Multiplexing | Communication System - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) PDF Download
Introduction
- Multiplexing is a process to send one or more signals over the same communication channel. The modulation process (Amplitude Modulation or Angle Modulation) is an example of multiplexing as both the message signal and the carrier signal are transmitted on the single communication channel. The main advantage of multiplexing is the multiple transmissions on the same communication channel.
- A channel acts as a medium between the transmitter and the receiver. It transmits the modulated signal received from the transmitter and sends it to the receiver. The receiver demodulates the received signal to recover the original form of signal. There are various communication channel types, such as optical fiber, coaxial cable, twisted pair cables, etc. These sources of communication channel transmit the data to long distances like Wi-Fi and two-way communication. We can also define multiplexing as the process of sharing a channel between multiple signals.
Multiplexing and Modulation
The transmission of a single-channel is called modulation, while multiple transmissions are called multiplexing. The function of modulation is to vary the properties of the incoming message signal depending on the output requirements. The function of multiplexing is to combine various signals. So, both the terms (modulation and multiplexing) modulate the signal and transmit it to the communication channel and are widely used in communication. In the demodulation, the receiver captures the signal and converts it back to its original form. Similarly, the recovery of multiple signals back to their original form is known as demultiplexing.
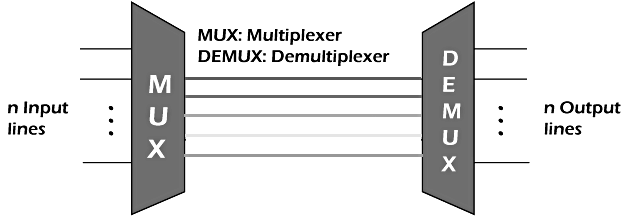
A simple diagram of multiplexing (MUX) and demultiplexing (DEMUX) is shown below:
In multiplexing, various signals are transmitted at different frequencies. It avoids any interference or mixing between the signals and helps in their easy separation at the receiving end.
Types of Multiplexing
There are five types of multiplexing, which are as follows:
- FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing)
- TDM (Time Division Multiplexing)
- CDM (Code Division Multiplexing)
- SDM (Space Division Multiplexing)
- PDM (Polarization Division Multiplexing)
- WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
FDM
Frequency Division Multiplexing refers to the multiplexing method where the total bandwidth of the channel is divided with respect to the frequency or frequency bands. It allows multiple signals of different frequencies to share a common channel, such as optical fiber. Each frequency band is different from the other and carries a separate signal. The signal in the form of bitstreams is also transmitted similarly. Another method is transmitting the higher-order bitstreams in parallel.
A parallel combination sends multiple bits at a time, as shown below:
The signals that are sent on a single communication channel are known as baseband signals. The transmitter consists of an electronic oscillator, modulator, and filters. The electronic oscillator generates a high frequency carrier signal, which carries information. The modulator combines the carrier signal and the baseband signal. It also alters the characteristics of the baseband signal, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase depending on the requirements. The filters can be used to reduce any noise or attenuation. The output of the modulator produces the sum and difference of modulating and carrier frequencies. The information is present in the two sidebands, which are present at both the sides of the carrier wave. Similarly, other signals at different frequencies are transmitted creating other channels of information.
Examples of FDM
Let's discuss the most common examples of FDM.
- Television Broadcasting
- Radio Broadcasting
- Telephone Broadcasting
1. Television Broadcasting: Television broadcasting refers to the process of sending multiple television signals on the same channel. All independent channels are transmitted with different frequencies to prevent any cross talk or interference.
For example:
Cable television
In cable broadcasting, multiple signals are transmitted using a single cable. It generally sends various television channels simultaneously on a single cable, such as coaxial cables.
2. Radio Broadcasting
Radio broadcasting refers to the process of sending multiple radio signals on the same channel (air). All independent channels are transmitted with different frequencies to prevent any cross talk or interference. The transmission is carried with the help of an antenna that sends and receives radio signals.
3. Telephone Broadcasting
Telephone broadcasting also refers to the process of sending telephones or audio signals on the same channel (telephone line). Telephone broadcasting uses communication satellites, broadband, modems, radio beams, etc., to transmit signals from one place to another. For example, twisted pair cable lines.
