Science and Technology: October 2022 Current Affairs | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) Technology
In News
National Telecommunications Institute for Policy Research, Innovation and Training (NTIPRIT) conducts a webinar on "NavIC — Opportunities for the Telecom Industry".
About
- The webinar is conducted by NTIPRIT in collaboration with ISRO and the telecom industry.
- It highlighted the importance and relevance of NavIC technology and making NavIC available on L-1 band in addition to the presently used L-5 band.
- The L band is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) designation for the range of frequencies.
- Also, the NavIC system should be made mandatory for mobile phones that can help in tracking the oxygen tankers and other essentials in the time of Covid-19.
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) Technology
- An autonomous regional satellite navigation system,also known as Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), is developed by ISRO.
- It has been designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary.
- It will provide two types of services:
- Standard Positioning Service (SPS): provided to all the users.
- Restricted Service (RS) : It is an encrypted service provided only to the authorised users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
- Presently, it consists of 7 active satellites located at a distance of approximately 36,000 Km.
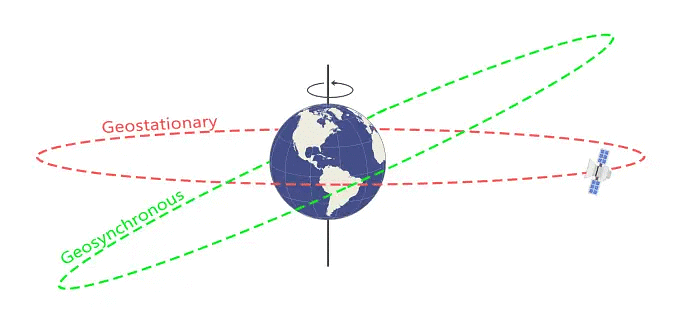
- 3 satellites are in Geostationary Orbit (GEO).
- 4 satellites are in inclined Geosynchronous Orbit (GSO).
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO): Geostationary orbits fall in the same category as geosynchronous orbits, but it’s parked over the equator. This one special quality makes it unique from geosynchronous orbits.
- Weather monitoring satellites like GOES are in geostationary orbits because they have a constant view of the same area.
- Geosynchronous Orbit (GSO): a geosynchronous orbit synchronizes with the rotation of the Earth.
- The time it takes for the Earth to rotate on its axis is 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds, which is the same as a satellite in a geosynchronous orbit.
- India became the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognised by the International Maritime Organisation(IMO).
- The other three countries that have its navigation systems are the US, Russia and China.
Some applications of Navic
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation, Disaster Management, Vehicle tracking and fleet management, Integration with mobile phones, Precise Timing, Mapping and Geodetic data capture etc.
Significance
- Revenue generation: It will bring healthy competition between various navigation services, and potentially significant revenues for the country.
- Technological Innovation: NAVIC should also propel technological innovations and spin-offs that render India progressively less reliant on technological imports from the West and elsewhere.
- India can combine NAVIC with GAGAN—its indigenous augmentation system—to service users on differential rates depending on the navigational precision they seek.
- Interoperability: NAVIC’s interoperability with GPS can ensure the minimization of technical snags when used complementarity with existing GPS-enabled solutions.
- Net security providers: It will bolster the ability of a nation to serve as a net security provider along with its neighbours.
- The US equivalent, Global Positioning System (GPS), played a significant role in relief efforts post disasters such as the tsunami in the Indian Ocean region in 2004 and the Pakistan-India earthquake in 2005.
