Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Exam > Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Notes > Computer Architecture & Organisation (CAO) > Horizontal & Vertical Microprogramming
Horizontal & Vertical Microprogramming | Computer Architecture & Organisation (CAO) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
The control unit (CU) is the engine that runs the entire functions of a computer with the help of control signals in the proper sequence. In the micro-programmed control unit approach, the control signals that are associated with the operations are stored in special memory units. It is convenient to think of sets of control signals that cause specific micro-operations to occur as being “micro-instructions”. The sequences of micro-instructions could be stored in an internal “control” memory.
The micro-programmed control unit can be classified into two types based on the type of Control Word stored in the Control Memory, viz., Horizontal micro-programmed control unit and Vertical micro-programmed control unit.
- In the Horizontal micro-programmed control unit, the control signals are represented in the decoded binary format, i.e., 1 bit/CS. Here ‘n’ control signals require n bit encoding. On the other hand.
- In a Vertical micro-programmed control unit, the control signals are represented in the encoded binary format. Here ‘n’ control signals require log2n bit encoding.
Difference between Horizontal and Vertical micro-programmed Control Unit: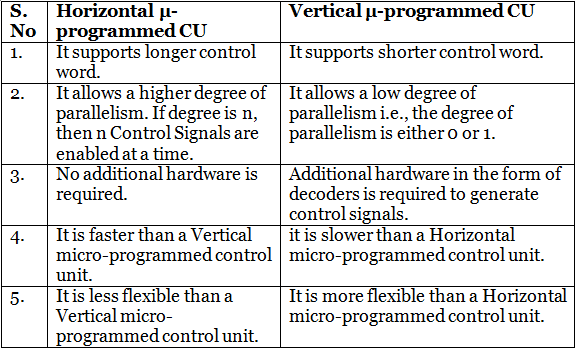
Example: Consider a hypothetical Control Unit that supports 4 k words. The Hardware contains 64 control signals and 16 Flags. What is the size of control word used in bits and control memory in a byte using:
(a) Horizontal Programming
(b) Vertical programming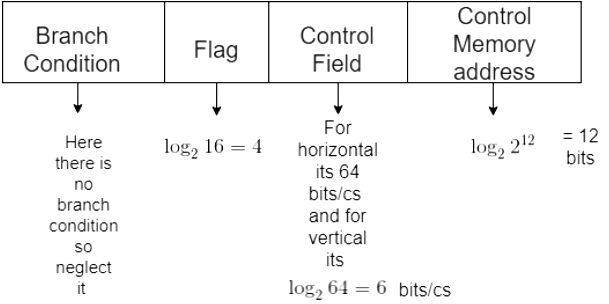
(a) For Horizontal
64 bits for 64 signals % 16 bits for flags
Control Word Size = 64 + 16 = 80 bits
Control Memory = 4 kW = ( (4* 80) / 8 ) = 40 kByte(b) For Vertical
6 bits for 64 signals i.e log264
4 bits for 16 flags i.e log216
12 bits for 4K words i.e log2(4*1024)
Control Word Size = 4 + 6 + 12 = 22 bits
Control Memory = 4 kW = ( (4* 22) / 8 ) = 11 kByte
The document Horizontal & Vertical Microprogramming | Computer Architecture & Organisation (CAO) - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) is a part of the Computer Science Engineering (CSE) Course Computer Architecture & Organisation (CAO).
All you need of Computer Science Engineering (CSE) at this link: Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
|
20 videos|87 docs|48 tests
|
|
20 videos|87 docs|48 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Computer Science Engineering (CSE) exam
|

|
Related Searches


















