against the President of India.
- Droupadi Murmu is India’s first tribal woman President of India.
About NCW:
- It was set up as statutory body in 1992 under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990
- It aims to review the Constitutional and Legal safeguards for women; recommend remedial legislative measures; facilitate redressal of grievances and advise the Government on all policy matters affecting women.
- The Commission shall consist of :-
- A Chairperson, nominated by the Central Government.
- Five Members with expertise in law and issues related to women, nominated by the Central Government.
- At least one Member each shall be from amongst persons belonging to the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes respectively
- Member Secretary must be a central gazetted officer having management and sociological expertise and nominated by the Central Government.
- The National Commission for Women submits all its reports to the Central Government, which is laid before the Parliament during sessions.
- During the investigation of any matter before it, National Commission for Women has all the powers of a civil court.
Functions:
- Inquiry, Investigation and Examination of matters related to safeguards of women
- Recommendation: to the Union as well State regarding improving the conditions of the women.
- Review different laws related to women and suggest amendments to them.
- Violation Cases: Takes up violation cases pertaining to the provisions of the Constitution and other laws related to women.
- Suo-Moto Notice on matters pertaining to deprivation of women’s rights, non-implementation of laws, non-compliance policy decisions related to women etc.
- Research: Undertake promotional and educational research to find ways to represent women in all spheres of life and improve their efficiency.
- Planning: Participate in the process of planning related to the socio-economic development of women.
- Progress Evaluation: Evaluate the progress related to the development of women in the State and the Union.
- Inspection: Inspect the jail, remand homes etc., where women are kept as prisoners.
- Funding: Litigations relating to funds affecting large women body.
Achievements:
- The Commission prepared Gender Profiles to assess the status of women and their empowerment.
- It acted suo-moto in several cases to provide speedy justice.
- It took up the issue of child marriage, sponsored legal awareness programmes, Parivarik Mahila Lok Adalats and reviewed laws such as Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961, PNDT Act 1994, Indian Penal Code 1860 to make them more stringent and effective
- It organized workshops/consultations, constituted expert committees on economic empowerment of women, conducted workshops/seminars for gender awareness and took up publicity campaign against female foeticide, violence against women etc. in order to generate awareness in the society against these social evils.
- The commission regularly brings out a monthly newsletter called “Rashtra Mahila”.
Green Steel
Context
A clean steel sector in Eastern India can become essential for the country's transition to ‘Green Steel’.
- To move towards ‘Green Steel’, the Petroleum and Natural Gas Ministry launched Pradhan Mantri Urja Ganga Project in Eastern India in 2019 to provide gas to all steel plants located in the area.
What is Green Steel?
- About:
- Green Steel is the manufacturing of steel without the use of fossil fuels.
- This can be done by using low-carbon energy sources such as hydrogen, coal gasification, or electricity instead of the traditional carbon-intensive manufacturing route of coal-fired plants.
- It eventually lowers greenhouse gas emissions, cuts costs and improves the quality of steel.
- Low-carbon hydrogen (blue hydrogen and green hydrogen) can help reduce the steel industry’s carbon footprint.
- National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHM) capitalizes on hydrogen for a cleaner alternative fuel option.
- Ways of Production:
- Substituting the Primary Production Processes with Cleaner Alternatives:
- Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS)
- Replacing conventional sources of energy with low-carbon hydrogen
- Direct electrification through electrolysis of iron ore
- Substituting the Primary Production Processes with Cleaner Alternatives:
- Significance:
- The steel industry is the largest industrial sector in terms of intensive energy and resource use. It is one of the biggest emitters of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- In view of commitments made at the Conference of the Parties (COP26) climate change conference, the Indian steel industry needs to reduce its emissions substantially by 2030 and hit net-zero carbon emissions by 2070.
- Challenge:
- At present, the country’s iron and steel sector is financially weak. However, Green Steel manufacturing is an expensive process involving high cost.
What is the Status of Steel Production in India?
- Production: India is currently the world’s 2nd largest producer of crude steel, producing 120 Million Tonnes (MT) crude steel during financial year 2021- 2022.
