Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) in Compiler Design | Compiler Design - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is used to represent the structure of basic blocks, to visualize the flow of values between basic blocks, and to provide optimization techniques in the basic block. To apply an optimization technique to a basic block, a DAG is a three-address code that is generated as the result of an intermediate code generation.
- Directed acyclic graphs are a type of data structure and they are used to apply transformations to basic blocks.
- The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) facilitates the transformation of basic blocks.
- DAG is an efficient method for identifying common sub-expressions.
- It demonstrates how the statement’s computed value is used in subsequent statements.
Examples of directed acyclic graph:
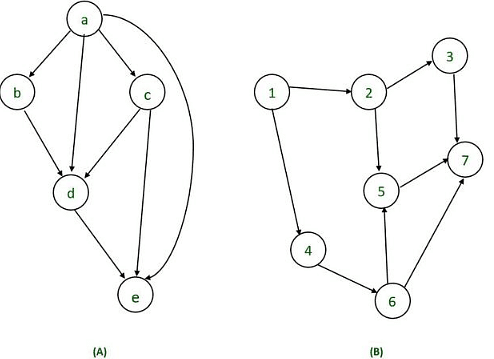
Directed Acyclic Graph Characteristics:
A Directed Acyclic Graph for Basic Block is a directed acyclic graph with the following labels on nodes.
- The graph’s leaves each have a unique identifier, which can be variable names or constants.
- The interior nodes of the graph are labelled with an operator symbol.
- In addition, nodes are given a string of identifiers to use as labels for storing the computed value.
- Directed Acyclic Graphs have their own definitions for transitive closure and transitive reduction.
- Directed Acyclic Graphs have topological orderings defined.
Algorithm for construction of Directed Acyclic Graph:
There are three possible scenarios for building a DAG on three address codes:
Case 1 – x = y op z
Case 2 – x = op y
Case 3 – x = y
Directed Acyclic Graph for the above cases can be built as follows :
Step 1
- If the y operand is not defined, then create a node (y).
- If the z operand is not defined, create a node for case(1) as node(z).
Step 2
- Create node(OP) for case(1), with node(z) as its right child and node(OP) as its left child (y).
