UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 8th January 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
What is Thullal?
Context
Recently, a traditional art Ottanthullal of Kerala which has a history of over 300 years was performed in Kerala School Kalolsavam 2023.
About thullal
- It is a recite-and-dance art form of Kerala, which was introduced in the 18th century by the famous Malayalam poet Kunchan Nambiar (1705 - 1770).
- It is famous for its humour and social satire and is marked by its simplicity.
- It follows the classical principles of Natyasasthra (a treatise on art compiled in the 2nd century B.C.E).
- It is enacted into three separate versions
- Ottanthullal
- Seethankan thullal
- Parayan thullal
- The Ottanthullal is the most popular among the three varieties of Thullal.
- The performance uses elaborate expressions and stories recited in verses to bring important mythological tales and stories to life.
- The costume and makeup of the performer are similar to that of a Kathakali artist.
- It is performed at temple festivals and cultural programmes.
- The Thullal performer is supported by a singer who repeats the verses and is accompanied by an orchestra of mridangam or thoppimaddalam (percussions) and cymbals.
Source: The Hindu
What is Meghalaya’s Living Root Bridge?
Context
A farmer recently takes forward the State’s traditional practice of building root bridges and connects two areas across Umkar river in Cherrapunjee.
About Meghalaya’s Living Root Bridge:
- Meghalaya is known for its living root bridges, locally known as jingkieng jri.
- They are on the tentative list of UNESCO’s World Heritage sites.
- Many bridges across the State are over a century old.
- A living root bridge is like a suspension bridge formed by guiding the pliable roots of the rubber fig tree (Ficus elastica) across a stream or river and allowing the roots to grow and strengthen over time.
- They are common in the southern part of the Northeast Indian state of Meghalaya.
Source: Indian Express
GS-II
Right to Strike
Context
The Kerala High Court has reiterated that government employees who participate in general strikes, affecting the normal life of the public and Public Exchequer, are not entitled to be protected under Article 19(1)(c) of the Constitution and are also a violation of the provisions of the Kerala Government Servants’ Conduct Rules, 1960.
What is Right to Strike?
- About:
- Strike is the collective refusal by employees to work under the conditions required by employers. Strikes arise for a number of reasons, though principally in response to economic conditions (defined as an economic strike and meant to improve wages and benefits) or labour practices (intended to improve work conditions).
- In each country whether it is democratic, capitalist, socialist, give the right to strike to the workers. But this right must be the weapon of last resort because if this right is misused, it will create a problem in the production and financial profit of the industry.
- This would ultimately affect the economy of the country.
- In India, the right to protest is a fundamental right under Article 19 of the Constitution of India.
- But right to strike is not a fundamental right but a legal right and with this right statutory restriction is attached in the Industrial Dispute Act, 1947.
- The Industrial Dispute Act, 1947 is subsumed under The Industrial Relations Code, 2020.
- Position in India:
- In India, unlike America, the right to strike is not expressly recognized by the law.
- The trade union Act, 1926 for the first time provided limited right to strike by legalizing certain activities of a registered trade union in furtherance of a trade dispute which otherwise breach of common economic law.
- Nowadays a right to strike is recognized only to a limited extent permissible under the limits laid down by the law itself, as a legitimate weapon of Trade Unions.
- The right to strike in the Indian constitution set up is not an absolute right but it flows from the fundamental right to form a union.
- As every other fundamental right is subject to reasonable restrictions, the same is also the case to form trade unions to give a call to the workers to go on strike and the state can impose reasonable restrictions.
- Right to strike under International Convention:
- Right to strike has also been recognised by the conventions of the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- India is a founder member of the ILO.
- The Supreme Court in Delhi Police v. Union of India (1986) upheld the restrictions to form association by the members of the non-gazetted police force after the Police Forces (Restriction of Rights) Act, 1966, and the Rules as amended by Amendment Rules, 1970, came into effect.
- In T.K. Rangarajan v. Government of Tamil Nadu (2003), the Supreme Court held that the employees have no fundamental right to resort to strike. Further, there is prohibition to go on strike under the Tamil Nadu Government Servants’ Conduct Rules, 1973.