- Reserves: More than 80 per cent of the country’s reserves are in the states of Odisha, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh and the northern regions of Andhra Pradesh. Important steel-producing centers are Bhilai (Chhattisgarh), Durgapur (West Bengal), Burnpur (West Bengal), Jamshedpur (Jharkhand), Rourkela (Odisha), Bokaro (Jharkhand).
- Consumption: India is the 2nd largest consumer of finished steel in 2021 (106.23 MT), preceded by China as the largest steel consumer as per World Steel Association.
Way Forward
- Cost-effective technologies must be adopted to decarbonize the steel sector. Many old plants need to be refurbished and energy efficiency measures for electricity-based manufacturing have bright prospects for further investment.
- Scrap can be utilized in lowering the energy used for making steel for which a suitable infrastructure for recycling and the Steel Scrap Recycling Policy needs to be constructed.
- The government and public sector should commit to the purchase of environmentally sustainable green steel to drive the demand for the same.
- Public and Private sectors need to generate green standards and similar types of labels for the market growth of green steel.
- Old and polluting plant facilities, which have reached the end of their life, should be removed.
‘herSTART’ platform

Context
The President of India recently launched ‘herSTART’, an initiative of the Gujarat University Startup and Entrepreneurship Council (GUSEC) aimed at supporting women-led startups.
- The President also laid the foundation stone for various projects related to education and tribal development in Gujarat.
About:
- The platform will include a digital platform to provide resources and training modules free of cost to aspiring women entrepreneurs, a digital community for them, and a digital publication to spread their success stories.
- The Platform encompasses the herSTART Incubator, a dedicated full-fledged Startup incubator for women entrepreneurs and innovators, and the herSTART Accelerator, a round-the-year accelerator programme for high-impact women-led startups.
- Gujarat is the first state in the country to form the Garima Cell with the aim of giving new energy and direction to the higher education system of the state.
Significance:
- The ‘herSTART’ platform will boost innovation and start-up efforts of women entrepreneurs and also help them connect with various government and private enterprises.
- Employment generation: through 450 Startup projects operational in Gujarat University. Of these, 125 startups specially inspired by entrepreneurial women are giving a new direction to the entrepreneurship and innovative ideas in women.
- India has moved from 81st position to 40th position in the Global Innovation Index (GII) of 2022 as a result of the Startup program.Reduction in the drop-out rate among the students of the tribal community due to Vanabandhu Kalyan Yojana, Eklavya Model Residential School and Kanya Nivasi Shala.
- Real-time monitoring of the education system of more than 55,000 schools in the state by the Vidya Review Centre.
- Upgrading the infrastructure of about 20,000 schools of the state through Mission School of Excellence.
Poverty and Shared Prosperity 2022: Correcting Course
Context
Recently, the World Bank released a report titled “Poverty and Shared Prosperity 2022: Correcting Course”.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Global Poverty Reduction:
- Global poverty reduction has been slowing down since 2015 but the Covid pandemic and the war in Ukraine have completely reversed the outcomes.
- By 2015, the global extreme-poverty rate had been cut by more than half.
- Since then, poverty reduction has slowed in tandem with subdued global economic growth.
- As such, the global goal of ending extreme poverty by 2030 would not be achieved.
- People living below the Poverty Line:
- In 2020 alone, the number of people living below the extreme poverty line rose by over 70 million; the largest one-year increase since global poverty monitoring began in 1990.
- Given current trends, 574 million people—nearly 7% of the world’s population—will still be living on less than USD 2.15 a day in 2030, with most in Africa.
- Rise in Inequalities:
- The poorest people bore the steepest costs of the pandemic: Income losses averaged 4% for the poorest 40%, double the losses of the wealthiest 20% of the income distribution.
- Global inequality rose, as a result, for the first time in decades.
- Global median income declined by 4% in 2020—the first decline since measurements of median income began in 1990.
What are the Suggestions?
- National policy reforms can help restart progress in reducing poverty.
- Stepped-up global cooperation will also be necessary.