- For the case (2), see if there is a node operator (OP) with one child node (y).
- Node n will be node(y) in case (3).
Step 3
Remove x from the list of node identifiers. Step 2: Add x to the list of attached identifiers for node n.
Example :
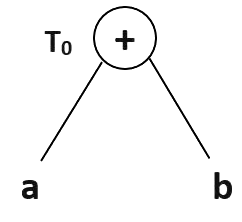
T0 = a + b —Expression 1
T1 = T0 + c —-Expression 2
d = T0 + T1 —–Expression 3
Expression 1 : T0 = a + b
Expression 2: T1 = T0 + c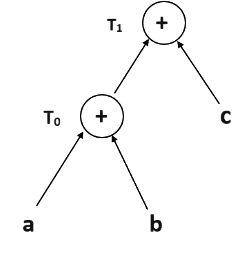
Expression 3: d = T0 + T1
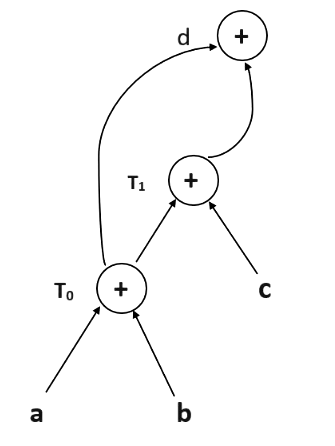 Final Directed acyclic graph
Final Directed acyclic graph
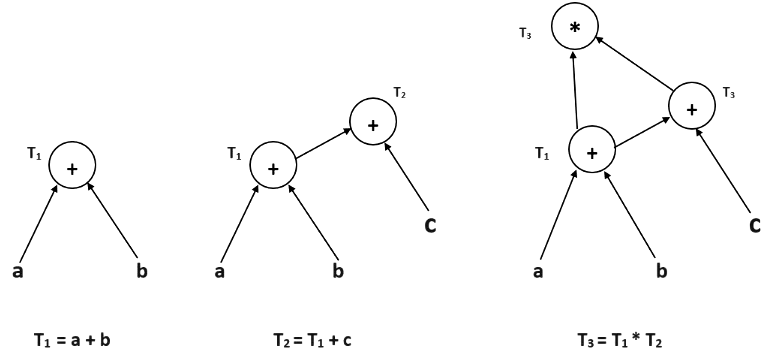
Example :
T1 = a + b
T2 = T1 + c
T3 = T1 x T2
Example :
T1 = a + b
T2 = a – b
T3 = T1 * T2
T4 = T1 – T3
T5 = T4 + T3
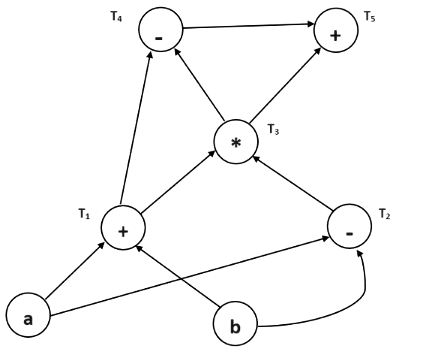
Example :
a = b x c
d = b
e = d x c
b = e
f = b + c
g = f + d
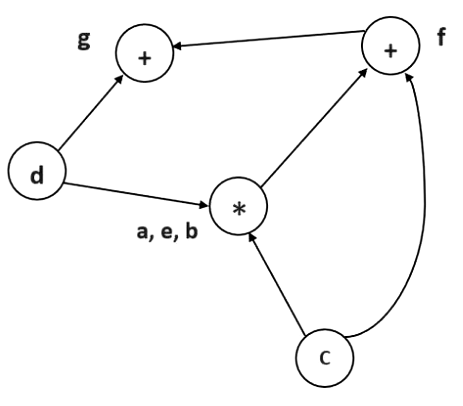 Final Directed acyclic graph
Final Directed acyclic graph
Example :
T1: = 4*I0
T2: = a[T1]
T3: = 4*I0
T4: = b[T3]
T5: = T2 * T4
T6: = prod + T5
prod: = T6
T7: = I0 + 1
I0: = T7
if I0 < = 20 goto 1
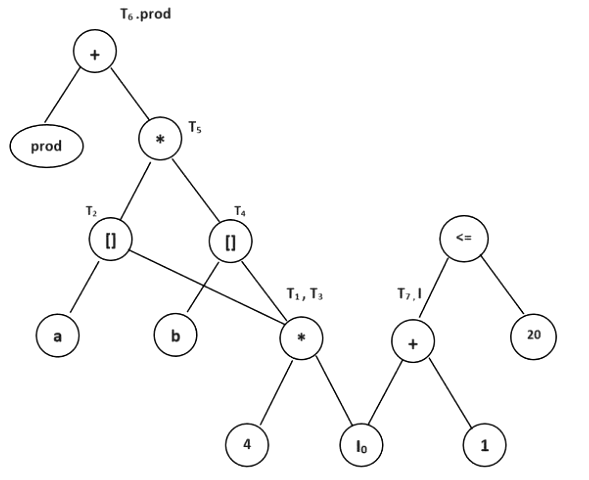 Final Directed acyclic graph
Final Directed acyclic graph
Application of Directed Acyclic Graph:
- Directed acyclic graph determines the subexpressions that are commonly used.
- Directed acyclic graph determines the names used within the block as well as the names computed outside the block.
- Determines which statements in the block may have their computed value outside the block.
- Code can be represented by a Directed acyclic graph that describes the inputs and outputs of each of the arithmetic operations performed within the code; this representation allows the compiler to perform common subexpression elimination efficiently.
- Several programming languages describe value systems that are linked together by a directed acyclic graph. When one value changes, its successors are recalculated; each value in the DAG is evaluated as a function of its predecessors.
|
26 videos|83 docs|30 tests
|





















