Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Biology for Grade 10 > Blood Vessels and Blood
Blood Vessels and Blood | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
Blood Vessels
- The body contains three different types of blood vessel:
- Arteries: transport blood away from the heart (usually at high pressure)
- Veins: transport blood to the heart (usually at low pressure)
- Capillaries: have thin walls which are “leaky”, allowing substances to leave the blood to reach the body’s tissues
- The walls of each type of blood vessel have a structure that relates to the function of the vessel
- Blood flows through the lumen of a blood vessel; the size of the lumen varies depending on the type of blood vessel (with arteries having a narrow lumen, and the veins a wider one)
- The lumen of the capillaries is extremely narrow, at the smallest the width of a red blood cell!
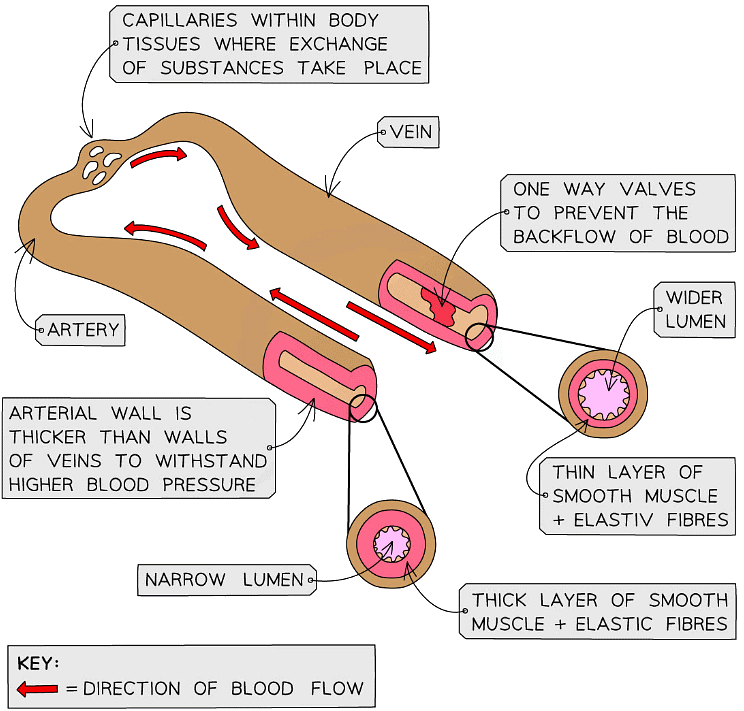
The blood vessels form a continuous network; the structure of each allows it to carry out its function
How structure relates to function
- Arteries must be able to withstand high pressures generated by the contracting heart, and maintain these pressures when the heart is relaxed
- The wall of the artery is relatively thick with layers of collagen, smooth muscle and elastic fibres
- The elastic fibres allow the artery wall to expand around blood surging through at high pressure when the heart contracts, these fibres then recoil when the heart relaxes – this alongside a narrow lumen maintains high blood pressure
- In contrast, veins receive blood that has passed through capillary networks; blood is at very low pressure and must be returned to the heart
- The wall of the vein is relatively thin with thinner layers of collagen, smooth muscle and elastic fibres
- The lumen of the vein is much larger than that of an artery
- Veins contain valves that prevent the backflow of blood, helping return blood to the heart
- The wall of the capillary is made solely from a single layer of endothelial cells (this layer is also found lining the lumen in arteries and veins)
- The wall is only one cell thick – this reduces the diffusion distance for oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and the tissues of the body
- The cells of the wall have gaps called pores which allow blood plasma to leak out and form tissue fluid
Rate Calculations: Blood Flow
- The rate of blood flow can be calculated if the volume of blood flow and the time is known
- For example; if 2460 ml of blood flows through a blood vessel in 4 minutes, the rate of blood flow = volume of blood / number of minutes = 2460 / 4 = 615 ml/minute
- From this you may be asked to determine how much blood flows through the same vessel in one hour = rate of blood flow (ml/min) x 60 = 615 x 60 = 36 900 ml
Structure & Function: Blood