- In fiscal policy, governments should act promptly on three fronts:
- Avoid Broad Subsidies, increase targeted cash transfers:
- Half of all spending on energy subsidies in low- and middle- income economies go to the richest 20% of the population who consume more energy.
- Cash transfers are a far more effective mechanism for supporting poor and vulnerable groups.
- Focus on Long-Term Growth:
- High-return investments in education, research and development, and infrastructure projects need to be made today.
- In a time of scarce resources, more efficient spending and improved preparation for the next crisis will be key.
- Mobilize Domestic Revenues without Hurting the Poor:
- Property taxes and carbon taxes can help raise revenue without hurting the poorest.
- So can broadening the base of personal and corporate income taxes.
- If sales and excise taxes do need to be raised, governments should minimize economic distortions and negative distributional impacts by simultaneously using targeted cash transfers to offset their effects on the most vulnerable households.
What is the State of Poverty in India?
- About:
- According to the World Bank published the paper titled 'Poverty has Declined over the Last Decade But Not As Much As Previously Thought'.
- Extreme poverty in India was 12.3% points lower in 2019 compared with 2011, as poverty headcount rate declined from 22.5% in 2011 to 10.2% in 2019, with a comparatively sharper decline in rural areas.
- Poverty reduction was higher in rural areas compared with urban India as rural poverty declined from 26.3% in 2011 to 11.6% in 2019, while in urban areas the decline was from 14.2% to 6.3% in the corresponding period.
- Poverty Estimation:
- Poverty estimation in India is carried out by NITI Aayog’s task force through the calculation of poverty line based on the data captured by the National Sample Survey Office under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI).
- Poverty line estimation in India is based on the consumption expenditure and not on the income levels.
Recent Measures Taken:
- Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana
- National Old Age Pension Scheme
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) 2005
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM)
- National Urban Livelihood Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana
GS-III
Digital Services Act (DSA): EU
Context
The European Union (EU) has given final approval to online safety-focused legislation called Digital Services Act (DSA), which is an overhaul of the region’s social media and e-commerce rules.
What is the Digital Services Act?
- About:
- As defined by the EU Commission, the DSA is “a set of common rules on intermediaries’ obligations and accountability across the single market”, and ensures higher protection to all EU users, irrespective of their country.
- Objective:
- The DSA will tightly regulate the way intermediaries, especially large platforms such as Google, Facebook, and YouTube, function when it comes to moderating user content.
What are the Features of the Digital Services Act?
- Faster Removals and Provisions to Challenge:
- As part of the overhaul, social media companies will have to add “new procedures for faster removal” of content deemed illegal or harmful.
- They will also have to explain to users how their content takedown policy works.
- The DSA also allows users to challenge takedown decisions taken by platforms and seek out-of-court settlements.
- Bigger Platforms have Greater Responsibility:
- The law avoids a one-size fits all approach and places increased accountability on the Big Tech companies.
- Under the DSA, ‘Very Large Online Platforms’ (VLOPs) and ‘Very Large Online Search Engines’ (VLOSEs), that is platforms, having more than 45 million users in the EU, will have more stringent requirements.
- Direct Supervision by the European Commission:
- The European Commission will be responsible for centrally supervising these requirements and their enforcement.
- More Transparency on how Algorithms Work:
- VLOPs and VLOSEs will face transparency measures and scrutiny of how their algorithms work.
- These platforms will be required to conduct systemic risk analysis and reduction to drive accountability about the society impacts of their products.
- VLOPs must allow regulators to access their data to assess compliance and let researchers access their data to identify systemic risks of illegal or harmful content.
- Clearer Identifiers for ads and who’s Paying for them:
- Online platforms must ensure that users can easily identify advertisements and understand who presents or pays for the advertisement.
- They must not display personalised advertising directed towards minors or based on sensitive personal data.
How does the EU’s DSA compare with India’s Online Laws?
Information Technology Rules, 2021 (IT Rules):
- About:
- In February 2021, India had notified extensive changes to its social media regulations in the form of the Information Technology Rules, 2021 (IT Rules) which placed significant due diligence requirements on large social media platforms such as Meta and Twitter.
