Important Questions & Answers: Learning | Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q.1. __________ stands for a relatively permanent change in a behavioural tendency which occurs as a result of reinforced practice.
Learning
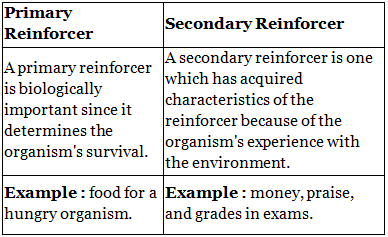
Q.2. State two points of difference between Primary reinforcer and Secondary reinforcer.
Q.3. A small girl catches an inflated balloon which bursts in her hands making a loud noise. She gets very scared. The next time she is made to hold a balloon, the fear response returns. Name the kind of learning involved in this situation.
S–S learning.
Q.4. Learning disabled children have disorders of attention. Explain.
- They get easily distracted and cannot sustain attention on one point for long.
- Attentional deficiency leads to hyperactivity, i.e. they are always moving, doing different things, trying to manipulate things incessantly.
Q.5. Explain Observational learning with examples.
Learning takes place by Observing others. Here is an example that explains it:
Example 1: Fashion designers employ tall, pretty, and gracious young girls and tall, smart, and well-built young boys for popularising clothes of different designs and fabrics. People observe them on televised fashion shows and advertisements in magazines and newspapers. They imitate these models.
Example 2: children observe adults’ behaviours, at home and during social ceremonies and functions. They enact adults in their plays and games. For instance, young children play games of marriage ceremonies, birthday parties, thief and policeman, house keeping, etc. Actually they enact in their games what they observe in society, on television, and read in books.
Observing superiors and likeable persons and then emulating their behaviour in a novel social situation is a common experience.
Children learn most of the social behaviours by observing and emulating adults.
Q6: Explain the nature of learning, highlighting its definition and key features. How do experiences play a crucial role in the learning process?
Learning is defined as any relatively permanent change in behavior or behavioral potential produced by experience. It is a fundamental process in human behavior, characterized by changes that are not temporary, such as those caused by fatigue or drugs.
Key features of learning include:
- Involvement of experience: Learning requires experiences that can be repeated over time.
- Formation of habits: Repeated experiences can lead to habitual behavior.
- Relatively permanent changes: Unlike temporary changes, learned behaviors persist over time.
Experiences play a crucial role in learning by providing the context and stimuli necessary for behavioral changes. For instance, a child learns to be cautious after a painful experience, demonstrating how direct experiences shape future behavior.
Q7: Discuss the different types of reinforcement in operant conditioning and provide examples for each type. Why is understanding these types important for behavior modification?
In operant conditioning, reinforcement can be classified into two main types: positive and negative.
- Positive Reinforcement: This involves presenting a pleasant stimulus after a desired behavior, such as giving a child praise for completing homework.
- Negative Reinforcement: This involves removing an unpleasant stimulus to strengthen a behavior, like turning off a loud alarm when a task is completed.
Understanding these types is crucial for behavior modification as they help in effectively shaping desired behaviors. Positive reinforcement encourages repetition of good behavior, while negative reinforcement helps in avoiding undesirable situations.
Q8: Define learned helplessness and describe its implications for understanding human behavior. Provide examples and discuss its significance in psychological research.
Learned helplessness is a psychological phenomenon that occurs when an individual repeatedly faces uncontrollable and adverse situations, leading to a sense of helplessness and failure. This concept has significant implications for understanding human behavior. Below are key points explaining learned helplessness:
- Definition and Origin: Learned helplessness refers to a condition where individuals believe they have no control over the outcomes of their actions, often due to past experiences of failure. This concept was first introduced by psychologists Martin Seligman and Steven Maier in their experiments with dogs. They found that dogs subjected to inescapable shocks eventually stopped attempting to escape, even when opportunities to do so were presented. This behavior illustrates the essence of learned helplessness.
- Impact on Motivation: When individuals experience learned helplessness, their motivation to engage in tasks diminishes. For example, students who consistently fail in exams may stop studying altogether, believing their efforts will not lead to success. This lack of motivation can create a cycle of failure, reinforcing the belief that they are incapable of achieving their goals.