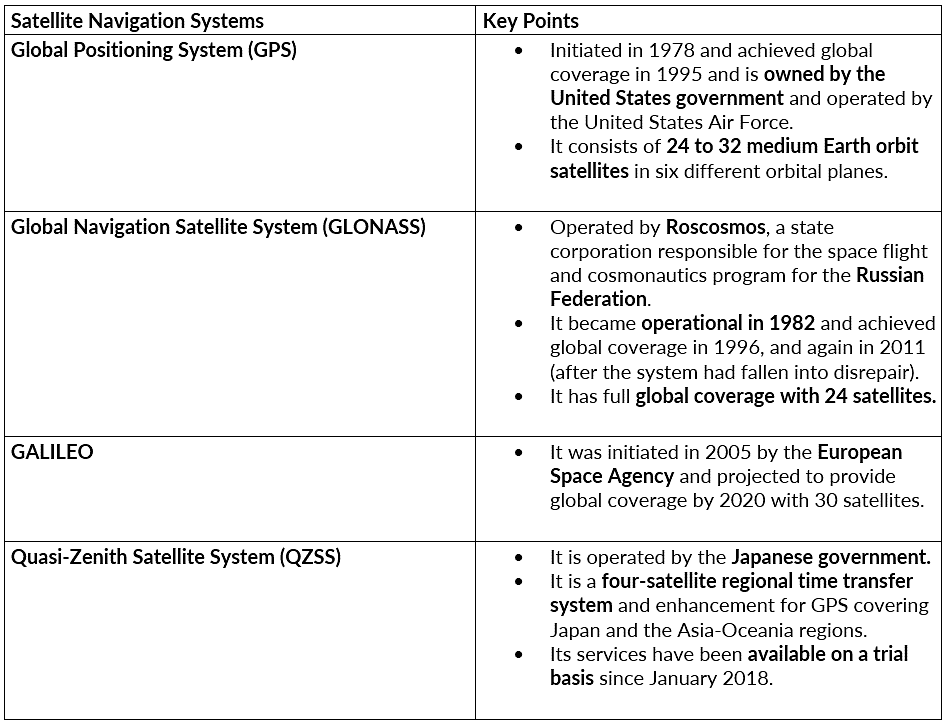
Other Satellite Navigation Systems
National Telecommunications Institute for Policy Research, Innovation and Training (NTIPRIT)
- It is an apex training institute of the Department of Telecommunications.
- Establishment: In 2010 as National Telecom Academy.
- Function & objectives: It involved in conduction of induction Training for probationary officers of Indian Telecommunication Service Group — A (ITS Group A) recruited through All India based Engineering Services Examination conducted by UPSC.
GPS Aided Geo Augmentation System (GAGAN)
- It is a Space Based Augmentation System (SBAS) jointly developed by ISRO and AAI to provide the best possible navigational services over Indian FIR (Flight Information Region) with the capability of expanding to neighbouring FIRs.
- GAGAN is a system of satellites and ground stations that provide GPS signal corrections, giving you better position accuracy.
- Services Offered: Aviation, Forest management, Railways signalling, Scientific Research for Atmospheric Studies, Natural Resource and Land Management, Location based services, Mobile, Tourism.
- GAGAN provides the additional accuracy, availability, and integrity necessary for all phases of flight, from en-route through approach for all qualified airports within the GAGAN service volume.
- GAGAN Payload is already operational through GSAT-8, GSAT-10 and GSAT-15 satellites.
- GAGAN GEO footprint expands from Africa to Australia and GAGAN system has capability to cater 45 reference stations for expansion to neighbouring countries.
Alzheimer Disease
Why in News?
Researchers have discovered a drug named Lecanemab that reduces cognitive decline in patients with early Alzheimer's, making it one of the first neuroprotective treatments for the disease.
What is the Significance of the Findings?
- There are a few pills that improve memory in early stages but they do not help in the other facets of Alzheimer’s. There is certainly a need for such neuro-protective drugs for dementia and there are several drugs in the pipeline.
- The increasing lifespan and very high burden of diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are expected to “dramatically” increase the prevalence of dementia in India.
- Dementia is an umbrella term for a group of disorders that lead to impaired memory, decision-making and social skills.
- The Dementia in India report 2020 estimates that there are 5.3 million people over the age of 60 years living with dementia in India, with the prevalence projected to increase to 14 million by 2050.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
- About:
- It is a neurological disorder which causes brain cells to degenerate and die. This leads to loss of memory, problems with words in speaking or writing, poor judgment, changes in mood and personality, confusion with time or place, etc.
- At the first stage, these symptoms are mild but they become more severe with time.
- It is a neurological disorder which causes brain cells to degenerate and die. This leads to loss of memory, problems with words in speaking or writing, poor judgment, changes in mood and personality, confusion with time or place, etc.
- Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults.
- Alzheimer's disease is thought to be caused by the abnormal build-up of proteins in and around brain cells. One of the proteins involved is called amyloid, deposits of which form plaques around brain cells and the other protein is called tau.
- Tau is a protein that when it occurs in tangled formations in the brain of Alzheimer patients, disrupts the ability of neurons to communicate with one another in the brain.
- Alzheimer’s is an incurable disease, as the death of brain cells cannot be reversed.
- Women have a higher risk of having Alzheimer’s disease than men.
- Treatment:
- There is currently no known cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment addresses several areas:
- Helping people maintain brain health.
- Managing behavioural symptoms.
- Slowing or delaying symptoms of the disease.
- There is currently no known cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment addresses several areas:
Role of Nanomaterials in Solving Environmental Issues
Why in News?
The use of modern technology like nanomaterials or Carbon Dots (CD) may offer solutions to environmental issues like water pollution.
- The urban development of modern society has resulted in the introduction of harmful and toxic pollutants into waterbodies, disturbing the integrity of the aquatic environment.
