UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 14th December 2022 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
India condemns OIC secretary general’s visit to PoK, his comments on J&K
India condemned the visit of the secretary general of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) to Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) and his comments on Jammu and Kashmir.
- It has said that the grouping has no locus standi in the matters related to the region.
- The government also said the OIC had already lost its credibility by taking a blatantly communal, partisan and factually incorrect approach on issues.
The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- OIC (formerly Organization of the Islamic Conference) is the second largest inter-governmental organization after the United Nations.
- OIC is the collective voice of the Muslim world to ensure and safeguard their interest on economic socio and political areas.
- It has membership of 57 states spread over four continents.
- It has a permanent secretariat in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Origin
- The Organization was established upon a decision of the historical summit which took place in Rabat, Kingdom of Morocco in 1969.
- This summit was a result of criminal arson of Al-Aqsa Mosque in occupied Jerusalem.
- This organization has been termed a toothless tiger by many analysts when it comes to dealing with disagreements among member states.
- Every member has a veto. As a result, the organization fails to take a critical stand on serious disputes that are shaping in the middle east.
India’s Relationship with OIC:
- At the 45th session of the summit in 2018, Bangladesh suggested that India should be given observer status. It was vetoed by Pakistan.
- This suggestion was on the basis that more than 10% of the world’s Muslim population live in India.
- It was Qatar that first proposed 'Observer' status for India at the OIC Foreign Ministers' meet in 2002.
- India was invited to attend the OIC meeting in 1969 but Pakistan prevailed upon and got the invite withdrawn.
- However, India, in 2019, made its maiden appearance at the OIC summit, as a guest of honour.
- The then External Affairs Minister Sushma Swaraj addressed the inaugural plenary in Abu Dhabi.
- Despite this, the organisation is known for its anti-India rhetoric under the influence of Pakistan.
Source: Indian Express
Why Chinese PLA troops target Yangtse, one of 25 contested areas
Context
Yangtse in the Tawang sector of Arunachal Pradesh has been repeatedly targeted by Chinese PLA troops, seeking to dislodge Indian troops from vantage points.
Twang Sector: a contested area
- Soldiers of the two sides clashed in an area called Yangtse, in the upper reaches of Tawang sector in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Tawang, indeed nearly all of Arunachal, is claimed by China.
- It is one of the more serious dispute points between India and China in the overall border question.
- Within Tawang, there are three agreed areas of differing Indian and Chinese perceptions of the LAC.
- A majority of these areas – Yangtse included – were identified by the two sides during multiple meetings. This includes:
- Joint Working Group (JWG) in the 1990s,
- during exchange of maps for the Middle Sector in 2000, and
- comparison of maps for the Western Sector in 2002.
- The remaining contested areas were identified over a period of time due to PLA actions.
- A majority of these areas – Yangtse included – were identified by the two sides during multiple meetings. This includes:
- Current situation
- The Tawang sector is dominated by Indian troops who can spot Chinese patrols when they come forward.
- Every time movement is noticed, Indian troops move for a faceoff.
- In 2016, around 250 Chinese troops showed up, crossing a point which India says marks the LAC.
- Historical importance of Tawang sector
- Tawang is the birthplace of the sixth Dalai Lama and an important pilgrimage centre for Tibetan Buddhists.
- The 14th Dalai Lama took refuge in Tawang after he crossed over from Tibet to India in 1959, spending some days in the monastery there before proceeding further.
- Context of India-China new crisis at Tawang
- The PLA’s motivation for creating a new crisis along the disputed border, this time in the east, appears to be to extend the points of confrontation and keep the issue of India China border alive
- This is at a time when the world is engaged in overcoming multiple crisis emanating from the War in Ukraine.
- The Yangtse incident came days after China said that the joint India-US military exercise Operation Yudhabhyas had violated the terms of the 1993 and 1996 border agreements.
- The 18th edition of the India-US joint military exercise Yudh Abhyas was held recently in Uttarakhand, about 100 km from the LAC.
- The 1993 agreement deals with maintaining peace and tranquility along the LAC.
- The 1996 pact was about confidence building measures in the military field along the LAC with China.
- The 18th edition of the India-US joint military exercise Yudh Abhyas was held recently in Uttarakhand, about 100 km from the LAC.
