Extended Binary Tree | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
Extended binary tree is a type of binary tree in which all the null sub tree of the original tree are replaced with special nodes called external nodes whereas other nodes are called internal nodes
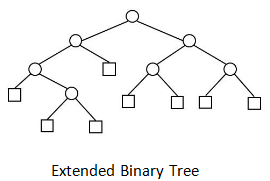
Here the circles represent the internal nodes and the boxes represent the external nodes.
Properties of External binary tree
- The nodes from the original tree are internal nodes and the special nodes are external nodes.
- All external nodes are leaf nodes and the internal nodes are non-leaf nodes.
- Every internal node has exactly two children and every external node is a leaf. It displays the result which is a complete binary tree.
Uses
It is useful for representation in algebraic expressions.
Below is an example of making an extended binary tree in C++ by making all the external nodes as ‘-1’
// C++ program to make an extended binary tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A Tree node
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
// Function for inorder traversal
void traverse(Node* root)
{
if (root != NULL) {
traverse(root->left);
cout << root->key << " ";
traverse(root->right);
}
else {
// Making external nodes
root = newNode(-1);
cout << root->key << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(4);
traverse(root);
return 0;
}
Output
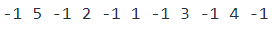
Time Complexity: O(N).
Auxiliary Space: O(N).
Application of extended binary tree:
Calculate weighted path length: It is used to calculate total path length in case of weighted tree.
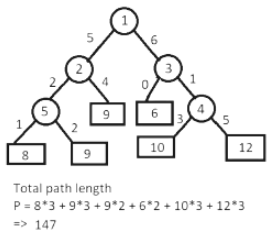
- Here, the sum of total weights is already calculated and stored in the external nodes and thus makes it very easier to calculate the total path length of a tree with given weights. The same technique can be used to update routing tables in a network.
- To convert binary tree in Complete binary tree: The above-given tree having removed all the external nodes, is not a complete binary tree. To introduce any tree as complete tree, external nodes are added onto it. Heap is a great example of a complete binary tree and thus each binary tree can be expressed as heap if external nodes are added to it.
|
158 docs|30 tests
|
