- Novel technological developments like nanotechnology provide innovative solutions for sustainable and efficient environmental cleanup.
What is Nanotechnology?
- About:
- Nanotechnology is the use and the development of techniques to study physical phenomena and develop new material and devices structures in the physical size range from 1 to 100 nanometres (nm).
- Nanotechnology influences almost all areas of our lives, including manufacturing, electronics, computers and information technologies, medicine, the environment and energy storage, chemical and biological technologies and agriculture.
- Nanotechnology in India:
- The emergence of nanotechnology in India has witnessed the engagement of a diverse set of players, each with their own agenda and role.
- Presently nanotechnology in India is mostly a government-led initiative. Industry participation has very recently originated.
- Nanotechnology R&D barring a few exceptions is largely being ensued at public-funded universities as well as research institutes.
What are Carbon Dots?
About:
- CDs are one of the youngest members of the carbon nanomaterial family.
- They were discovered in 2004 and have an average diameter of less than 10 nanometres.
- CDs possess remarkable optical properties, which differ peculiarly based on the precursor used for synthesis.
- They are becoming more popular as candidates in applications such as sensing and bioimaging due to their good electron donors and acceptors.
- Bioimaging relates to methods that non-invasively visualise biological processes in real time.
- Moreover, CDs are inexpensive, highly biocompatible, and environment-friendly.
Role of CDs in Managing Environmental Issues:
- Pollutant Sensing:
- CDs provide an excellent possibility for fluorescence and colourimetric environmental pollutants detection.
- They are widely used as a fluorescent nanoprobe for pollutant detection because of their high fluorescence emission.
- They also enable the detection of pollutants with colour change by the colourimetric method.
- Contaminant Adsorption:
- The technology can provide many surfaces adsorption sites due to their small size and large specific surface area.
- Water Treatment:
- CDs can also be useful for water treatment as they are promising nano-fillers in fabricating thin-film nanocomposite membranes where they can form chemical bonds with other compounds.
- CDs have been produced from water hyacinth waste, which showed green fluorescence under UV light. They were also proven to be fluorescent sensors to detect herbicides causing trouble in aquatic bodies.
- Pollutant Degradation:
- The technology can also be useful for pollutant degradation by providing a cutting-edge approach for next-generation photocatalysis.
- Photocatalysis includes reactions that take place by utilising light and a semiconductor.
- Organic pollutants in polluted water can act as electron and hole transferring agents, while carbon dots act as photosensitiser.
- Antimicrobial:
- Antimicrobial mechanisms of CDs mainly include physical/mechanical destruction, oxidative stress, photocatalytic effect and inhibition of bacterial metabolism.
- CDs in contact with the bacteria cell under visible or natural light could efficiently generate reactive oxygen species.
- This can damage Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) or Ribonucleic Acid (RNA), causing bacteria death.
What is Categorization of Green Synthesis of Carbon Dots?
- Generally, the synthesis of carbon dots can be categorised into “top-down” and “bottom-up” methods.
- The top-down approach converts large carbon structures into quantum-sized carbon dots by laser ablation, arc discharge, and chemical or electrochemical oxidation.
- In the bottom-up method, CDs are produced from carbonising small molecule precursors by pyrolysis, carbonisation, hydrothermal processes or microwave-assisted synthesis.
To read more information, Applications of Nanotechnology
Mangalyaan Mission Over
In News
- Recently, the ISRO confirmed that the Mars Orbiter craft has lost communication with ground station, it's non-recoverable and with this the Mangalyaan mission has attained end-of-life.
About Mangalyaan Mission
- Background:
- The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan is a space probe launched by the Indian Space Research Organization in 2013.
- Features:
- Mangalyaan was India's first interplanetary mission.
- The indigenously-built space probe has been in Martian orbit since 2014.
- The mission made India the first Asian country and the fourth in the world after Roscosmos, NASA, and the European Space Agency, to get to the planet.
- Objective of Mangalyaan:
- India's Mangalyaan mission is aimed at studying Martian atmosphere.
- Its objective is to explore Martian surface features, mineralogy, morphology and atmosphere using indigenous scientific instruments.
- A crucial objective of MOM was to develop technologies required in planning, designing, management and operations of an interplanetary mission.
- Rocket used
- MOM was launched aboard PSLV C-25 (an XL version of the PSLV).
- Cost of Mangalyaan
- ISRO spent $75 million to launch the mission, making it the least-expensive Mars mission to date.
First-Ever List of Fungal Infections
Context
- WHO recently published a report highlighting the first-ever list of fungal “priority pathogens” – a catalogue of the 19 fungi that represent the greatest threat to public health.
