AC Distribution System | Power Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Introduction
- A system where electrical energy is distributed among the consumers from generating stations or substations in the form of AC is an AC distribution system. In other words, the electric system between the transmission systems step-down substation and the consumer’s meter is known as the ac distribution system.
- It is divided into two systems, namely primary and secondary ac distribution systems.
- This section will cover the topic of the ac distribution system along with its classification. Under the classification, we will discuss the feeders, their types, and the three-phase and single-phase AC distribution system.
Primary AC Distribution System
In primary AC distribution, the distribution system is of a 3-phase, 3-wire system.
Operating Voltage: usually 11kV.
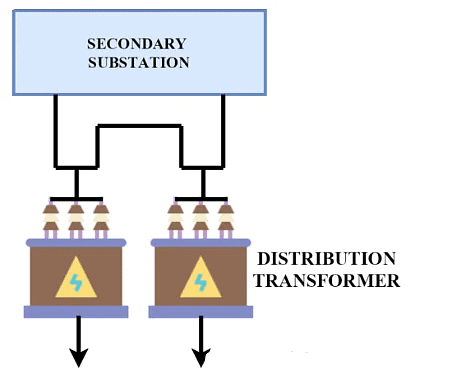
- The electrical power generated at the generating stations is transmitted at a transmission voltage of voltage above 33kV. This power is transmitted up to the substations located at various places (such as load centers or cities). These substations are termed secondary substations.
- In the secondary substation, the voltage is stepped down to a level of 11kV.
- The area which has a load requirement of about 5MVA employs 33/11kV substation and 3-4 outgoing feeders each carrying a load of 1-2 MVA.
- For loads above 8MVA, secondary substations are of 66/11kV, and transmission is done at 66kV which results in reduced line losses in the system.
- The number of outgoing feeders from substations having a load requirement of about 8MVA is 6 to 8.
- Now we will discuss the various types of feeders that emerge from the secondary substation.
Types of Feeders in Primary AC Distribution
The following are the types of feeders in the primary ac distribution system.
1. Radial Feeders
- Radial feeders have the simplest design and are economical. Most primary ac distribution systems employ radial feeders.

Here, the feeder line originates from the secondary substation and branches into sub-feeders and laterals and it extends over all the areas where the power is to be served.
A distribution transformer of 11kV/415V connects the feeder and distributer.
Disadvantage:
- Poor reliability
- Poor Voltage Regulation
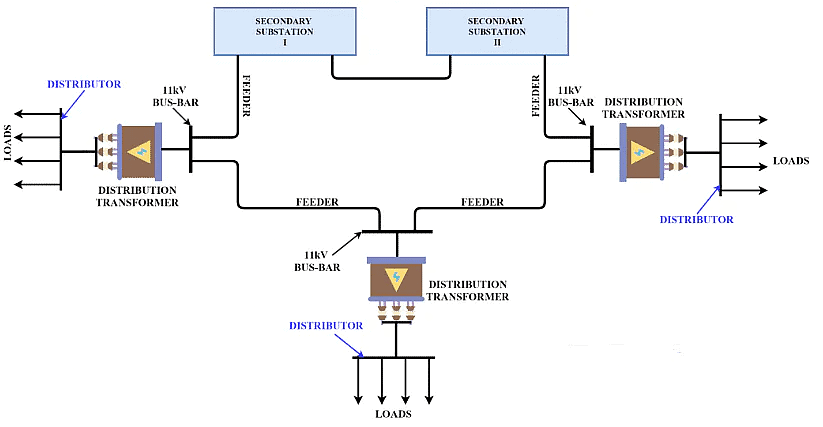
2. Parallel Feeders
- Parallel Feeders are more reliable than the radial feeder, as in the parallel feeders two radial feeders originate from the substation which supplies the power to the load in parallel. During fault or failure, a healthy system is employed where the reliability of the system and continuity of supply is of utmost importance. This system is expensive than radial.

3. Loop Feeders
- This feeder system is the most reliable and ensures the continuity of supply during the abnormal conditions of the distribution system network.

- It has better voltage regulation and less power loss.
- Here, two or more radial feeder originates from the secondary substation that is laid on different routes of the loads and is finally tied together.
- If the feeder lines are tied through the normally open switch, they are called an open-loop system and if they are tied with a normally closed switch they are called ring main feeders.
- This system of ac power distribution requires a huge amount of investment.
4. Interconnected Network System
- The feeder ring main is powered by two or more power stations or substations in an interconnected network system. This system ensures better reliability and flexibility.

