Important Formulas: Linear Equations in One Variable | The Complete SAT Course - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Algebraic Equation |

|
| What is Linear Equation in One Variable |

|
| Important Formulas |

|
| Important Points to Note |

|
| How to Solve Linear Equation in One Variable |

|
Algebraic Equation
- An algebraic equation is an equality involving variables.
- It says that the value of the expression on one side of the equality sign is equal to the value of the expression on the other side.
What is Linear Equation in One Variable
- Linear equations in one variable is an algebraic equation of equality that involves only one variable, the greatest exponent of which is 1.
- There is a single root or solution for every linear equation in one variable.
- This root or solution is a value that when replaced with the variable makes the equation true.
Example: Consider the linear equation in one variable: 4x+6=14
Can you tell what is the number that should replace ‘x’ so that the given equation results in a true statement?
The linear equation will result in a true statement when the value of ‘x’ is 2.
4∗2+6=8+6=14
The linear equation will not result in a true statement if the value of ‘x’ is taken other than 2. Thus, the given equation 4x + 6 = 14 results in a true statement only when ‘x’ is replaced by 2. In this case, we call the number 2, the root or the solution of equation 4x + 6 = 14.
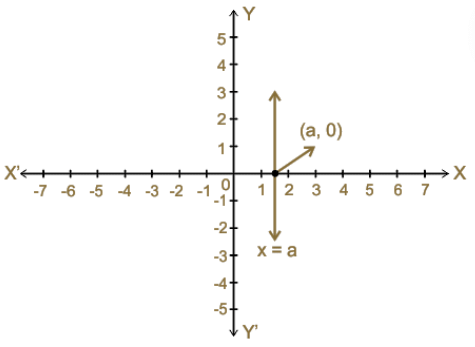 Graph: Linear Equation in One Variable
Graph: Linear Equation in One Variable
Standard form of linear equations in one variable is written as ax+b=0, (a is not equal to zero) where x is the one variable while a and b are any real numbers.
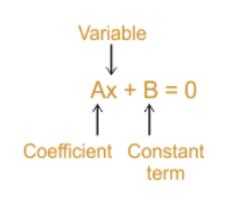
Important Formulas
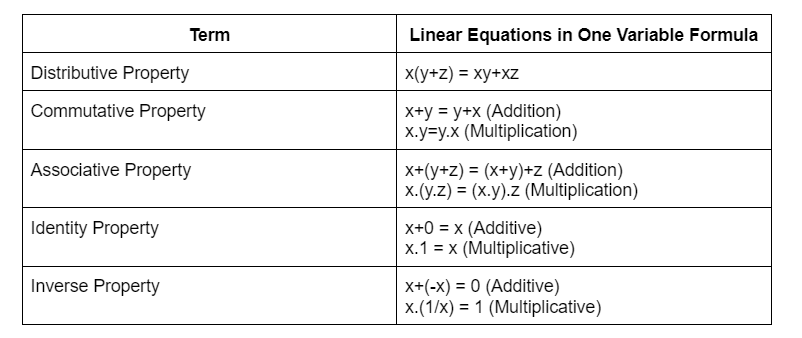
Important Points to Note
- All equations contain the equality (=) sign.