- These included appointing key personnel to handle law enforcement requests and user grievances, enabling identification of the first originator of the information on its platform under certain conditions, and deploying technology-based measures on a best-effort basis to identify certain types of content.
- One of the most contentious proposals is the creation of government-backed grievance appellate committees which would have the authority to review and revoke content moderation decisions taken by platforms.
- Objection to the Law:
- Social media companies have objected to some of the provisions in the IT Rules, and WhatsApp has filed a case against a requirement which mandates it to trace the first originator of a message.
- One of the reasons that the platform may be required to trace the originator is if a user has shared child sexual abuse material on its platform.
- WhatsApp has, however, alleged that the requirement will dilute the encryption security on its platform and could compromise personal messages of millions of Indians.
- IT Act, 2000:
- India is also working on a complete overhaul of its technology policies and is expected to soon come out with a replacement of its IT Act, 2000.
- It is expected to look at ensuring net neutrality and algorithmic accountability of social media platforms among other things.
Sugar Production in India
Context
India emerges as the world’s largest producer and consumer of sugar and world’s 2nd largest exporter of sugar.
- In Sugar Season (Oct-Sep) 2021-22, a record of more than 5000 Lakh Metric Tons (LMT) sugarcane was produced in the country
- With this, India has emerged as the world’s largest producer and consumer of sugar as well as the world’s 2nd largest exporter of sugar.
- Maharashtra emerged as the highest sugar exporter and producer in India in 2021-22 Sugar Season (SS) exporting almost 60 per cent of total exports in India.
- Supportive international prices and Indian Government Policy led to this feat of Indian Sugar Industry.
- The exports earned foreign currency of about Rs. 40,000 crores for the country.
Factors that led to largest Producer of Sugar:
- Synchronous and collaborative efforts of Central and State Governments, farmers, sugar mills, ethanol distilleries with very supportive overall ecosystem for business in the country led to this feat.
- During 2021-22, sugar mills procured sugarcane worth more than 1.18 lakh with no financial assistance (subsidy) from Government of India.
- 95% of cane dues have already been cleared.
- In 2020-21, more than 99.9% cane dues are cleared.
- Scheme for Extending Financial Assistance to Sugar Undertakings (SEFASU) and National Policy on Biofuels are two of the government initiatives to support sugarcane production and the sugar industry.
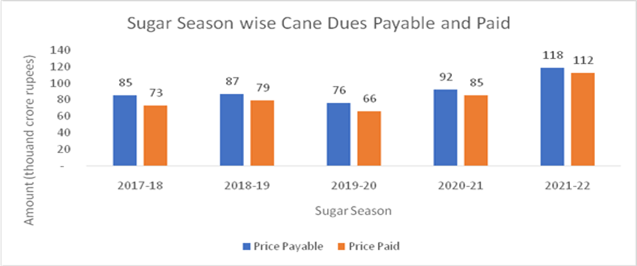
Ethanol Production:
- Government has been encouraging sugar mills to divert sugar to ethanol.
- Growth of ethanol as biofuel sector in last 5 years has amply supported the sugar sector as use of sugar to ethanol has led to better financial positions of sugar mills due to:
- faster payments,
- reduced working capital requirements and
- less blockage of funds due to less surplus sugar with mills.
- Ethanol production capacity of molasses/sugar-based distilleries has increased to 605 crore liters per annum and the progress is still continuing to meet targets of 20% blending by 2025 under Ethanol Blending with Petrol (EBP) Programme.
- In new season, the diversion of sugar to ethanol is expected to increase from 35 LMT to 50 LMT which would generate revenue for sugar mills amounting to about ₹ 25,000 crores.
Sugarcane Cultivated:
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
- Top Sugarcane Producing States: Maharashtra>Uttar Pradesh > Karnataka
- It can be grown on all varieties of soils ranging from sandy loam to clay loam given these soils should be well drained.
- It needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting.
- It is the main source of sugar, Gur (jaggery), khandsari and molasses.