- The role of blood in the body is to transport useful substances to every cell of the body, and to remove harmful waste substances
- It also plays a vital role in transferring heat from “active” organs to cooler parts of the body (such as the extremities – hands and feet)
- Blood is a tissue consisting of the fluid plasma (which is largely water with dissolved substances in it)
- Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended in blood plasma
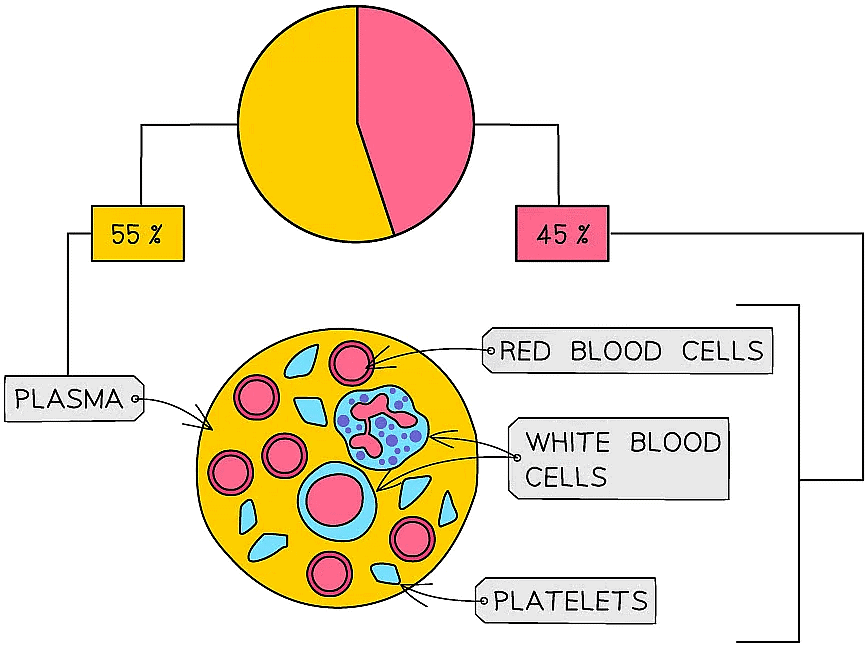
The human blood is composed largely of plasma and red blood cells, with white blood cells and platelets making up a smaller proportion of total volume
Red blood cells
- Red blood cells (RBCs) are cells with a distinctive biconcave disc shape
- This shape is a result of RBCs not having a nucleus
- The biconcave shape gives RBCs a large surface to volume ratio; this is a key adaptation to maximise the efficiency of diffusion of gases into and out of the cell
- The cytoplasm of an RBC is packed with the protein haemoglobin
- Oxygen binds reversibly with haemoglobin, forming the red pigment oxyhaemoglobin:
- oxygen + haemoglobin ⇌ oxyhaemoglobin
White blood cells
- White blood cells (WBCs) are part of the immune system, responsible for defending the body from infection by recognising and destroying pathogens
- WBCs defend the body in three particular ways:
- Phagocytes engulf and digest pathogens, destroying them
- Lymphocytes produce specific antibodies that help enhance phagocyte activity by sticking them together (clumping) or disabling pathogens
- Some lymphocytes produce a type of antibody called an antitoxin which is able to bind to toxic substances produced by pathogens, neutralising them
- WBCs have a variety of adaptations:
- Phagocytes have a lobed nucleus and are autonomous - they leave the blood and patrol the tissues
- Lymphocytes have a large nucleus and can produce antibodies extremely quickly
Platelets
Platelets are fragments of cells (they contain cytoplasm but no nucleus)
- When damage to a blood vessel occurs, the platelets are involved in forming a blood clot to prevent blood loss
- Individuals with insufficient platelets cannot clot their blood effectively – this can be life-threatening if excessive damage occurs
Recognising Blood Cells
- In an exam, you may be shown a photograph or diagram and be asked to identify the types of blood cell present
- Observing and drawing cells under the microscope is also an important skill you will need to develop
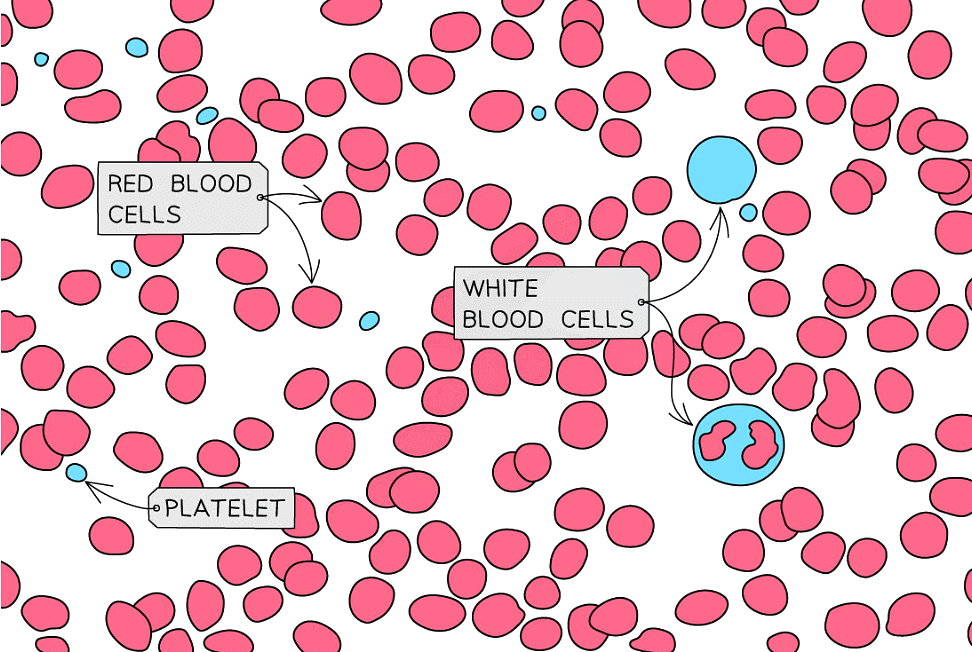
This is an image of how blood might look under a microscope. White blood cells are larger than red blood cells, with platelets being smaller again
The document Blood Vessels and Blood | Biology for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Biology for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
102 videos|100 docs|15 tests
|
Related Searches




















