Antenna Arrays | Electromagnetics - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Antenna Theory - Antenna Arrays
- An antenna, when individually can radiate an amount of energy, in a particular direction, resulting in better transmission, how it would be if few more elements are added it, to produce more efficient output. It is exactly this idea, which led to the invention of Antenna arrays.
- An antenna array can be better understood by observing the following images. Observe how the antenna arrays are connected.
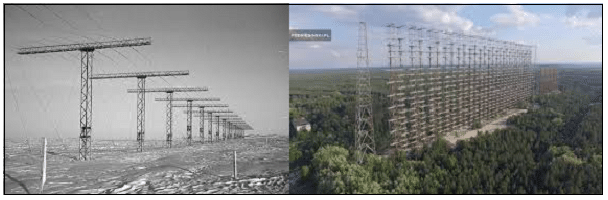 An antenna array is a radiating system, which consists of individual radiators and elements. Each of this radiator, while functioning has its own induction field. The elements are placed so closely that each one lies in the neighbouring one’s induction field. Therefore, the radiation pattern produced by them, would be the vector sum of the individual ones. The following image shows another example of an antenna array.
An antenna array is a radiating system, which consists of individual radiators and elements. Each of this radiator, while functioning has its own induction field. The elements are placed so closely that each one lies in the neighbouring one’s induction field. Therefore, the radiation pattern produced by them, would be the vector sum of the individual ones. The following image shows another example of an antenna array. The spacing between the elements and the length of the elements according to the wavelength are also to be kept in mind while designing these antennas.
The spacing between the elements and the length of the elements according to the wavelength are also to be kept in mind while designing these antennas.
The antennas radiate individually and while in array, the radiation of all the elements sum up, to form the radiation beam, which has high gain, high directivity and better performance, with minimum losses.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of using antenna arrays −- The signal strength increases
- High directivity is obtained
- Minor lobes are reduced much
- High Signal-to-noise ratio is achieved
- High gain is obtained
- Power wastage is reduced
- Better performance is obtained
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of array antennas −- Resistive losses are increased
- Mounting and maintenance is difficult
- Huge external space is required
Applications
The following are the applications of array antennas −- Used in satellite communications
- Used in wireless communications
- Used in military radar communications
- Used in the astronomical study
Types of Arrays
The basic types of arrays are −- Collinear array
- Broad side array
- End fire array
- Parasitic array
- Yagi-Uda array
- Log-peroidic array
- Turnstile array
- Super-turnstile array
Antenna array types are mainly categorized into four types which are explained as below:
1. Broadside Type
In the broadside antenna array, similar elements are placed in a parallel way all across the line that is normal to the antenna’s axis. This is the widely employed antenna configuration and all the elements are positioned horizontally with similar spacing between them and every element in the array is provided with a current having a similar phase and magnitude levels. When there is excitation to the elements, then the array delivers maximum radiation in the normal direction of the antenna axis, whereas in the other directions less amount is delivered. This forms a bidirectional radiation pattern.
The characteristics of the broadside type of antenna array are:
- The broadside array can vary between 2λ to 10λ.
- Employed mainly for overseas broadcasting systems and used for LF, HF, and ML frequency ranges.
- The total number of elements used in the array is based on spacing, price, and beamwidth necessity.
- When a broadside antenna array is operated along with a reflector, the directivity and gain of the antenna array in the broadside type can be increased.
2. End-Fire Type
The arrangement of elements in the end-fire type is the same as that of the broadside antenna array and the difference occurs in the excitation pattern provided to the end-fire antenna. Here, the elements are provided with 1800 out of phase. This type of arrangement delivers maximum radiation across all the array axis.
The end-fire antenna is excited with current having a similar magnitude level but has phase difference across the line thus creating a unidirectional radiation pattern. It is said that phase differences should vary corresponding to the progressive distance between elements.
The characteristics of the end-fire type of antenna array are:
- The total number of elements used in the array is based on spacing, price, and beamwidth necessity.
- When a broadside antenna array is operated along with a reflector, gain and directivity can be increased.
- Employed mainly for overseas broadcasting systems and used for point-to-point communication purposes.
- The distance between the elements is either λ/4 or (3λ)/4.
- The total number of either dipoles or elements of the same size should be used.
3. Collinear Type
The name of the antenna itself signifies that the arrangement of different elements is stacked in a single line. The line arrangement can be in the horizontal or vertical directions. The excitation is fed to every element in the antenna having a current with a similar phase and magnitude. The radiation pattern is in the normal direction to the antenna array axis. So, the collinear antenna arrays’ major lobe provides a circular symmetry pattern that enables an omnidirectional radiation pattern.
When the elements are placed at a distance of 0.3 to 0.5λ between them, the array offers maximum gain whereas this directs to constructional and feeding issues. In order to avoid those problems, the elements are closely placed. The directivity of the antenna gets increased when the array length is increased.
The characteristics of the collinear type of antenna array are:
- A collinear array with two elements is widely used because it supports multi-band functionality.
- Few of the applications employ the combination of collinear, end-fire, and broadside types of antennas as this enhances the directivity and gain to the maximum extent.
- A collinear array with 4 elements is not practically employed as it does not deliver the required amount of power gain.
4. Parasitic Type
- These are the multi-element type of antenna arrays delivering maximum gain and directivity. Even without providing excitation to every element in the array, it assists in solving feedline issues. Here, the fundamental operation is feeding a few of the elements in a parasitic arrangement. In the parasitic type antenna array, the excitation is provided only for the driven element whereas the rest of the elements are parasitically excited.
- The elements which are fed in a direct approach are termed parasitic elements and these receive power from the radiation released from the driven component which is close to it. This is called electromagnetic coupling.
- The current developed in the parasitic element because of the driven component is based on the distance (mostly λ/4 and a 900 phase difference) that is present in between two elements together with the tuning. The parasitic array radiation pattern is the outcome of the reflector which is behind the driven component adding back-reflected signals with the forward wave.
|
11 videos|94 docs|89 tests
|





















