UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Important Trenches of the World
Important Trenches of the World - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
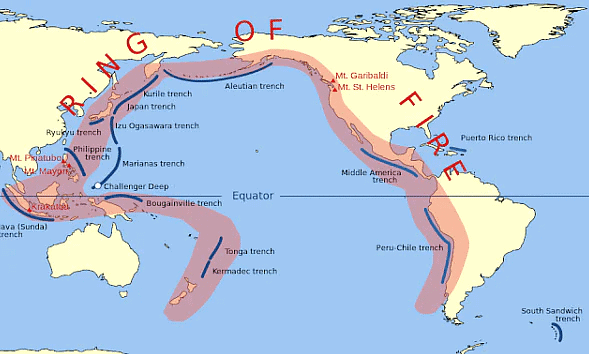
- Oceanic trenches are topographic depressions of the seafloor, relatively narrow in width, but very long. These oceanographic features are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Oceanic trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of convergent plate boundaries, along which lithospheric plates move towards each other at rates that vary from a few millimeters to over ten centimeters per year.
- A trench marks the position at which the flexed, subducting slab begins to descend beneath another lithospheric slab. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km (120 mi) from a volcanic arc.
- Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. Ocean trenches have a highly specialized fauna. The greatest ocean depth measured is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 11,034 m (36,201 ft) below sea level.
- The longest trench is the Peru-Chile Trench, which extends some 5,900 km (about 3,700 miles) along the west coast of South America.
- Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about 3 km2/yr.
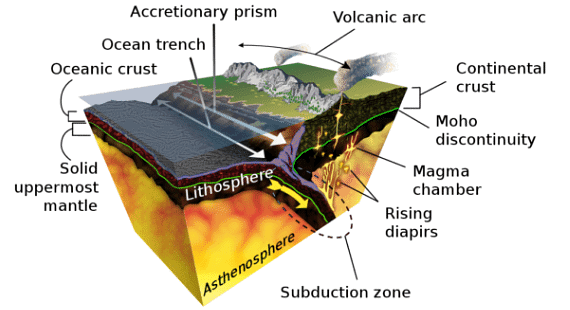
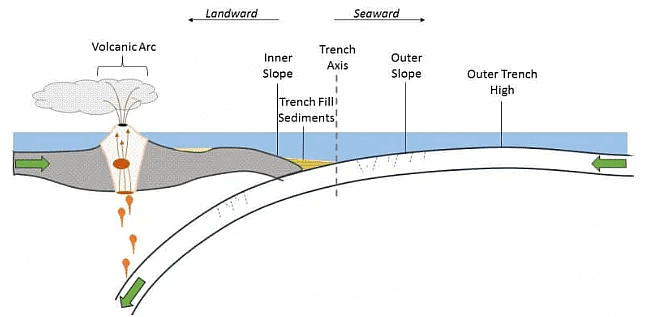
- Globally, there are over 50 major ocean trenches covering an area of 1.9 million km2 or about 0.5% of the oceans. Trenches that are partially infilled are known as “troughs” and sometimes they are completely buried and lack bathymetric expression.
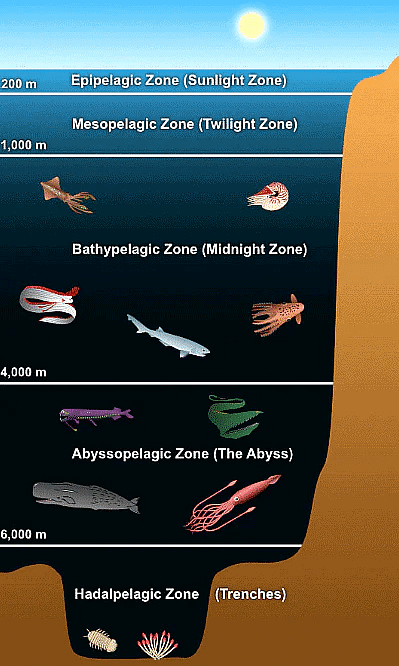
Hadal zone
- The hadal zone, also known as the hadopelagic zone, is the deepest region of the ocean, lying within oceanic trenches.
- The hadal zone is found from a depth of around 6,000 to 11,000 metres (20,000 to 36,000 ft), and exists in long but narrow topographic V-shaped depressions.