- Recent aggressive actions of China in eastern sector
- As part of the Chinese strategy to assert its territorial claims over Indian territory, Beijing, in January 2022, announced Chinese names for 15 places in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Earlier, in April 2017, its Ministry of Civil Affairs had issued official Chinese names for six places in the state.
- China’s national legislature in October 2021 adopted a new law on the protection and exploitation of the land border areas that came into effect on January 1, 2022.
- The new law formalises some of China’s recent actions in disputed territories with both India and Bhutan.
- It has deployed a high number of reserve troops along the LAC in the Eastern Command and has conducted annual training exercises of longer duration in depth areas.
- Besides increased patrolling activities in the region, it has constructed dual-use border villages and troop habitats which can be used by both military and civilians.
- As part of the Chinese strategy to assert its territorial claims over Indian territory, Beijing, in January 2022, announced Chinese names for 15 places in Arunachal Pradesh.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Geminids meteor shower
Context
This year, the Geminids will peak around December 13-14, when, with a clear sky and away from bright city lights, you can watch scores of meteors streak across the sky.
- This year however, the moon is bright, and so only 30-40 meteors per hour will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere.
What are meteor showers:
- Meteors come from leftover comet particles and bits from asteroids
- Meteors are usually fragments of comets.
- As they enter the Earth’s atmosphere at high speed, they burn up, creating a spectacular “shower”.
- When these objects come around the Sun, they leave a dusty trail behind them.
- Every year Earth passes through these debris trails, which allows the bits to collide with our atmosphere where they disintegrate to create fiery and colourful streaks in the sky
About Geminids:
- One of the best and most reliable annual meteor showers
- With new moon and clear weather, the Geminids can produce approximately 100-150 meteors per hour for viewing.
- The Geminids are unique because unlike most meteor showers, they originate not from a comet, but from an asteroid –3200 Phaethon.
- As the 3200 Phaethon moves close to the Sun while orbiting it, the rocks on its surface heat up and break off.
- When the Earth passes through the trail of this debris, the Geminids are caused.
- The name Geminids – from constellation Gemini, from whose location in the sky the meteor shower appears to originate.
- It serves to aid viewers in determining which shower they are viewing on a given night.
- The constellation is not the source of Geminids.
- Geminids are visible throughout the night sky, not just in Gemini constellation
How to watch:
- Chances of a successful viewing are higher from locations far away from the lights of cities.
- Generally, pollution makes viewing meteor showers from India difficult.
- But in areas where there is no light or air pollution, viewers do not need to use any special equipment to view the showers.
- Make sure to give your eyes enough time to adjust to the darkness, which can take about 30 minutes.
- Additionally, viewers should try to stay away from their phones, as looking at bright screens affects night vision.
Asteroid 3200 Phaethon:
- Discovered on October 11, 1983.
- Named after the Greek mythology character Phaethon, son of the Sun God Helios.
- It takes 4 years to complete one round of the Sun.
Miscellaneous:
- Gemini constellation is located northeast of the constellation Orion and between the Taurus and Cancer constellations.
Source: Indian Express
Base Editing
Context
Described by scientists as “the most sophisticated cell engineering to date,” an experimental treatment would provide the teenager Alyssa, diagnosed with blood cancer, a new lease of life.
About T-Cell blood cancer:
- T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (T-ALL).
- T-ALL affects the stem cells in the bone marrow that produce a particular kind of white blood cells (WBC) called T lymphocytes (T cells).
- These cells provide a person immunity by killing cells carrying infections, activating other immune cells, and regulating the immune response.
- At least 20% of these WBC are atypical– as they accumulate in the bone marrow, they crowd out “good” WBCs and hence weaken the immune system.
- These unhealthy cells can also accumulate in other parts of the body like the liver, spleen and lymph nodes.
- While found in both children and adults, T-ALL’s incidence decreases with age.
Its treatment:
- Similar to any leukaemia– chemotherapy and stem cell/bone marrow transplant.
- Chemotherapy – either kills the cancerous cells or stops them from further dividing.
- It may also wreck immunity system along with it.
- If chemotherapy fails, bone marrow transplant is done.
- Patients receive an infusion of healthy bone marrow cells that will hopefully multiply and restore immunity.
- Overall treatment for T-ALL is pretty effective– children have a survival rate of over 85 per cent after five years of receiving this treatment.
Treatment received by Alyssa:
- Alyssa received a dose of healthy T-cells from a donor that would hopefully attack her cancerous cells without destroying each other.