Source: The Hindu
Unmanned Combat Systems and Concerns
Context
India is on a drive to induct Unmanned Combat Systems (UCS) into the military. In August, 2022 it inducted “Swarm Drones” into its mechanized forces, reiterating the importance of autonomous systems in creating a “future-proof” Indian Navy (IN).
- Despite their growing usage in armed conflict, artificially intelligent unmanned combat systems raise questions of law, ethics and accountability.
- About:
- Unmanned Combat Systems (UCS) are going to be the new age weapons overturning the rules of future war and have been the focus of research and development of military powers.
- There are no generally accepted definitions for these so-called boasted core weapons of the 21st century.
- UCS from the research heading, is an integrated combat system comprising unmanned combat platforms, task payloads, command and control (C2) systems and network systems.
- For field applications, they can be categorized into,
- Deep space unmanned systems
- Unmanned aerial vehicle systems
- Ground unmanned systems
- Surface unmanned systems
- Underwater unmanned systems
- Significance:
- Faced with the increasingly complex international situation and brutal military wars, the lives and safety of combat soldiers are greatly threatened.
- At this time, the unmanned combat System is becoming increasingly important and has gradually become an important attack and defense force on the information battlefield.
- The biggest feature of the ground unmanned combat platform is that it can carry certain weapons and equipment under the premise of unmanned participation, and be remotely controlled through the configured wireless communication equipment to conduct reconnaissance, surveillance, electronic interference, and direct combat.
- UCS has a higher degree of automation, good remote control, strong digital communication ability and anti-interference, excellent target detection and recognition ability, good concealment, and strong adaptability to the ground environment.
- Risk of Shared Liability:
- AI Warfare enhances the risk of shared liability between networked systems, particularly when weapon algorithms are sourced from abroad, and when the satellite and link systems that enable combat solutions are not under the control of the user.
- Confidence Undermining:
- AI is characterized by a predisposition to certain kinds of data. Biases in the collection of data, in the set of instructions for data analysis, and in the selection of probabilistic outcomes muddle rational decision-making, undermining confidence in automated combat solutions.
- Inconsistent with Laws of War:
- AI may automate weapon systems in ways that are inconsistent with the laws of war.
- Cannot Make Informed Decision:
- A system of targeting human beings based on probabilistic assessments by computers that act merely on machine-learned experiences, they contend, is problematic because the computer neither has access to all relevant data to make an informed decision nor recognises that it needs more information to come up with an optimal solution.
- If it erroneously used force in a theater of conflict, there is no one to be held accountable, as blame can’t be pinned on a machine.
Way Forward
- All parties to an armed conflict that any use of armed drones during the conduct of hostilities must comply with relevant IHL (International humanitarian law). principles.
- Hence, before deploying any armed drones, parties to the conflict must ensure that the armed drone is and can be directed against a military objective and will not cause excessive civilian harm.
- In order to foster transparency and accountability for drone strikes, parties need to properly articulate their policies governing the use of drones, including how the likelihood for civilian harm is assessed, and provide for remedies for victims.
- All parties to the armed conflict that beyond compliance with IHL, parties need to consider the humanitarian impact of their use of armed drones for the civilian population, including the disruption of civilian infrastructure and mental health trauma.
- It is worth acknowledging that AI in warfare is not just a matter of combat effectiveness but also of warfighting ethics. AI-infused unmanned systems on the maritime battlefront pose a degree of danger, making it incumbent upon the military to deploy its assets in ways that are consistent with national and international law.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
What are Floatovoltaics?
Context
Covering 10% of the world’s hydropower reservoirs with ‘floatovoltaics’ would install electrical capacity equivalent to that provided by all electricity-generating fossil fuel plants in operation worldwide.
About:
- Floatovoltaics, floating solar plants, or FSPV (floating solar photovoltaic) are panel structures that are installed on water bodies like lakes, basins, and reservoirs instead of on solid structures like a roof or terraces.
