Solved Numericals: Deviation from Ideal Gas Behaviour | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Q.1. PV/nRT is known as _______
(a) compressibility factor
(b) volume factor
(c) pressure factor
(d) temperature factor
Correct Answer is Option (a)
PV/nRT is known as compressibility factor and is represented by the letter Z. It is a ratio of PV and nRT; where p is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the universal gas constant and T is temperature.
Q.2. What is the temperature known as where a real gas obeys Boyle’s law or as an ideal gas?
(a) Boyle temperature
(b) Charge temperature
(c) Critical temperature
(d) Absolute Temperature
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The temperature at which a real gas obeys Boyle’s law and other ideal gas law at a certain range of pressure is called Boyle temperature or Boyle point. It is unique for every gas and depends upon its nature.
Q.3.Above Boyle temperature real gases show _______ deviation from ideal gases.
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) no
(d) both positive and negative
Correct Answer is Option (a)
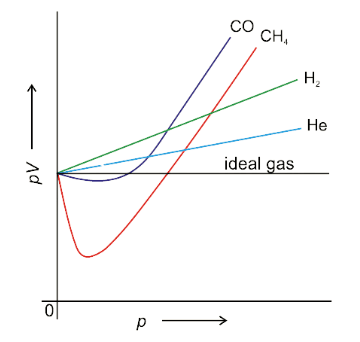
Above Boyle temperature, the value of the compressibility factor is greater than 1. So the gases show positive deviation from ideal gases as the forces of attraction between the gas molecules are very low.
Q.4. The value of a in van der Waal equation is _______ /dependent on _______
(a) pressure
(b) temperature
(c) pressure and temperature
(d) independent of pressure and temperature
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Value of an in van der Waal equation represents a measure of the magnitude of intermolecular attractive forces within the gas and it is also independent of temperature and pressure. The van der Waal’s equation is given by (P – an2/V2)(V – nb) = nRT.
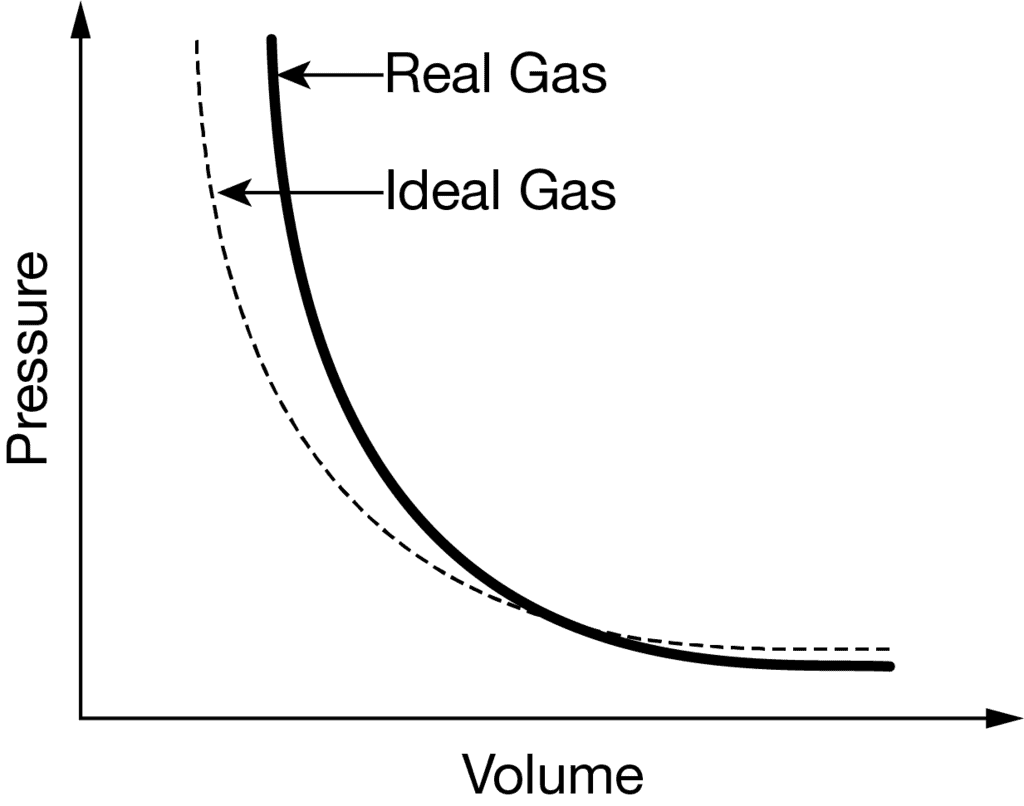
Q.5. The plot PV vs v at constant temperature is a straight line for real gases.
(a) true
(b) false
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The plot of PV vs P is not a straight line for real gases because they deviate from Ideal behaviour. are there are two types of deviations one is a positive deviation and the other is a negative deviation.
Q.6. Which of the following conditions do you think a real gas behaves as an ideal gas?
(a) high pressure
(b) low pressure
(c) intermediate pressure
(d) at any pressure
Correct Answer is Option (b)
At low-pressure conditions, Z = 1 handset behaves as an ideal gas but at high-pressure Z is greater than 1 and for intermediate pressure that is less than 1. So at low-pressure condition, a real gas behaves as an ideal gas.
Q.7. Compressibility can be expressed as _______
(a) real volume divided by the ideal volume
(b) real universal gas constant by ideal universal gas constant
(c) real temperature by ideal temperature
(d) real volume divided by real pressure
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The deviation of real gas behaviour from ideal gas behaviour is known from the compressibility factor. This compressibility factor can also be measured as the ratio of real volume to ideal volume.
Q.8. Which of the following is a corrected equation of ideal gas equation?
(a) (P – an2V2)(V – nb) = nRT
(b) (P – an2/V2)(V + nb) = nRT
(c) (P + an2/V2)(V – nb) = nRT
(d) (P – an2/V2)(V – nb) = nRT
Correct Answer is Option (d)
(P – an2/V2)(V – nb) = nRT; where p is pressure, a is the magnitude of intermolecular attractive forces within a gas, n is the number of moles, v is volume, b is a van der Waal constant, R is the universal gas constant and T is temperature.
Q.9. What are the units of “b” in van der Waals equation?
(a) L/mol
(b) L mol
(c) 1/L mol
(d) L
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The ideal gas equation is given as (P – an2/V2)(V – nb) = nRT. So by considering the equation, we can understand that the units of the volume are equal to the units of a number of moles X be so the units of b. So b’s units = volume / number of moles so it is L/mol.
Q.10. A gas that is of 2 moles occupies a volume of about 500 ml at 300 Kelvin and 50 atmospheric pressure, calculate the compressibility factor of the gas.
(a) 1.863
(b) 0.7357
(c) 0.5081
(d) 1.8754
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Compressibility factor Z = PV/nRT; Z = 50 atm x (500/1000) ml / 2 x 0.082 x 300 k = 25/6×8.2 = 0.5081. That means Z < 1, so this is a negative deviation from ideal gas behaviour. So the gas is more compressible than expected.
|
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|