- Known as CAR-T therapy, this principle has been around for a while, but Alyssa’s case was different.
- Traditionally, CAR-T therapy involves following steps:
- First, an individual’s own T-cells are removed, which are then modified and reintroduced to the individual.
- Adding a gene to T-cells that causes them to seek out and destroy cancerous cells.
- The modified cells are known as CAR-T cells.
- Problem with CAR-T therapy: Very often, when an individual is really sick, it is simply impossible to obtain enough healthy T-cells to create CAR-T cells.
- While donors can provide healthy T-cells to an individual, these T-cells from a foreign body attack every single cell in that patient’s body, making the treatment counterproductive.
- Thus, scientists have resorted to what is known as base editing– through this technique of genetic editing, they make it possible for one donor to supply T-cells to multiple recipients, without the traditional risks associated with it.
- Thus, Alyssa received genetically modified cells that were programmed to specifically attack her cancer while leaving the rest of her body alone.
What is base editing?
- Bases are the language of life.
- Just as letters in the alphabet spell out words that carry meaning, the billions of bases in our DNA spell out the instruction manual for our body.
- Scientists can zoom into a precise part of the genetic code to alter the molecular structure of just one base, effectively changing its genetic instructions.
- A team at the Great Ormond Street Hospital managed to use base-editing to create a new type of T-cell from a healthy donor that would not attack other cells in Alyssa’s body, not kill each other, survive chemotherapy and finally, hunt down all other T-cells in Alyssa’s body (healthy and cancerous).
Source: Indian express
Agri, space depts ink pact to develop support system using data from satellites
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture and Department of Space signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to develop a Krishi-Decision Support System (Krishi-DSS) using satellite data.
- This will enhance the evidence-based decision-making capability of all the stakeholders in the agriculture sector by way of integration with MOSDAC and BHUVAN (Geo-platform) and ICAR systems.
About BHUVAN portal:
- Bhuvan (means earth in Sanskrit) is a Geoportal platform developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and was launched in 2009.
- It is known for its association with the Government of India to enable the use of Geospatial technology.
- Geospatial Technology is an emerging field of study that includes Geographic Information System (GIS), Remote Sensing (RS) and Global Positioning System (GPS).
- It enables us to acquire data that is referenced to the earth and use it for analysis, modelling, simulations and visualisation.
- It hosts a wide range of services that cover visualisation of satellite data, thematic maps, free data downloads, near real-time disaster services, apps for crowd sourcing and diverse geospatial applications.
- Bhuvan has since its inception enabled the Indian government to host public geospatial data as information layers for visualisation and public consumption. g., Toll Information System for National Highways Authority of India.
- The information for the platform is obtained from the Government of India sources or through Crowdsourcing.
MOSDAC (Meteorological and Oceanographic Satellite Data Archival Centre):
- It is a data repository for the missions of the ISRO and Government of India, dealing with meteorology, oceanography and tropical water cycles.
- Data acquired from missions is disseminated in near real time from Space Applications Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad through the MOSDAC website.
Krishi-Decision Support System (Krishi-DSS):
- Background: A DSS is an interactive software-based system used to help decision-makers compile useful information from a combination of raw data, documents and personal knowledge, to identify and solve problems and to make an optimised decision.
- About Krishi-DSS:
- It is being developed on the lines of Gati Shakti, using RISAT-1A and VEDAS of the Department of Space.
- Earth Observation Satellite - 04 (EOS-04, formerly known as RISAT-1A) is an ISRO Radar Imaging Satellite designed to provide all-weather high-quality images for applications such as Agriculture, Forestry, Soil Moisture, Hydrology and Flood mapping.
- Visualisation of Earth Observation Data and Archival System (VEDAS) provides a platform (data, infrastructure and guidance) hosted by SAC for utilisation of information from space-borne sensors to support the decision-making system.
- RISAT-1A data will be extremely useful in developing decision support systems for agriculture, bioresources, environment, water resources and disaster management.
- Hence, Krishi-DSS help in agriculture to collect and analyze data from a variety of sources with the ultimate goal of providing end users with insight into their critical decision-making process.
- It is being developed on the lines of Gati Shakti, using RISAT-1A and VEDAS of the Department of Space.
Source: Indian express
Wildlife Protection
Context
The expeditious passage of the Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Bill, 2021 (WPA) needs comment.