- The biggest impetus behind the rise of large-scale FSPV has been that it doesn’t take up any land space, which could be then used for construction and agriculture.
- The world’s first large-scale FSPV system was installed in 2011, in Napa Valley, California.
India:
- In recent years, floating solar power plants have become part of India’s plans of solar expansion.
- According to a 2020 study by TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute) reservoirs cover 18000 square Kilometer in India and can generate 280 GW through floating solar panels.
- Currently less than 1% of solar installations are floating.
- The largest floating solar power plant in India is currently the Ramagundam in Peddapalli district of Telangana, with a capacity of 100 MW.
- Currently a plant is being built on the Narmada’ Omkareshwar Dam in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh is being built with a capacity of 600 MW, which will soon be the largest floating solar power plant in the world.
- The project is touted to be worth Rs 3000 crore.
- What are the benefits of floating solar panels?
- the water’s cooling effect makes them more efficient than land-based ones;
- they don’t interfere with desert ecosystems; and
- they keep precious water from evaporating.
- Even though reservoirs are artificial ecosystems, they provide habitats for wildlife.
Source: The Hindu
What is Zebrafish?
Context
Recently, scientists discovered that a protein found in Zebrafish can regenerate aged discs in human vertebrae.
What are the key facts about Zebrafish?
- It is a small (2-3 cm long) freshwater fish found in tropical and subtropical regions. The fish is native to South Asia's Indo-Gangetic plains, where they are mostly found in the paddy fields and even in stagnant water and streams.
- It attracts developmental biologists due to its adequate regeneration capacity of almost all its organs, including the brain, heart, eye, and spinal cord.
- It has a similar genetic structure (around 70%) to humans.
- IUCN Red List Status: Least concerned.
Source: Indian Express
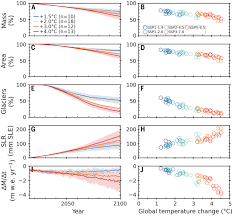
Global Glacier Change in the 21st Century
Context
Recently, a report titled “Global glacier change in the 21st century: Every increase in temperature matters”, which states half the Earth’s glaciers may disappear by 2100.
- The researchers used two decades of satellite data to map the planet’s glaciers with greater precision than ever before.
- The United Nation’s (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s sixth assessment report released in 2022 also warned that we are running out of time to attain the 1.5°C target.
- Glaciers Melting at Unprecedented Rate:
- Glaciers are receding at unprecedented rates due to climate change and rising temperatures.
- The amount of ice lost by glaciers between 1994 and 2017 was around 30 trillion tones and they are now melting at a pace of 1.2 trillion tonnes each year.
- The glaciers in the Alps, Iceland and Alaska are some of those that are melting at the quickest rates.
- Half the Earth’s glaciers are destined to vanish by 2100, even if we adhere to the Paris Climate Agreement goal of limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
- A minimum of 50 % of the loss will occur within the next 30 years. 68% of glaciers will vanish if global warming continues at the current rate of 2.7°C.
- If this happens, by the end of the following century, there would be practically no glaciers left in central Europe, western Canada and the United States.
- Some of these glaciers can be saved from extinction by reducing global warming, the researchers noted.
- Glaciers, which hold 70 % of the Earth’s freshwater, currently encompass around 10 % of the planet’s land area.
- Increasing Risk of Disaster:
- Melting glaciers raise sea levels dramatically, jeopardizing up to two billion people’s access to water and increasing the risk of natural disasters and extreme weather events like floods.
- Global sea level rose by 21 % between 2000 and 2019. This was solely due to meltwater from melting glaciers and ice sheets.
- Recommendations:
- The rapidly increasing glacier mass losses as global temperature increases beyond 1.5C stresses the urgency of establishing more ambitious climate pledges to preserve the glaciers in these mountainous regions.
Source: DownToEarth
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 8th January 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the three main subjects covered in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of General Studies Paper-I (GS-I) in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of General Studies Paper-II (GS-II) in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. How does General Studies Paper-III (GS-III) contribute to the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of the Daily Current Affairs section in the UPSC exam? |  |