GS - 3 | UPSC Mains Answer Writing: Practice PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Economy |

|
| Security, Disaster Management and Environment |

|
| Science and Technology |

|
| Sample Answer |

|
GS-III can be demanding. The paper covers a broad range of subjects including the economy, agriculture, science and technology, environment, internal security, and disaster management. While the topics are factual in nature, the questions often require applied understanding and the ability to link concepts with current developments.
Even though the syllabus is well-defined, aspirants often face challenges in organizing their preparation due to the interdisciplinary nature of the paper. Integrating current affairs, understanding government policies and schemes, and presenting data-driven, analytical answers are key to scoring well in this paper.
In this chapter, we will break down the major themes of the syllabus, identify the common pitfalls, and lay down a structured approach for preparation and answer writing. The goal is to help you develop clarity in thought and precision in expression—two essential tools to tackle this paper confidently.
GS-III syllabus can broadly be divided into the following segments:
- Indian Economy and Related Issues
- Agriculture
- Science & Technology
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Internal Security

Questions in this segment tend to be objective, straightforward, and sourced mostly from current affairs. If an aspirant has a good grip over fundamental principles of macroeconomics and followed the news diligently, he or she can effortlessly navigate through this section, garnering a good overall score in GS-3. The following points will help you refine your subject preparation and answer presentation.
Opening your Answers with Statistics
How do we gauge the health of an economy? Through data. Data helps us accurately and concisely convey the status of a sector. Economy and statistics are so closely intertwined that data becomes a critical tool to illuminate the answer. Also wherever possible, it helps to mention the source of that data in parenthesis to establishes authenticity. The best sources for collecting latest numbers are the Economic Survey, Budget, Newspapers, and NITI Aayog’s 3-year action plan and other such research documents. Make a summary sheet of important statistics— sector or topic wise. It’ll help you to revise and recollect them quickly.
For example, take this question: “Do you agree with the view that steady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economy in good shape?” For such questions, instead of giving a subjective, opinionated statement, start your answer with data relating to GDP growth rates in recent years. Similarly, a question on MSMEs would require you to mention basic data relating to them such as their share in employment generation and in GDP. A question on boosting country’s exports would necessitate basic facts on the quantum of our exports and the current trade deficit figures. Data adds value to your arguments.
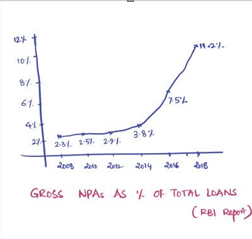
Illustrating through Graphs and Charts
To make a point about a particular trend or a pattern, say rising Non- Performing Assets in the banking sector or dwindling ground water levels, it is helpful if you can illustrate them through graphs. Within one snapshot, it conveys concrete information to the examiner. You will find graphs and charts extensively in the Economic Survey and newspapers.
When you come across them, think of topics and questions in which you can use them. It’s not necessary that every question in economy section needs a graph. Be selective and experiment in your mock tests.
Example
Structuring through Sub Headings
- This advice applies to all GS papers and I’ve discussed this in previous chapters, but nevertheless needs to be repeated.
- Divide the question into distinct parts and as you answer, give subheadings in a way that resembles the terms and phrases asked in the question. This gives a sense of coherence and order to your answer.
- Example: How has globalisation led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalisation detrimental to the development of the country?
- The above question has two parts and here’s how the structure of an answer should be:
- Introduction— Definition of Globalisation and formal sector Subheading 1: How globalisation led to reduction in formal employment
- Subheading 2: Informalisation is detrimental because
- Conclusion
Answering Broadly
- Economy as a discipline is not merely about concepts such as inflation, GDP, taxes or investment. It is a much broader subject, impinging upon most aspects of our living. This is why in your answers too, make an effort to include a wide range of dimensions.
- For instance, in a question on ‘inclusive growth’, try to include one point each from diverse categories such as health, education, skill development, agriculture, infrastructure, women, tribals, financial inclusion etc. mentioning the relevant government schemes (MNREGA, PMAY, PDS, Ayushmann Bharat etc).
- Of course, this isn’t a blanket rule that you apply for all questions. It’s ideal for questions that deal with broad topics such as poverty reduction, inclusive growth etc. Sometimes if the number of points are very high, club them under broad categories. For example, in a question dealing with how India should resolve the LWE problem, there can be many solutions. So instead of listing them down without any order, categorise them under social measures, economic measures, cultural measures, political measures etc. and then write 2-3 points under each of these sub headings.
Preparing a Topical Summary
Questions in Economy are often repeated with similar themes over years. Therefore, it helps to prepare 250-word summary for topics mentioned in the syllabus such as Planning, PDS, FDI, Inclusive growth, E-technology in the aid of farmers etc. For each concept, prepare on the lines of
