Various Implicants in K-Map | Digital Logic - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Prerequisite – K – Map (Karnaugh Map)
Implicant is a product/minterm term in Sum of Products (SOP) or sum/maxterm term in Product of Sums (POS) of a Boolean function. E.g., consider a boolean function, F = AB + ABC + BC. Implicants are AB, ABC, and BC.
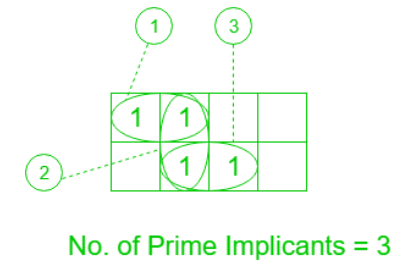
Prime Implicants:
A group of squares or rectangles made up of a bunch of adjacent minterms which is allowed by the definition of K-Map are called prime implicants(PI) i.e. all possible groups formed in K-Map.
Example:
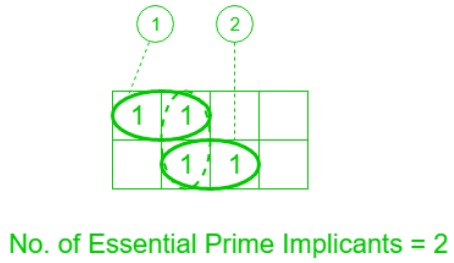
Essential Prime Implicants:
These are those subcubes(groups) that cover at least one minterm that can’t be covered by any other prime implicant. Essential prime implicants(EPI) are those prime implicants that always appear in the final solution.
Example:
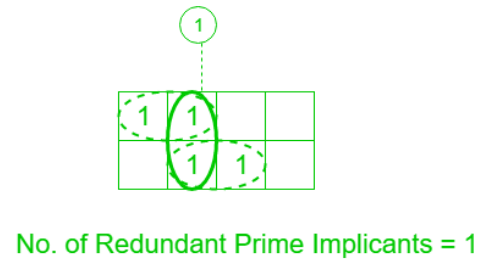
Redundant Prime Implicants:
The prime implicants for which each of its minterm is covered by some essential prime implicant are redundant prime implicants(RPI). This prime implicant never appears in the final solution.
Example:
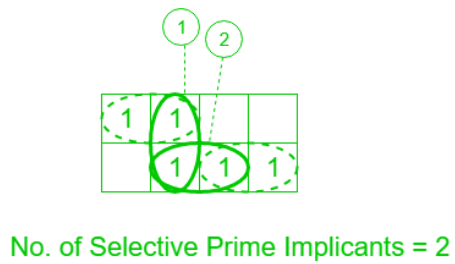
Selective Prime Implicants:
The prime implicants for which are neither essential nor redundant prime implicants are called selective prime implicants(SPI). These are also known as non-essential prime implicants. They may appear in some solution or may not appear in some solution.
Example:
Example 1: Given F = ∑(1, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 15), find number of implicant, PI, EPI, RPI and SPI.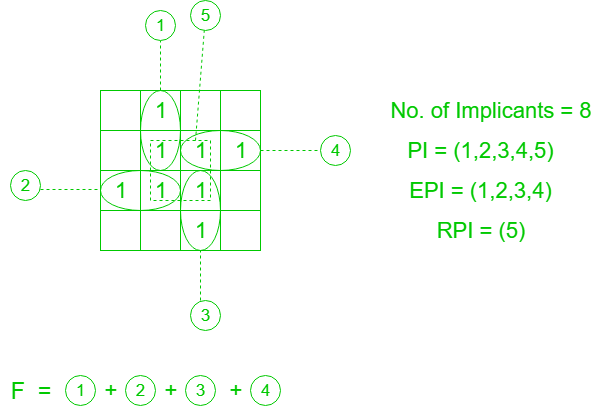
BD + A'C'D + A'BC+ ACD+ABC'
No. of Implicants = 8
No. of Prime Implicants(PI) = 5
No. of Essential Prime Implicants(EPI) = 4
No. of Redundant Prime Implicants(RPI) = 1
No. of Selective Prime Implicants(SPI) = 0
Example 2: Given F = ∑(0, 1, 5, 8, 12, 13), find number of implicant, PI, EPI, RPI and SPI.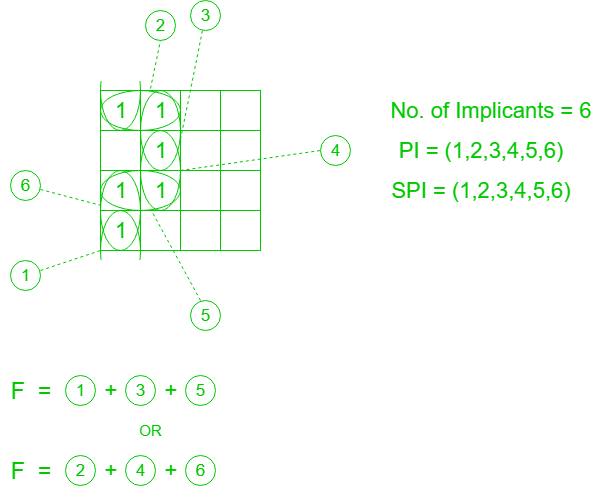
A'B'C'+ C'DB + C'D'A
No. of Implicants = 6
No. of Prime Implicants(PI) = 6
No. of Essential Prime Implicants(EPI) = 3
No. of Redundant Prime Implicants(RPI) = 3
No. of Selective Prime Implicants(SPI) = 6
Example 3: Given F = ∑(0, 1, 5, 7, 15, 14, 10), find number of implicant, PI, EPI, RPI and SPI. 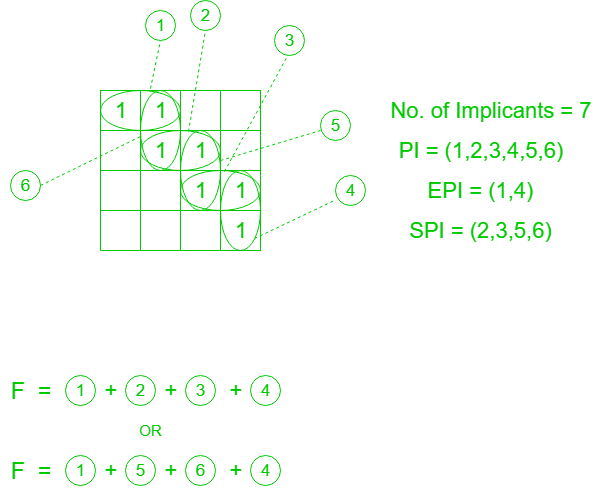
No. of Implicants = 7
No. of Prime Implicants(PI) = 6
No. of Essential Prime Implicants(EPI) = 4
No. of Redundant Prime Implicants(RPI) = 2
No. of Selective Prime Implicants(SPI) = 4
|
53 docs|15 tests
|