Solved Practice Questions on Aufbau Principle | Inorganic Chemistry PDF Download
Q.1. Electrons revolving in orbit have a fixed
(a) Angular momentum
(b) Shape
(c) Thickness
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Electrons revolving in orbit have a fixed angular momentum.
Q.2. Which of the following orbital will have the lowest energy?
(a) 1s
(b) 2s
(c ) 3s
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
1s will have the lowest energy as per the Aufbau principle.
Q.3. According to the Aufbau principle, the electron occupies that sub-shell with the
(a) Lowest energy
(b) Highest energy
(c) Zero Energy
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (a)
According to the Aufbau principle, the electron occupies that sub-shell with the lowest energy.
Q.4. Which of the following will have the highest energy?
(a) 3s
(b) 3d
(c) 4s
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b)
3d will have the highest energy as per the Aufbau principle.
Q.5. The Aufbau principle does not give the correct arrangement of filling up of atomic orbitals in
(a) Copper and Zinc
(b) Chromium and Zinc
(c ) Copper and Chromium
(d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The Aufbau principle does not give the correct arrangement of filling up of atomic orbitals in copper and chromium.
Q.6. An atom of an element contains 29 electrons and 35 neutrons.
Deduce:
(a) The number of protons
(b) The electronic configuration of the element.
(c) The name of the element.
(a) The number of protons is equivalent to the number of electrons. Thus, it will have 29 protons.
(b) The electronic configuration of the element will be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1.
(c) The atomic number of copper is 29. Hence, it is copper.
Q.7. The electronic configuration of an element A is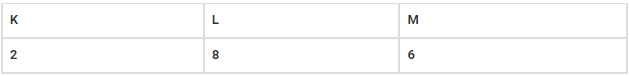
(a) What is the group number of element A?
(b) What is the period number of element A?
(c) How many valence electrons are there in element A?
(d) What is the valency of element A?
(e) Is element A, a metal or a non-metal?
(a) As element A has six valence electrons, it belongs to group 16 of the periodic table.
(b) As element A has three valence shells, it belongs to period 3 of the periodic table.
(c) There are six valence electrons in element A.
(d) The valency of element A would be equal to 8 – the number of valence electrons, i.e. 8 – 6 = 2.
(e) Element A is a non-metal.
Q.8. What is the Aufbau principle?
The Aufbau principle states that the electrons are filled in an atom in increasing order of energy. The atomic orbital with less energy is filled before the atomic orbital with high energy. It is used to specify the location of an electron in different energy levels.
Q.9. Answer the following questions.
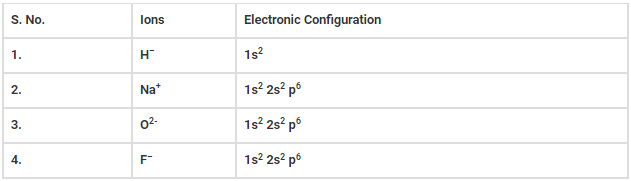
(a) Write the electronic configurations of the following ions.
(i) H−
(ii) Na+
(iii) O2−
(iv) F−
(b) What are the atomic numbers of elements whose outermost electrons are represented by the following.
(i) 3 s1
(ii) 2 p3
(iii) 3 d1
The electronic configuration of following ions are listed below.
The atomic number of elements with the given outermost electrons are.
Q.10. Why are half-filled or fully filled orbitals more stable?
The half-filled or fully filled orbitals are more stable for two reasons.
- Symmetry: The half-filled or fully filled orbitals are more stable because it has a symmetrical distribution of electrons.
- Exchange Energy: The half-filled or fully filled orbitals are more stable because electrons in degenerate orbitals have parallel spins, and they exchange their positions. When the orbitals are half-filled or completely filled, the number of exchanges is maximum. Therefore, it acquires greater stability.
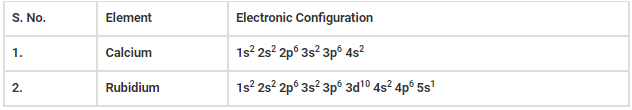
Q.11. Write calcium and rubidium’s ground state electronic configuration using the Aufbau principle.
Calcium and rubidium’s ground state electronic configuration will be
Q.12. Match the following
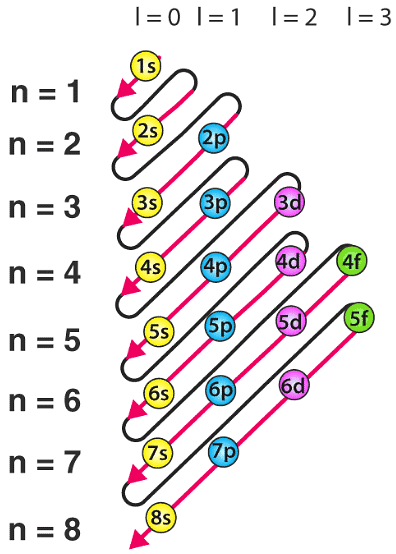
Q.13. How are electrons filled in an atom? Explain with the help of a neat and clean diagram.
Electrons are filled in an atom in increasing order of energy. The atomic orbital with less energy is filled before the atomic orbital with high energy.
Q.14. Why is the electronic configuration of potassium 2,8,8,1 and not 2,8,9?
The electronic configuration of potassium 2,8,8,1 and not 2,8,9 because according to the octet rule, the outermost shell of an atom can accommodate 8 electrons (except the K shell, which can accommodate 2 electrons). Hence, the electronic configuration of potassium is 2,8,8,1 and not 2,8,9.
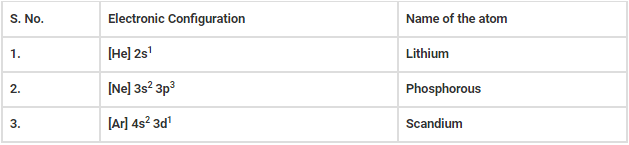
Q.15. Name the atom indicated by the following configuration.
(a) [He] 2s1
(b) [Ne] 3s2 3p3
(c) [Ar] 4s2 3d1
The atom indicated by the following configuration is mentioned below.
|
40 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Practice Questions on Aufbau Principle - Inorganic Chemistry
| 1. What is the Aufbau principle? |  |
| 2. How does the Aufbau principle explain the arrangement of electrons in an atom? |  |
| 3. What are the implications of the Aufbau principle for the periodic table? |  |
| 4. Can the Aufbau principle be violated? |  |
| 5. How does the Aufbau principle relate to chemical reactivity? |  |