- An interconnected network of the primary distribution system is employed in large cities, metropolitan areas where the continuity of supply is of utmost importance.
Secondary AC Distribution System
- The electrical power generated at the generating stations is transmitted through the transmission system up to the secondary substation and from the secondary substation, this power is distributed by the primary ac distribution system and then by the secondary ac distribution system to the consumers or loads.
- In practical life, the electrical loads of different consumers vary from one another. Due to this variation, the loads are unbalanced and for unbalanced load, 3-phase, 4-wire system is employed for the ac distribution of electrical power.
- The 3-phase, 4 wire system makes it easy to distribute the power to end loads at the single-phase as most of the lighting loads and small appliances work on single-phase ac. Also, the unbalanced load introduces unbalance currents and in a 3-phase, 4 wire system has a neutral wire through which the unbalance current can flow.
Three-Phase 4-wire AC Distribution System
The figure below portrays a three-phase, 4-wire ac distribution system.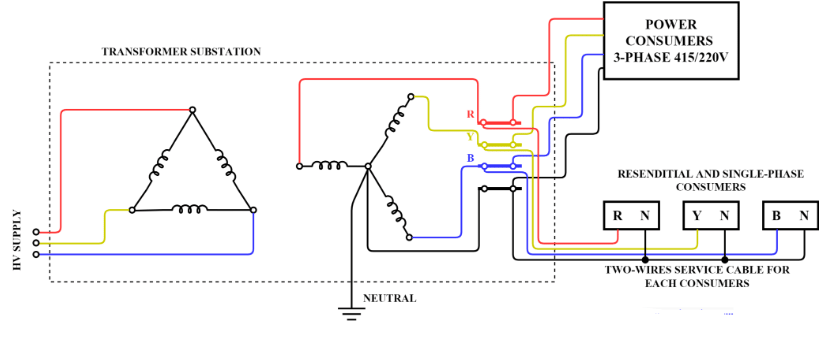
- Here, a transformer substation is located at the load center.
- The transformer substation is equipped with high voltage switchgear and bus bars, low voltages fuses or links, and MCCB (Modulated Case Circuit Breaker).
- The primary transformer is supplied by high voltage feeder cables, the secondary low voltage bus-bars are color-coded with respective phase colors such as red for the R phase, yellow for the Y phase, and blue for the B phase. For neutral, black color is used.
- Large commercial and industrial consumers who require power in bulk take power in a three-phase system itself.
Single Phase Two Wire AC Distribution System
- For the residential consumers who utilize electrical power mainly for lighting and running small rating electrical appliances, they are supplied with a single-phase two-wire distribution system.
- A concentric cable or multi-core (two-core) cable can be used for this purpose.
Types of Secondary AC Distribution
The following are the types of feeders in the secondary ac distribution system.
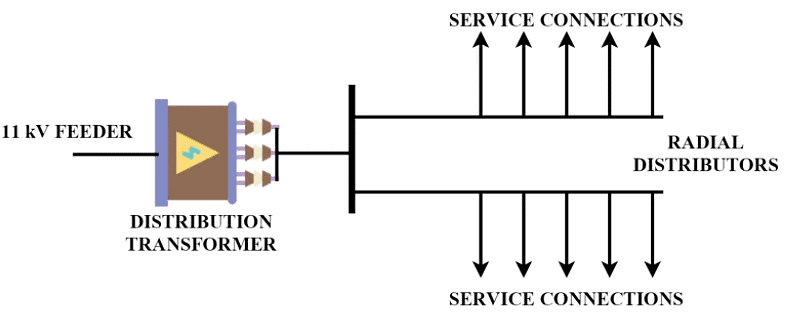
1. Radial Feeders
- In a radial system, a low voltage distributor radiated out from a single distribution transformer and distributes power along the area through which the distributor runs.

- It is the simplest and least expensive distribution system.
- The main drawback of this system is that it has poor voltage regulation, less
2. Open-Loop System
- In an open-loop system, two low voltage distributors run from a single distribution transformer thereby supplying power to the area through which it runs. The two distributors are then tied up by a normally open switch at the far end.

- This system of distribution somewhat improves the reliability compared to the radial system of distribution. During the event of a fault on one of the distributors, the power can be supplied from another distributor.
3. Network System of Distribution
- In a network system of distribution, power is supplied from two or more distribution transformers through interconnected distribution lines.

- Such a system finds its best application and advantage to supply power in high-load density areas such as metropolitan cities.
- This system of ac distribution increases the reliability of the distribution system, improves voltage regulation, and provides better load distribution.
|
21 videos|67 docs|45 tests
|