Important Formulas: Rational Numbers | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Type of Numbers
1. Numbers
N = {1,2,3,4,5……….}
It is the counting numbers
2. Whole number
W= {0,1,2,3,4,5……..}
It is the counting numbers + zero
3. Integers
Z={…-7,-6,-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6…}
4. Positive integers
Z+= {1,2,3,4,5……..}
5. Negative integers
Z-={…-7,-6,-5,-4,-3,-2,-1}
6. Rational Number: A number is called rational if it can be expressed in the form p/q where p and q are integers (q> 0).
Example: ½, 4/3 ,5/7 ,1 etc.
Terms
1. Additive Identity/Role of Zero
Zero is called the identity for the addition of rational numbers. It is the additive identity for integers and whole numbers as well
a + 0 = a
2. Multiplicative identity/Role of one
1 is the multiplicative identity for rational numbers. It is the multiplicative identity for integers and whole numbers as well
a × 1 = a
Properties of Rational Numbers
Closure Property
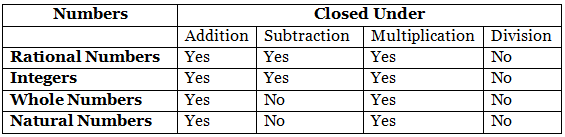 Commutativity Property
Commutativity Property
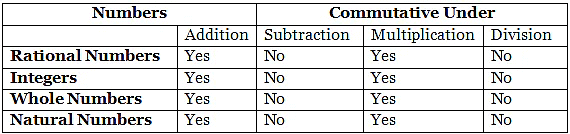
Associativity Property
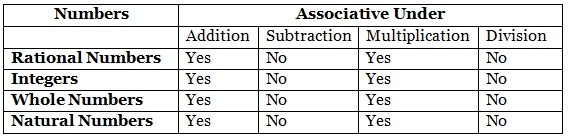
Distributive Property
The distributive property of multiplication over addition states that for any three rational numbers a, b, and c :
a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
This means that if you multiply a rational number by the sum of two other rational numbers, the result will be the same as multiplying the number by each term of the sum separately and then adding the results.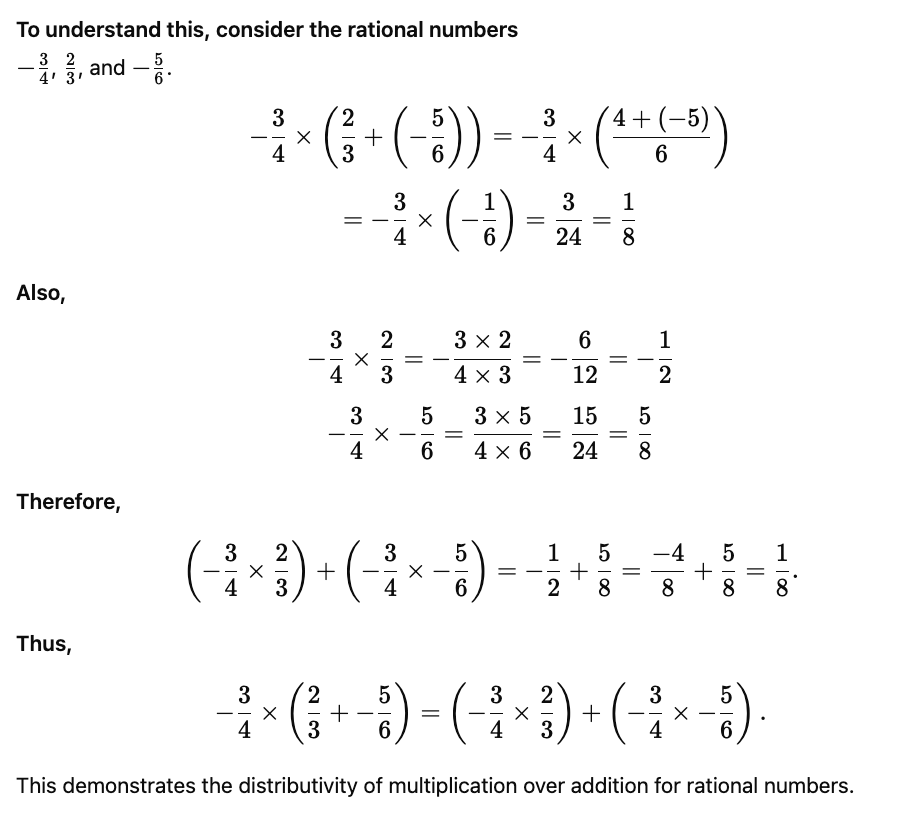
|
81 videos|415 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Rational Numbers - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are rational numbers? |  |
| 2. How do you identify if a number is rational? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of rational numbers? |  |
| 4. How do you perform operations on rational numbers? |  |
| 5. Can irrational numbers be considered as rational numbers? |  |


