- Deep-sea trenches of the hadal depth zone (6-11 km) are hotspots for high microbial activity because they receive an unusually high flux of organic matter, made up of animal carcasses, and sinking algae, originating from the surrounding shallower seabeds.
- Conditions in the hadalpelagic zone are extreme. No sunlight penetrates, the temperature is a constant 4°C, and the pressure is 60–110 MPa.
India’s Deep Ocean Mission
- Union Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India has also launched a ‘Deep Ocean Mission’ for exploration of polymetallic nodules in Central Indian Ocean Basin.
- Polymetallic nodules contain multiple metals like copper, nickel, cobalt, manganese, iron, lead, zinc, aluminum, silver, gold, and platinum etc. in variable constitutions and are precipitate of hot fluids from upwelling hot magma from the deep interior of the oceanic crust.
- Of these, cobalt, copper, and nickel are of much importance and in great demand in India as cobalt is used extensively in medical treatment and nickel in batteries.
- It will reduce India’s dependence on imports of cobalt and other rare earth metals.
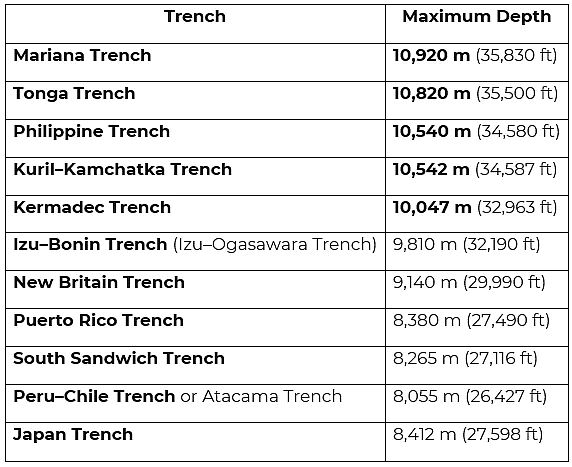
Important Trenches of the World (Deepest oceanic trenches)
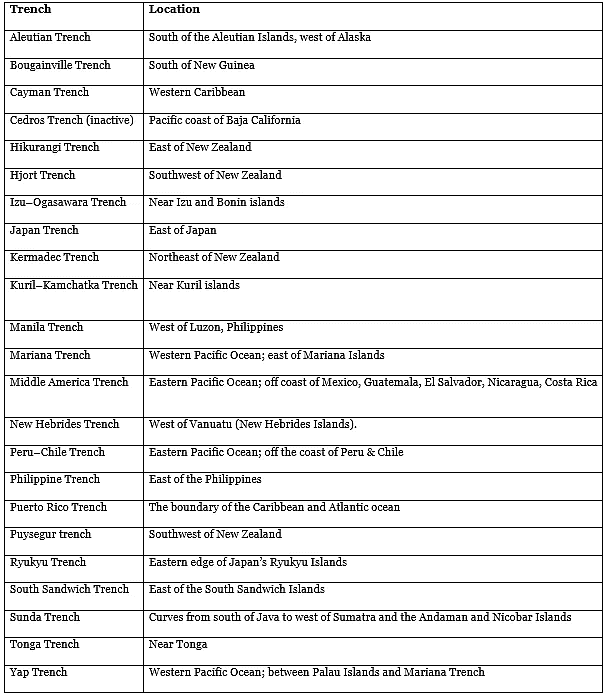
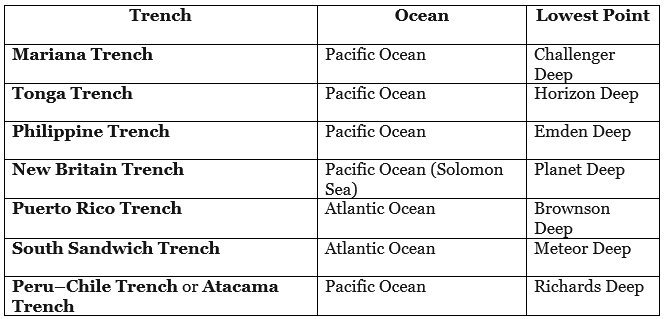
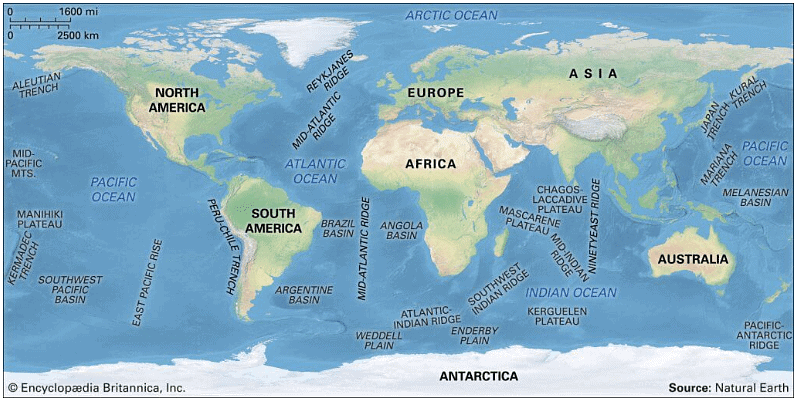
