MCAT Exam > MCAT Notes > Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT > Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides | Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT PDF Download
Carbohydrates Definition
- Carbohydrates are molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
- There are twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon or oxygen atoms.
- The general formula for a carbohydrate can be written as Cx(H2O)y.
- They act as the source of energy (e.g. glucose), as a store of energy (e.g. starch and glycogen) and as structural units (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitins in insects).
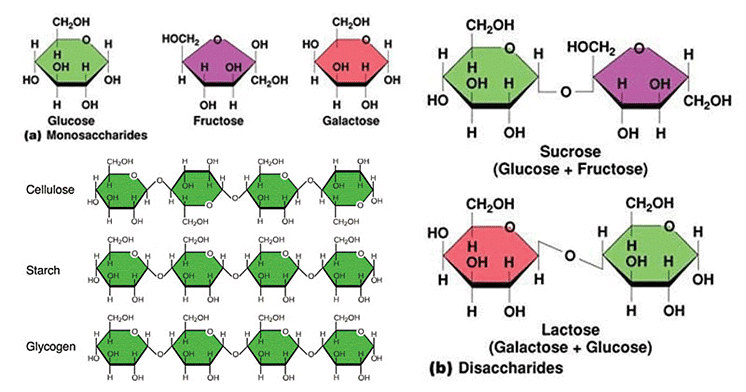
- Most carbohydrates are polymers.
- Polymers are large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers.
- Monomers are small, basic molecular units.
- Carbohydrates can be divided into three groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides – Structure, Properties, and Examples
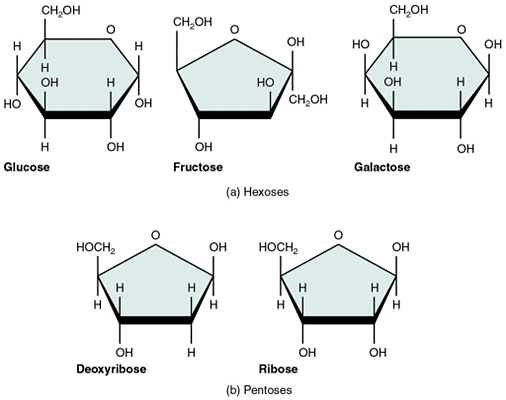
- Monosaccharides are simple sugars in which there are one oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom present in the molecule.
- They have general formula as (CH2O)n.
- Monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
- The test for reducing sugar is called Benedict’s test.
- They are sugars, which taste sweet, are soluble in water and are insoluble in non-polar solvents.
- They exist in straight chains or in the ring or cyclic forms.
- They are classified according to the number of carbon atoms in each molecule as trioses (3C), tetroses (4C), pentoses (5C), hexoses (6C), heptoses (7) and so on.
- The names of all sugars end with -ose.
- Examples: Glyceraldehyde (triose), Erythrose (tetrose), Ribose (pentose), Glucose (hexose), Fructose (hexose), Galactose (hexose), Sedoheptulose (heptose), etc.
- They are used as a source of energy in respiration.
- They are important building blocks for large molecules.
Disaccharides – Structure, Properties, and Examples
- Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides joined together by a condensation reaction.
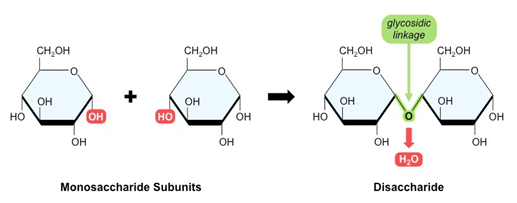
- The condensation reaction is the joining of two molecules with the formation of a new chemical bond and a water molecule is released when the bond is formed.
- A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides. If carbon 1 on one monosaccharide joins to carbon 4 on another monosaccharide, it is called a 1,4-glycosidic bond.
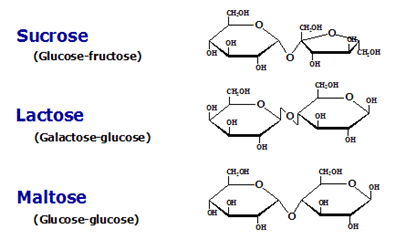
- Examples: Maltose is formed from two α-glucose molecules joined together by a glycosidic bond. Sucrose is formed from a condensation reaction between a glucose molecule and a fructose molecule. Lactose is formed from glucose and a galactose molecule.
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
- Disaccharides can be split apart into two monosaccharides by breaking the glycosidic bond by adding water molecules, which is known as hydrolysis reaction. The water provides a hydroxyl group (-OH) and hydrogen (-H), which helps the glycosidic bond to break.
- Sucrose is the transport sugar and Lactose is the sugar found in milk which an important constituent of the diet of young mammals.
Polysaccharides – Structure, Properties, and Examples
- Polysaccharides are polymers formed by combining many monosaccharide molecules (more than two) by condensation reactions.
- Molecules with 3-10 sugar units are known as oligosaccharides while molecules containing 11 or more monosaccharides are true polysaccharides.
- Polysaccharides do not taste sweet.
- Because their molecules are so enormous, the majority of polysaccharides do not dissolve in water.
- Polysaccharides made solely from one kind of monosaccharides are called homopolysaccharides (Starch) while those made of more than one monomer are called heteropolysaccharides (Hyaluronic acid).
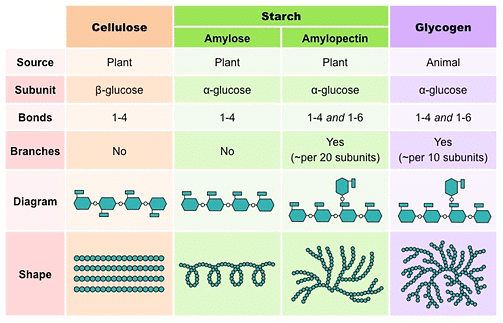
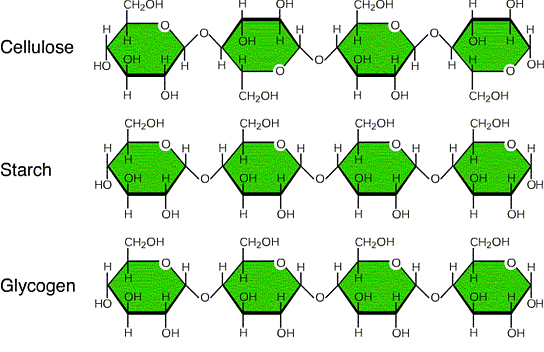
- Starch is made up of long chains of α-glucose (Amylose and Amylopectin). Glycogen is made of α-glucose linked together by glycosidic bonds. Cellulose is also made of many β-glucose molecules linked by glycosidic bonds between carbon 1 and carbon 4.
- Starch is the main energy storage materials in plants. Glycogen is the main energy storage materials in animals. Cellulose is the major component of cell walls in plants.
- The test for starch is called an Iodine test.
The document Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Polysaccharides | Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT is a part of the MCAT Course Biology and Biochemistry for MCAT.
All you need of MCAT at this link: MCAT
|
129 videos|60 docs|24 tests
|
Related Searches




















