Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Biology for Grade 10 > Required Practical: Growth
Required Practical: Growth | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
RP2: Investigating Bacterial Growth
- Aim: To investigate the effect of antiseptics or antibiotics on bacterial growth using agar plates and measuring zones of inhibition
- You will:
- Use aseptic technique to place filter paper discs soaked in different antiseptics/antibiotics onto uncontaminated agar plates containing bacteria
- Measure the zone of inhibition around the growing colonies to compare the effect of different antiseptics/antibiotics
- Calculate the area of each zone
- In this practical, you are not required to prepare the plates used to investigate bacterial growth but you should be aware of good microbial aseptic techniques (see Culturing Microorganisms)
- Preventing contamination is vital in any microbiology investigation to ensure that you are only investigating the effect of any antiseptic or antibiotic on the bacterial species you want to
- You will most likely use coli or Micrococcus luteus bacterial cultures in your practical
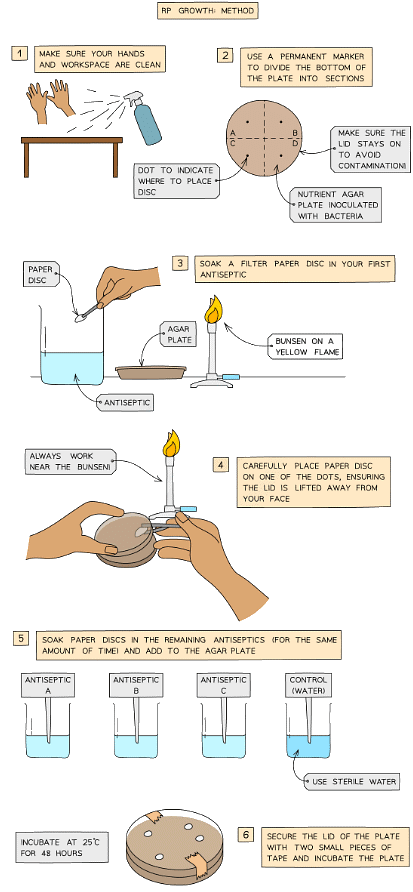
Whilst carrying out this practical you should try to identify the main hazards and be thinking of ways to reduce the risk of accidents
- You may use commercially produced antibiotic discs rather than soaking discs in disinfectants
- Incubating the plates allows the bacteria in the agar to multiply by binary fission, this may be visible by the agar darkening or by colonies appearing
- The antiseptics present in the discs will diffuse out into the agar, with the concentration decreasing with distance from the disc
- Where the concentration is sufficient to prevent bacterial growth or kill bacteria, the agar will remain clear
- It is possible to judge which antiseptic or antibiotic is the most effective by eye, but it is far more accurate to calculate the diameter of each zone and from this calculate the area of each inhibition zone
- Clear zones of inhibition are not always perfectly circular, so the diameter of each zone should be measured twice at 90° angles to each other) and a mean diameter and area calculated for each clear zone
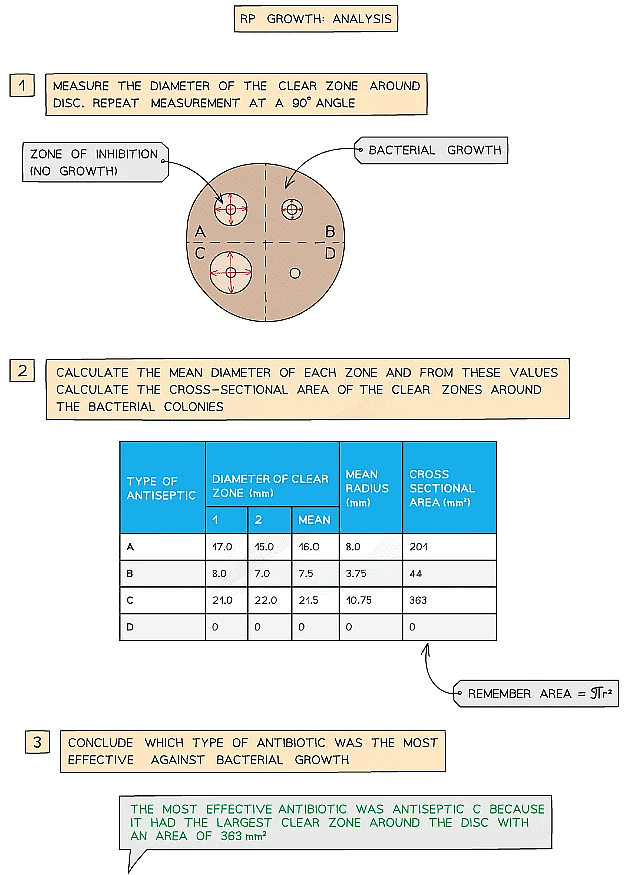
Record the diameter of each clear zone to the nearest whole mm, and remember to calculate the area using the radius (taken as half the value of the mean diameter of each zone)
Why use a control?
- It is vital that one of the paper discs placed on the bacterial agar plate is not soaked in antiseptic or antibiotic but sterile water instead
- This is to ensure that any differences in bacterial growth observed can be attributed to the presence of the antiseptic or antibiotic used and not some other factor (such as the paper discs for example)
The document Required Practical: Growth | Biology for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Biology for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
110 videos|105 docs|15 tests
|
Related Searches




