Deepest Ocean trenches in the World
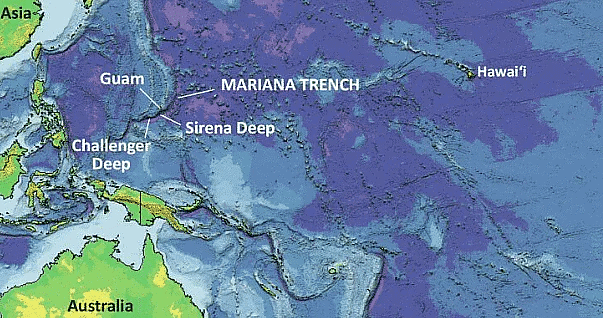
Mariana Trench
- Mariana Trench is located in the western Pacific Ocean, the Marina Trench is considered to be the deepest part of the Earth’s surface. In fact, it is the Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench that is known as the deepest point.
- Appears as a crescent-shaped scar, the trench measures around 2,550 km long, 69 km wide on average and has a maximum depth of 10.91 km at the Challenger Deep. At the same time, some other efforts measured the deepest portion at 11.034 km.
- The deep holes in the Mariana trench were formed due to the collision of converging plates of the oceanic lithosphere.
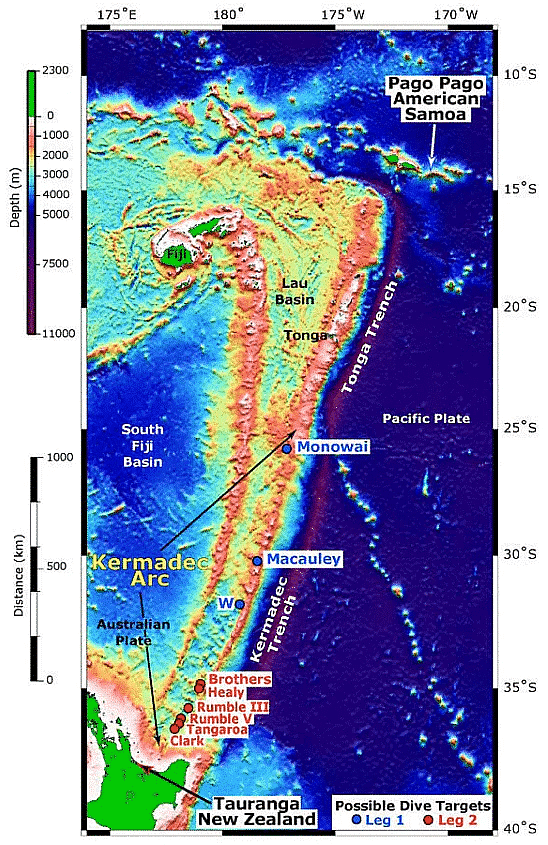
Tonga Trench
- Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean and at the Kermadec Tonga Subduction Zone’s northern end, the Tonga Trench lies around 10.882 km below sea level. The deepest point in the Tonga trench, known as the Horizon Deep, is considered to be the second deepest point on earth after the Challenger Deep and the deepest trench of the Southern Hemisphere.
- Stretches at a distance of 2,500 km from New Zealand’s North Island northeast to the island of Tonga, the Tonga trench was formed due to the subduction of the Pacific plate by the Tonga plate.