- Definition Latest statistics
- Govt policies and schemes in that sector
- Current status and the problems ailing the sector
- Expert recommendations and solutions (very important) Conclusion
Use Economic Survey to make these notes. These concise notes will help you recollect points quickly and effectively.
Security, Disaster Management and Environment
Introduction
Majority of topics under these categories are technical in nature: Subjects such as Environment impact assessment, disaster management, cyber security, terrorism and insurgency etc. For such topics, it’s helpful to start your answers with definition along with a suitable example or a statistic.
Current Affairs
GS-3 questions are usually based on current affairs. So wherever possible, even though not asked directly, try to link your answer to the current affairs and govt initiatives. For instance, if there is a question on cyber security or data privacy, you can add value to your answer by quoting real life examples such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal.
Similarly, any answer on energy scenario should mention current events such as the Paris agreement and India’s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution targets.
Maps and Digrams
Be innovative in using maps and charts in these topics. Draw maps to illustrate in questions on border management, LWE affected areas (red corridor), illegal trade routes (golden triangle, golden crescent) etc., Even the concept of Border Security can be effectively depicted through a flow chart. In one of the mock tests, I drew the following to explain threats India faces from its neighbours.(I practiced this prior to the exam)
Conclusion
Conclude your answer with recommendations from committees, if any.
Also, in security and disaster management, prepare a collection of best practices in India and across the world and mention them in your answers. For instance, in Singapore, all critical installations and public spaces are 3D mapped in advance so that in the time of disaster, it will help authorities make an informed decision. Mentioning such innovative examples will make your answer stand out from the rest. Also keep a track of global initiatives, agreements and summits that are reported in the papers, and make it a point to mention them in your answers.
Civil Services Exam is generalist in nature, testing only the basic knowledge of an aspirant about a diverse span of subjects. Even in a specific topic like Science and Tech, the crux of all questions is to test whether you have a foundational understanding of the concept. So, you need not understand specific equations for gravitational waves, but you are expected to know what this discovery entails, and how it is useful or detrimental.
In science and technology, first equip yourself well with static knowledge on topics— nanotechnology, space technology, bio technology, and the like. Apart from the above, you need to learn fundamental terms and technologies used in Space (PSLV, GSLV, Cryo Engine etc), Nanotech, Nuclear Research (Fast breeder reactor, Uranium enrichment, Nuclear fission and fusion etc.), Defence (Cruise missile, Ballistic missile, Stealth Bomber etc), Biotech (Gene editing, Stem Cells, GM food etc), Communication (LIDAR, RADAR, LiFi, 5G etc). Any comprehensive material of a coaching institute will be sufficient for this.
While preparing for this section, the following broad framework is helpful in answering most of the questions.
- A simple explanation of the concept and its constituent parts (a schematic if apt)
- Why it is in news
- What are its potential benefits (wherever possible, make it multi- dimensional, across sectors)
- Potential threats it may pose and how we must tackle them
- What we can do to make it safe and beneficial for the public
Sample Answer
Question: Justify the need for FDI for the development of the Indian economy. Why is there is a gap between MoUs signed and actual FDIs? Suggest remedial steps to be taken for increasing actual FDIs in India.
Ans: FDI refers to a long-term investment by a company of one country in a firm located in another country.
FDI is needed for development of Indian Economy because:
1. Stable long term investment and non-debt creating Inflow of capital into industries and backward regions
2. Transfers latest technology Eg: Amazon in Hyderabad
3. Human resource development, higher productivity and efficiency
4. Creates new jobs in the economy
5. Generates tax revenue for the government
FDI is needed for development of Indian Economy because:
- Stable long term investment and non-debt creating Inflow of capital into industries and backward regions
- Transfers latest technology Eg: Amazon in Hyderabad
- Human resource development, higher productivity and efficiency
- Creates new jobs in the economy
- Generates tax revenue for the government
Remedial Steps:
1. Explore more opportunities for DTAAs and Bilateral Investment Treaties
2. Improve EoDB by establishing single window clearance— Eg: TS- iPass Act of Telangana which gives automatic approval within 15 days
.3. Land reforms: Conclusive titling along with land leasing reforms are needed
4. Strengthening Insolvency and Bankruptcy code to ensure quick closure of firms
5. IPR: Robust legal protection of intellectual property rights
6. Ensure fair and predictable taxation policies
These reforms will go a long way in attracting FDI and help in realising a 5 trillion economy by 2024.
|
8 videos|605 docs
|
FAQs on GS - 3 - UPSC Mains Answer Writing: Practice
| 1. What is the meaning of GS - 3 in UPSC? |  |
| 2. What are the important topics to study for GS - 3 in UPSC? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for GS - 3 in UPSC? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific books or resources recommended for GS - 3 in UPSC? |  |
| 5. How much weightage does GS - 3 carry in the UPSC Civil Services Examination? |  |





