- While the aspects of protecting species from the wildlife trade, in line with international standards, have received thoughtful scrutiny by civil society, the impact of the criminal legal framework adopted by the WPA is less known.
- Pitting wildlife species against communities as human-animal conflict has eluded the true cost of criminalisation under the WPA.
The Wildlife Protection Act (WPA), 1972
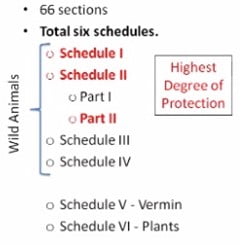
- It is the primary legislation protecting the country’s unique flora and fauna.
- It has safeguarded numerous species of wild animals and plants by prohibiting all forms of hunting and, more importantly, creating inviolate areas where wildlife conservation may be carried out.
WPA (Amendment):
- It further invests in the conception of protected areas and species by bringing in newer species to be protected, augmenting the penal repercussions.
- Rationalising schedules: From 6 to 4 – removing schedule for vermin (V) and a new schedule for CITES listed species.
- Obligations under CITES: Central government to designate a: (I) Management Authority, which grants export or import permits for trade of specimens, and (iii) Scientific Authority, which gives advice on aspects related to impact on the survival of the specimens being traded.
- Invasive alien species: to regulate or prohibit the import, trade, possession or proliferation of the same.
- Better Management of Protected Areas: It provides for certain permitted activities like grazing or movement of livestock and Bonafede use of drinking and household water by local communities.
- Protection of Forest Lands: It is so critical because it equally inculcates the protection of rights of the people who have been residing there since ages.
- Section 43 of the act amended which permitted the use of elephants for ‘religious or any other purposes’
Challenges to the Act:
- Social Injustice: A study by the Criminal Justice and Police Accountability Project (the CPA Project examined arrest records of the police and Forest Department in Madhya Pradesh and found that persons from oppressed caste communities such as Scheduled Tribes and other forest-dwelling communities form the majority of accused persons in wildlife-related crimes.
- Use of muscle: The Forest Department was found to use the threat of criminalisation to force cooperation, apart from devising a system of using community members as informants and drawing on their loyalty by employing them on a daily wage basis.
- Pendency’s in cases: Cases that were filed under the WPA did not pertain solely to the comparatively serious offence of hunting; collecting wood, honey, and even mushrooms formed the bulk of prosecution in PAs.
- Over 95% of the cases filed by the Forest Department are still pending
- Misplaced regulations: Hunting offences against lesser protected species formed over 17.47% of the animals ‘hunted’ between 2016-20.
- Animals hunted the highest, only one in top five belonged to Schedule I (peacock).
- Surprisingly, fish (only certain species relegated to Schedule I) formed over 8% of the cases filed.
- A whopping 133 cases pertaining to fishing (incorrectly classified as Schedule V species) were filed in the last decade in Madhya Pradesh.
- Forest Rights Act subservient to the WPA – due to natural overlap of recognising forest rights in intended-as-inviolate PAs, thereby impeding its implementation.
- Collective Forest Rights not recognised in buffer zones over usage of forest resources, fishing, and protecting forest resources.
- Criminalisation of Fishing – which forms an important part of subsistence for tribal communities
- Due to their occurrence in Pas, they become punishable by three to seven years.
- In a case from 2016 documented by the CPA Project, the catch weighed less than 500 grams, yet the accused were charged with causing damage to a wildlife habitat under a host of WPA provisions.
- Fear mongering is a crucial way in which the department mediates governance in protected areas, and its officials are rarely checked for their power.
- Criminal cases filed by the department are rarely compounded since they are meant to create a ‘deterrent effect’ by instilling fear in communities.
- Unchecked discretionary policing allowed by the WPA and other forest legislations have stunted the emancipatory potential of the FRA.
Way forward:
- The need for criminal laws to assist wildlife conservation has remained unchallenged since its conception.
- From regulated hunting to complete prohibition and the creation of ‘Protected Areas (PA)’ where conservation can be undertaken without the interference of local forest-dwelling communities, State and Forest Department control over forests and the cattiest underpinnings of conservation would not have been possible without criminal law.
Source: The Hindu
|
39 videos|4303 docs|908 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 14th December 2022 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-II and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare for GS-II and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What are some important topics to focus on for GS-II in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. Which subjects should I prioritize for GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How can I improve my answer writing skills for GS-II and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
|
39 videos|4303 docs|908 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|






