Philippine Trench
- The third deepest point in the world, the Galathea Depth in the Philippine trench is 10.54 km below sea level. Also known as Mindanao Trench, this submarine trench is located in the Philippine Sea, spreads in a length of 1,320km and 30km width in the east of the Philippines.
- Prominent among other trenches in the Philippine Sea, this trench was formed due to a collision between the Eurasian Plate and the smaller Philippine plate. The other major trenches in the Philippine sea include Manila Trench East Luzon Trench, Negros Trench, Sulu Trench, and Cotabato Trench.
Kuril- Kamchatka Trench
- Another deepest part of the ocean belonging to the Pacific Ocean, this trench lies at a considerable depth of 10.5 km below sea level. Lying close to Kuril Island and off the coast of Kamchatka, this trench is responsible for a number of oceans bed volcanic activities in the region.
- The trench was formed due to the subduction zone that was developed in the late Cretaceous, which created the Kuril island and the Kamchatka volcanic arcs.
Kermadec Trench
- Another submarine trench lies on the floor of the South Pacific Ocean, the Kermadec Trench stretches around 1,000 km between the Louisville Seamount Chain and the Hikurangi Plateau.
- Formed by the subduction of the Pacific plate under the Indo-Australian Plate, the Kermadec Trench has a maximum depth of 1o.04 km.
Izu-Ogasawara Trench
- Located in the western Pacific Ocean, the Izu-Ogasawara Trench has a maximum depth of 9.78km. Also known as Izu-Bonin Trench, this deep trench stretches from Japan to the northern section of the Mariana Trench and it is also an extension of the Japan Trench.
- Apart from the Izu-Ogasawara Trench, the western Pacific Ocean houses the Izu Trench and the Bonin Trench.
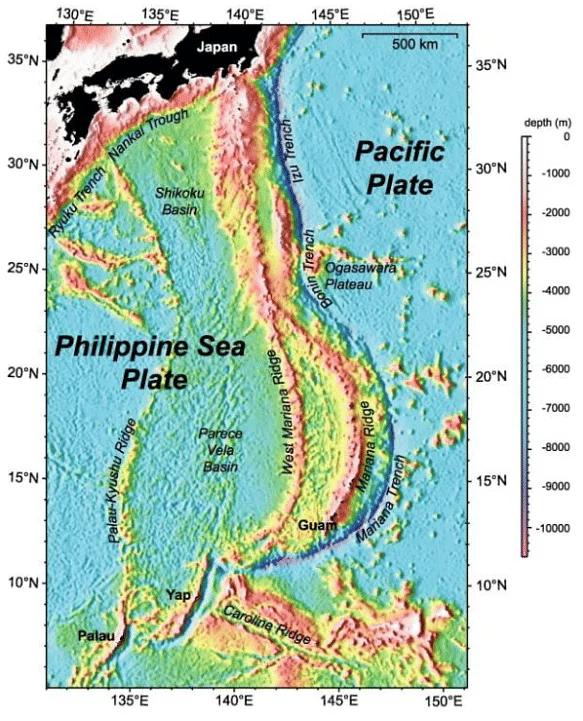
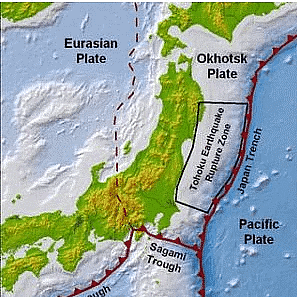
Japan Trench
- Another deep submarine trench located east of the Japanese islands, the Japan trench is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire in the northern Pacific Ocean.
- With a maximum depth of 9 km, the Japan trench stretches from the Kuril Islands to the Bonin Islands and is also the extension of the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench and the Izu – Ogasawara Trench to the north and south respectively.
- The trench was formed due to the subduction of the oceanic Pacific plate beneath the continental Okhotsk Plate. And, it’s the tsunamis and earthquakes that lead to the movement on the subduction zone with the Japan Trench.