- The expression on the left of the equality sign is the Left Hand Side (LHS). The expression on the right of the equality sign is the Right Hand Side (RHS).
- In an equation, the values of the expressions on the LHS and RHS are equal. This happens to be true only for certain values of the variable. These values are the solutions of the equation.
- We assume that the two sides of the equation are balanced. We perform the same mathematical operations on both sides of the equation, so that the balance is not disturbed. We get the solution after generally performing few steps.
- A linear equation in one variable has only one solution.
How to Solve Linear Equation in One Variable
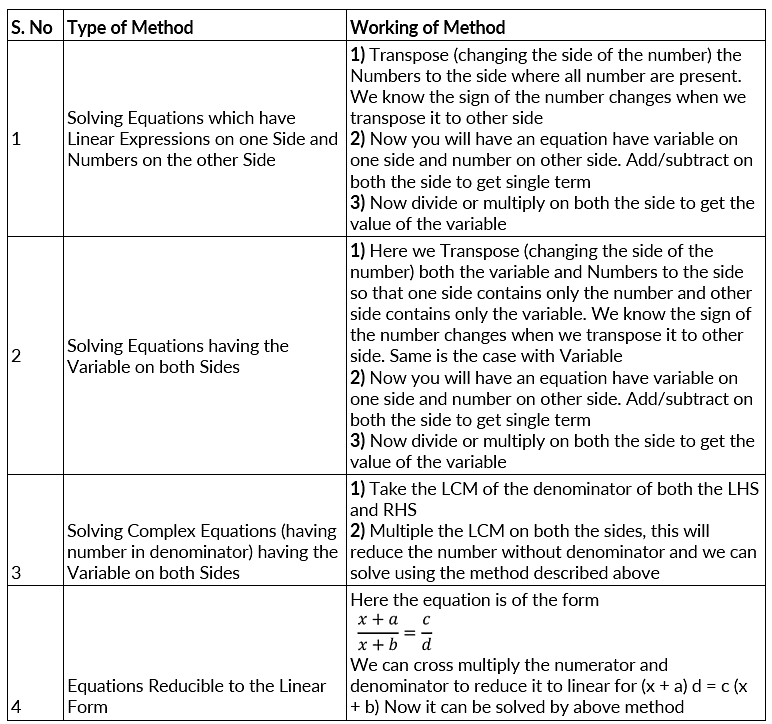
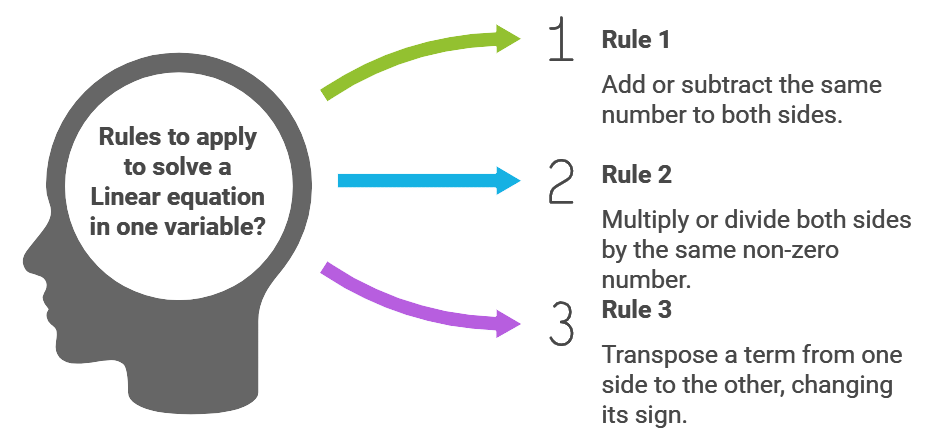
Rules to Solve
Rule 1: Adding the same number (positive or negative) to both sides of an equation, then the resulting equation will be equivalent to the original equation.
Rule 2: Multiplying or dividing both sides of an equation by the same non-zero number, then the resulting equation will be equivalent to the original equation.
Rule 3: Transposing a term from one side to the other side of the equation, then the resulting equation will be equivalent to the original equation, but remember that the sign of the transposed term changes.
|
405 videos|217 docs|164 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Linear Equations in One Variable - The Complete SAT Course - Class 10
| 1. What is a linear equation in one variable? |  |
| 2. How do you solve a linear equation in one variable? |  |
| 3. What are some important formulas related to linear equations in one variable? |  |
| 4. What are the important points to note when solving linear equations in one variable? |  |
| 5. Can a linear equation in one variable have more than one solution? |  |