Highlights of the report:
- Fungal pathogens are a major threat to public health as they are becoming increasingly common and resistant to treatment with only four classes of antifungal medicines currently available, and few candidates in the clinical pipeline.
- Most fungal pathogens lack rapid and sensitive diagnostics and those that exist are not widely available or affordable globally.
- The WHO fungal priority pathogens list (FPPL) is the first global effort to systematically prioritize fungal pathogens, considering the unmet research and development (R&D) needs and the perceived public health importance.
- The list’s publication is opportune as fungi are becoming an increasingly common threat to public health. Global warming and increasing international travel and trade are fuelling this rise.
- The COVID-19 pandemic saw an increase in mucormycosis or black fungus infections among those hospitalised.
- Black Fungus, White Fungus, Yellow Fungus, and Green Fungus have been attributed to COVID-19 and led to prolonged morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients.
- A three-layered approach emerged in the strategies suggested by policymakers, governments and public health professionals.
- The strategy includes:
- Strengthening laboratory capacity and surveillance.
- Sustaining investments in research, development and innovation
- Enhancing public health interventions for prevention and control.
Types of fungal infections:
- Green Fungus: Green Fungus or Aspergillosis is the latest addition to COVID-triggered fungal infection that has been reported in Indore.
- Symptoms: High fever, Chest pain, Cough, Nose bleeding, Shortness of breath, Weightless, Weakness or Fatigue.
Who are at risk of getting infected with Green Fungus?
- People with a history of allergy.
- People with frail immunity
- People suffering from lung disease
Yellow Fungus:
- Yellow Fungus, another COVID-triggered fungal infection has been reported in Ghaziabad.
Symptoms: Cough, Fever, Diarrhea, Dark spots on lungs, Reduced oxygen level.
Note: The symptoms of the White Fungus are similar to that of the COVID-19 infection.
Who are at risk of getting infected with White Fungus?
- People with comorbidities such as diabetes.
- People who are on steroids for long.
- COVID-19 patients who are on oxygen support.
White Fungus
White Fungus or Aspergillosis was detected in four patients at Patna Medical College and Hospital (PMCH) in Bihar.
Symptoms: Cough, Fever, Diarrhea, Dark spots on lungs and Reduced oxygen level.
Risk of getting infected with White Fungus:
- People with comorbidities such as diabetes.
- People who are on steroids for long.
- COVID-19 patients who are on oxygen support.
Black Fungus: Increased cases of Black Fungus or Mucormycosis have been observed in COVID-19 patients in the national capital.
The symptoms of Black Fungus infection are:
For Brain Mucormycosis: One-sided facial swelling, Headache, Nasal or sinus congestion, Black lesions on nasal bridge or upper inside of the mouth, Fever.
For Pulmonary Mucormycosis: Fever, Cough, Chest pain, Shortness of breath
For Gastrointestinal Mucormycosis: Abdominal pain, Nausea and vomiting, Gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Risks of getting infected with Black Fungus: Diabetes, Cancer, Organ transplant, Stem cell transplant, Neutropenia, Long-term corticosteroid use, Hemochromatosis (excess of iron), Skin injury due to surgery, burns, or wounds etc.
Lassa Fever
In News
- Recently published study has found that climate change will aid the spread of Lassa fever to the central and eastern parts of the continent in the next 50 years.
About Lassa fever
- It is a zoonotic disease endemic to parts of west Africa.
- Causes : It is caused by the Lassa virus, a member of the Arenaviridae family.
- Transmission : It’s transmitted through the urine and droppings of infected multimammate rats found in most tropical and subtropical countries in Africa.
- They are able to contaminate anything they come in contact with.
- The Lassa virus spreads through human to human contact with tissue, blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions.
- This includes coughing, sneezing, kissing, sexual intercourse and breastfeeding. In hospitals the disease is spread through contaminated equipment.
- Fatality rate : The fatality rate for hospitalised patients is generally high and can reach 80 per cent at times.
- Vaccines and Treatment : There is currently no vaccine approved to prevent the disease.
- Antiviral drug ribavirin is often used to treat Lassa fever although the usage is not a licensed treatment.
- Other procedures used are supportive care including hydration, oxygenation, and treatment of specific complications arising due to the disease. Preventive vaccines are currently under research and development.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on Science and Technology: October 2022 Current Affairs - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC
| 1. What is Indian Constellation (NavIC) Technology and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What is Alzheimer's Disease and what are its symptoms? |  |
| 3. How do nanomaterials help in solving environmental issues? |  |
| 4. What was the Mangalyaan Mission and what were its objectives? |  |
| 5. What is Lassa Fever and how is it transmitted? |  |
