Advantages of FDM
The advantages of FDM are as follows:
- No requirement of synchronization
- Easy modulation and demodulation
- High latency than TDM
Disadvantages of FDM
The disadvantages of FDM are as follows:
- High chances of crosstalk and distortion
- Complex circuit design
- Expensive
- Suitable for low speed channels
TDM
Time Division Multiplexing refers to the multiplexing method where the total bandwidth of the channel is divided with respect to the time slots. TDM has the advantage of utilizing the maximum transmission channel bandwidth as compared to other types of multiplexing. It uses time instead of frequency to separate the signals or data streams arranged in the sequence one after the other. It helps the receiver to recover the information in respective order. A time gap is selected based on which the signals are transmitted.
For example:
Pulse Modulation
It is an analog modulation technique based on TDM. In pulse modulation, the data in the form of pulses varying in amplitude, frequency, or phase are transmitted. The space or gap between the two pulses can be utilized by other pulses for transmission.
A simple block diagram explaining the transmission of data using the TDM technique is shown below: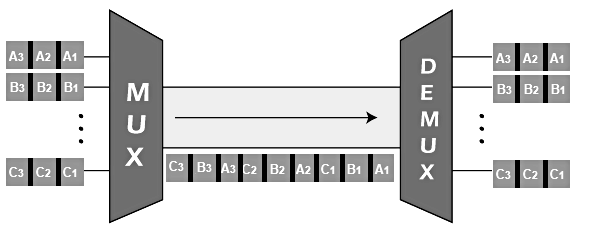
The above diagram has three bits in each input. It depicts that each bit of a particular input is arranged in a specific sequence, which is the same for n number of input bits. Each bit of every input is arranged in sequential order. Similarly, n numbers of bits are transmitted using TDM.
TDM is further categorized as:
- Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing
- Asynchronous Time Division Multiplexing
1. Synchronous TDM
The time slots in synchronous TDM are pre-assigned to each frame. Any delay in the transmission of data may result in the empty transfer of data. It means that a slot is transmitted empty if it is not used at the assigned time.
2. Asynchronous TDM
The time slots in asynchronous TDM are flexible to each frame. The data can be assigned to the time slot when the connected devices are ready to transmit the data. It means that a slot cannot be transmitted empty. It does not allow any wastage of a specific time slot.
Advantages of TDM
The advantages of TDM are as follows:
- Effective utilization of bandwidth
- Low interference
- Low distortion
- Simple circuit design
- High transmission speed
Disadvantages of TDM
The disadvantages of TDM are as follows:
- The requirement of proper sequence and planning
- Slots imbalance can occur
- Low latency than FDM
- It requires synchronization
CDM
Code Division Multiplexing is a technique that uses a coding scheme for the transmission process. It assigns a code to every transmitter. Each transmitter with a different code is transmitted on the same communication channel and demultiplexing using the same process. The coding scheme secures the transmission process with less interference. The concept of CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) in digital communication is the same as CDM and allows multiple users to share a common communication channel.
The code of every station cannot interfere because a code of a station multiplied by the other always yields 0. A code of a station can be multiplied by itself, which yields a positive number.
Advantages of CDM
The advantages of CDM are as follows:
- Low interference
- Secure transmission
- Large user capacity
- Increased user resources
Disadvantages of CDM
The disadvantages of CDM are as follows:
- It requires time synchronization
- Its performance is affected by the rising users
SDM
- Space Division Multiplexing is used to transmit the independent channels in space. It is also known as Spatial Multiplexing. It is commonly used in wireless technologies, such as fiber optics and Wi-Fi. Optical fiber transmission can use a single-core optical fiber, multicore optical fiber, and bundles of fibers to transmit the data from the transmitter to the receiver.
- In the case of wireless transmission through space, multiple antennas at the transmitting and receiving sides are incorporated. The channel separation is maintained by using insulation and waveguides.
For example:
SDMA (Space Division Multiple Access)
It is a digital communication multiplexing method that uses a point-to-point conductor for each channel in the communication system. It is generally used in mobile communication where a channel can be reused for the transmission process. It offers high capacity spatial multiplexing using advanced antenna technology to transmit multiple signals on the same communication channel. The use of advanced technology helps in filtering the noise or interference from the incoming signals.