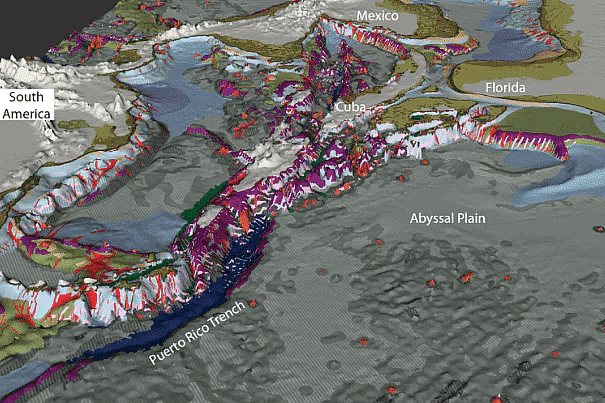
Puerto Rico Trench
- Located between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, the Puerto Rico trench marks the deepest point in this region and the eighth deepest point found on the earth’s surface.
- Lies at a depth of 8.64 km, spotted at Milwaukee Deep, and measures a length of over 800 km, this trench has been responsible for many tragic tsunamis and earthquake activities in this region.
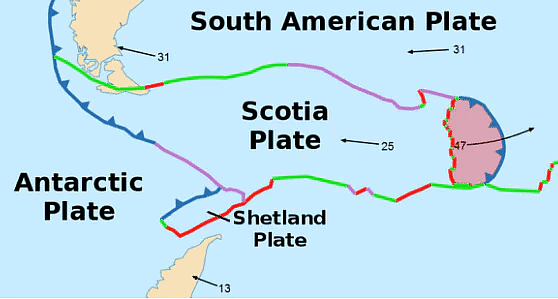
South Sandwich Trench
- The deepest trench in the Atlantic Ocean after Puerto Rico Trench, South Sandwich Trench is at a depth of about 8.42 km, described as Meteor Deep, and runs for over 956 km, making it one of the most noticeable trenches of the world.
- Located 100 km to the east of the South Sandwich Islands in the southern Atlantic Ocean, this trench was formed by the subduction of the South American Plate’s southernmost portion beneath the small South Sandwich Plate.
- This South Sandwich Trench is also associated with an active volcanic arc.
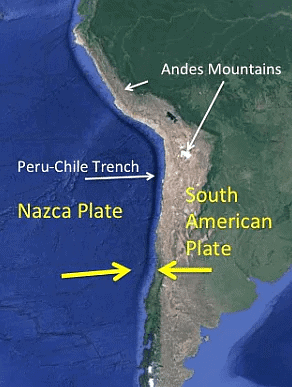
Peru–Chile Trench
- The Peru–Chile Trench (the Atacama Trench) is located around 160 km off the coast of Peru and Chile in the eastern Pacific Ocean.
- The Atacama Trench has a maximum depth of 8.06 km below sea level. The deepest point of the trench is known as Richards Deep.
- The Atacama Trench was formed as a result of a convergent boundary, between the subducting Nazca and the South American Plates.
FAQs on Important Trenches of the World - UPSC
| 1. What are some of the important trenches of the world? |  |
Ans. Some of the important trenches of the world include the Mariana Trench, the Tonga Trench, the Kermadec Trench, the Philippine Trench, and the Peru-Chile Trench.
| 2. How deep is the Mariana Trench? |  |
Ans. The Mariana Trench is the deepest trench in the world, reaching a depth of approximately 36,070 feet (10,994 meters).
| 3. What is the significance of trenches in oceanography? |  |
Ans. Trenches play a vital role in oceanography as they provide valuable insights into the Earth's geological processes, plate tectonics, and the distribution of marine life. They also help scientists understand the formation of oceanic trenches and their impact on the surrounding ecosystems.
| 4. What are the main factors that contribute to the formation of trenches? |  |
Ans. Trenches are mainly formed due to the convergence of tectonic plates, where one plate subducts beneath another. This subduction process occurs when one oceanic plate collides with a continental plate or another oceanic plate, leading to the formation of a trench.
| 5. How do trenches impact marine life? |  |
Ans. Trenches create unique and extreme environments for marine life. The high pressures, extreme temperatures, and lack of sunlight in the deep trenches pose challenges for organisms. However, certain species have adapted to these conditions and have developed specialized adaptations to survive in these harsh environments. The study of life in trenches helps scientists understand the limits of life on Earth and the potential for extraterrestrial life in similar extreme environments.
Related Searches



