- Relation to Mental Health: Learned helplessness is closely associated with psychological conditions such as depression and anxiety. Individuals who feel helpless may exhibit symptoms like low self-esteem, withdrawal from social activities, and a negative outlook on life. Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for mental health professionals as it helps in developing interventions aimed at fostering resilience and coping strategies.
- Human Examples: In real life, learned helplessness can manifest in various scenarios, such as in the workplace. An employee who faces constant criticism and no recognition may eventually stop trying to improve their performance, believing their efforts will not be rewarded. Similarly, children who experience repeated failures in sports may develop a belief that they are not athletic, leading them to avoid physical activities altogether.
- Significance in Research: The study of learned helplessness has profound implications for psychological research and therapy. It has led to a better understanding of how negative experiences can shape behavior and mindset. Researchers use the concept to explore resilience, coping mechanisms, and the importance of creating supportive environments that empower individuals to take control of their lives, particularly in educational and therapeutic settings.
Q9: Discuss the determinants of verbal learning and explain how each factor influences the learning process.
Verbal learning is influenced by several key determinants. Understanding these factors can help enhance learning outcomes. Here are the main determinants:
- The number of associations: The more associations a learner can make within a given time frame, the more effective their learning will be. When learners create connections between new information and what they already know, it helps to reinforce memory and understanding. For example, if a student learns the word "apple" and relates it to "fruit," "red," and "health," these connections enhance recall.
- Familiarity and frequency: Material that is familiar or frequently encountered is easier to learn. When learners have encountered a word or concept multiple times, they are likelier to remember it. This is because familiarity reduces cognitive load, allowing learners to focus on new or complex information without being overwhelmed.
- Relationships among words: The way words relate to each other can aid in learning. Words that have a logical relationship or belong to the same category tend to be recalled together. For instance, when learning a list of animals, recalling "dog," "cat," and "fish" may be easier due to their shared category, which aids in organization during recall.
- Dependency on preceding words: Some words depend on earlier words in a list for context or meaning. This means that the sequence in which information is presented can affect how well it is learned. For example, understanding the term "predator" might depend on first learning "prey," establishing a relationship that aids memory.
- Learning time and list length: As the length of the list increases, the time required to learn that list also increases. This principle indicates that learners must allocate sufficient time and effort for longer lists, emphasizing the importance of pacing in study sessions to enhance retention.
Q10: Explain the phases of skill acquisition and the significance of practice in developing skills.
Skill acquisition is a process that involves several distinct phases, each contributing to how a person learns to perform a task. Here are the phases and their significance:
- Cognitive Phase: In this initial phase, learners focus on understanding and memorizing instructions. They are often conscious of the steps involved in the task, making this phase crucial for building a foundation. For example, a person learning to drive must first understand the rules of the road before they can effectively operate a vehicle.
- Associative Phase: During this phase, learners begin to link sensory inputs with appropriate responses. Errors decrease as practice continues, helping to refine performance. This phase is important because it allows learners to understand which actions lead to desired outcomes, enhancing their ability to perform the skill effectively over time.
- Autonomous Phase: In this final phase, the skill becomes automatic, requiring less conscious effort. Learners can perform the skill with minimal distraction and can multitask. This phase is significant because it represents mastery, where the individual can perform the skill efficiently without overthinking each step, such as a seasoned driver navigating traffic effortlessly.
- Performance Plateaus: Throughout the learning process, learners may experience plateaus where performance seems to stagnate. Recognizing this is important, as it indicates the need for continued practice and possibly new strategies to break through and improve further.
- Importance of Practice: Practice is essential for skill development. It not only helps improve performance but also leads to automaticity, where skills can be executed without conscious thought. Regular practice helps reinforce neural pathways, making the skill more ingrained and easier to recall when needed.
.
|
43 videos|88 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions & Answers: Learning - Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What are some effective learning strategies for students? |  |
| 2. How does motivation impact learning outcomes? |  |
| 3. What role does feedback play in the learning process? |  |
| 4. How can technology enhance learning? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of collaborative learning? |  |
