Advantages of SDM
The advantages of SDM are as follows:
- Low power consumption
- Wireless transmission
- High efficiency
- High accuracy
Disadvantages of SDM
The disadvantages of SDM are as follows:
- Complex circuit design
- Expensive
- Complex maintenance
- High insertion losses
PDM
- Polarization Division Multiplexing is an optical fiber transmission technique that uses polarization of EM (Electromagnetic) waves. Polarization refers to the vibrations in a wave traveling in a specific direction. EM waves carry electromagnetic energy like X-rays, infrared, infrared, etc. It allows two-channel carrying information to transmit based on the same carrier frequency by using two orthogonal polarization states. It is commonly used for VHF (Very High Frequency) applications, such as satellite communication and fiber optics.
- The two orthogonally polarized antennas in the microwave satellite communication increase the total bandwidth to twice. A dual-polarized signal can carry upto two independent data streams, while a single polarized signal can carry or receive only one data stream at a time. PDM allows high transmission speed upto 100G/ bits. It is generally used with optical QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) and Phase Modulation.
Advantages of PDM
The advantages of PDM are as follows:
- High spectral efficiency
- High optical transmission capability
- It is suitable for VHF applications
Disadvantages of PDM
The disadvantages of PDM are as follows:
- Polarization drifts can occur due to physical changes in the environment
- Polarization dependent loss can occur
WDM
Wavelength Division Multiplexing is also a type of optical communication that takes place through the optical fiber. It allows the transmission of multiple signals with different wavelengths or colors (laser). It is also called as wavelength duplexing or bidirectional multiplexing because it allows the transmission in both directions. All the signals are combined and transmitted through a single optical fiber. Demultiplexer at the receiving end split the incident beam into the separate signals as the output. The links or signal sources are known as transducers.
A simple diagram of WDM is shown below: WDM is further categorized as CWDM and DWDM. CWDM (Course Wavelength Division Multiplexing) can operate upto 8 channels with a separation of 20 nanometers between every two adjacent channels. It is inexpensive and consumes less power. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) can operate with larger number of channels. It is expensive and transmits huge data through a single optical fiber link.
WDM is further categorized as CWDM and DWDM. CWDM (Course Wavelength Division Multiplexing) can operate upto 8 channels with a separation of 20 nanometers between every two adjacent channels. It is inexpensive and consumes less power. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) can operate with larger number of channels. It is expensive and transmits huge data through a single optical fiber link.
Advantages of WDM
The advantages of WDM are as follows:
- Bidirectional transmission
- High bandwidth
- High security
- Easy implementation
- High flexibility
Disadvantages of WDM
The disadvantages of WDM are as follows:
- Needs proper spacing for effective transmission
- Cost increases with increased channel capacity
Applications of Multiplexing
There are various applications of multiplexing. Let's discuss some of the most common applications.
- Analog Broadcasting: Analog broadcasting refers to the transmission of analog signals from one place to the other. The carrier signal is added to the message signal during the modulation process. It sends multiple analog signals on the same medium at different times to the receiver through the communication channel. TDM is widely used in analog pulse modulation to transmit the train of pulses varying in amplitude, width, and position. The other pulses can effectively use the space or gap between the pulses for transmission.
- Digital Broadcasting: Digital broadcasting refers to the transmission of digital signals from one place to the other. Here, several bit data streams are multiplexed to a fixed data stream. It helps in transmitting multiple audio and video signals over the same communication channel. The transmission of multiple channels on the television is the common example.
- There are two modes of transmitting data through communication satellites (artificial satellites), MCPC and SCPC. MCPC (Multiple Channels per Carrier) carries multiple radio and television channels on a single carrier. SCPC (Single Channel per Carrier) carries a single radio and television channel on a single video carrier. It means that multiplexing is SCPC is not practical.
- Video Processing: TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) in video processing is a common technique to transmit multiple signals separated with a specific time gap. Multiplexing combines the audio and video signals into one coherent data stream. Both audio and video signals have different bit rates. The device that combines these two signals is known as a muxer or multiplexer. The reverse is performed at the receiving end, where a demuxer or demultiplexer separates the components of the received stream.
- Telegraphy: It was the earliest invented technology communication through electric wires that use electric batteries to send messages at the transmitting and receiving end. The invention of the telephone was based on the FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) that allows simultaneous transmission of multiple audio signals on the same telephone line. The telephone lines are also multiplexed with the neighboring area, which is further connected to the central switching office.
|
14 videos|38 docs|30 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam
|

|

