Nobel Prize Chemistry 2022
Context
This year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry has gone to Carolyn Bertozzi and Barry Sharpless of the United States and Morten Meldal of Denmark who have made a strong case for adopting an alternative approach to producing new complex molecules, which minimises waste and increases overall efficiency.
About:
- Sharpless is the originator of the concept of ‘Click Chemistry’.
- He found the first chemical reaction that satisfied the criteria for ‘Click’ reactions using a nitrogen-containing cyclic compound and discovered that use of copper as a catalyst eliminated the by-products.
- Carolyn Bertozzi in 2004 developed a few ‘click’ reactions that work inside living organisms.
- The name “Click”, has been taken from the click sound that airline seat belts make when they are fastened.
- While trying to produce any particular compound or a complex molecule, one must look for starting molecules that easily react with each other or fit into each other, or ‘click’ with each other.
- The reacting molecules should be in a made-for-each-other kind of situation for this particular reaction.
- This makes the resultant chemical reaction more efficient.
Significance:
- Mimicking nature is expected to bring in effectiveness and sustainability in man-made processes and products as well.
- Vast potential in the pharmaceutical industry – The industry uses a lot of naturally occurring but industrially synthesised molecules. Every kilogram of a drug produced results in the generation of nearly 25-100 kg of chemical waste, making it inefficient.
- Bertozzi’s methods have shown the promise of treating advanced cancer. Cancer drugs based on her approach are now undergoing clinical trials.
GS- IV
Abortion Rights Vs Ethics
Context
Recently, in a landmark judgment, the Supreme Court of India allowed abortions up to 24 weeks for all women, including unmarried women.
Why is there a Debate over Abortion Rights and the Ethical Dilemma?
Issues with Respect to Women’s Right:
- Woman’s Right over her Body:
- A woman's right over her body has been advocated as a premise for freedom.
- One cannot force a woman to bear a child in her womb and give birth to a child if she does not want to do so for various reasons.
- Health:
- Unwanted pregnancies affect both physical and mental health.
- Gender Equality:
- The right to abortion is vital for gender equality.
- The right to abortion should be part of a portfolio of pregnancy rights that enables women to make a truly free choice whether to end a pregnancy.
Issues with respect to Feotus:
- Right to Life: Abortion amounts to the murder of a living being.
- Motherly Care: It is a unique unspoken bond shared between two lives, which cannot be questioned or regulated by laws.
Issues with respect to Society in General:
- Responsibility of State: The State has the responsibility of valuing each life.
- Inclusion of all: Abortion should not become a mechanism of social control for avoiding the appearance of differences or disabilities.
- Giving better life for Existing Children: Many times, parents want abortion to be able to give a good life to existing children instead of dividing their meager resources into more children.
What are the Arguments against Abortion?
- Abortion is not viewed by some as liberating, but rather as a way for society not to cater to women's needs.
- Women don't need free abortion access, but their needs for financial and social survival as mothers are what they need for equality:
- inexpensive, readily available childcare
- a workplace or school that acknowledges the needs of mothers,
- e.g., providing flexible scheduling and maternity leave,
- state support that helps to reintegrate a woman into the workforce
What should be the Ethical approach to Abortion?
- Ethical approaches to abortion frequently invoke four principles.
- Respect for patients’ autonomy
- Nonmaleficence (do no harm)
- Beneficence (beneficial care) and
- Justice
- The abortion dilemma has overlapping issues from different realms like legal, medical, ethical, philosophical, religious and human rights and it should be analysed from different perspectives.
- There cannot be any hard and fast rule over abortion and it must be discussed and deliberated to evolve a common consensus.
|
39 videos|4287 docs|905 tests
|
FAQs on Daily Current Affairs UPSC- 7th October 2022 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the important topics covered in GS-II? |  |
| 2. What are the key areas of focus in GS-III? |  |
| 3. How can one prepare for GS-IV, also known as the Ethics, Integrity, and Aptitude paper? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of daily current affairs in UPSC preparation? |  |
| 5. How can one effectively utilize the daily current affairs for UPSC preparation? |  |
|
39 videos|4287 docs|905 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

























