Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation > Operating System
Operating System | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
- An Operating System (OS) is an interface between computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives and printers.
- Some popular Operating Systems include Linux Operating System, Windows Operating System, VMS, OS/400, AIX, z/OS, etc.
Structure of a Computer System:
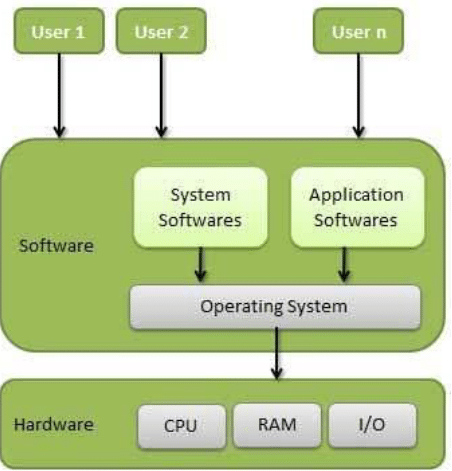 Functions of operating system:
Functions of operating system:
Following are some of important functions of an operating System.
- Memory Management
- Processor Management
- Device Management
- File Management
- Security
- Control over system performance
- Job accounting
- Error detecting aids
- Coordination between other software and users
Memory Management:
- Memory management refers to management of Primary Memory or Main Memory. Main memory is a large array of words or bytes where each word or byte has its own address. Main memory provides a fast storage that can be accessed directly by the CPU. For a program to be executed, it must in the main memory.
- An Operating System does the following activities for memory management −
- Keeps tracks of primary memory, i.e., what part of it are in use by whom, what part are not in use.
- In multiprogramming, the OS decides which process will get memory when and how much.
- Allocates the memory when a process requests it to do so.
- De-allocates the memory when a process no longer needs it or has been terminated.
Processor Management:
In multiprogramming environment, the OS decides which process gets the processor when and for how much time. This function is called process scheduling. An Operating System does the following activities for processor management −
- Keeps tracks of processor and status of process. The program responsible for this task is known as traffic controller.
- Allocates the processor (CPU) to a process.
- De-allocates processor when a process is no longer required.
Device Management:
- An Operating System manages device communication via their respective drivers. It does the following activities for device management −
- Keeps tracks of all devices. Program responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller.
- Decides which process gets the device when and for how much time.
- Allocates the device in the efficient way
- De-allocates devices.
File Management:
- A file system is normally organized into directories for easy navigation and usage. These directories may contain files and other directions.
- An Operating System does the following activities for file management −
- Keeps track of information, location, uses, status etc. The collective facilities are often known as file system.
- Decides who gets the resources.
- Allocates the resources.
- De-allocates the resources.
Other Important Activities
Following are some of the important activities that an Operating System performs −
- Security − By means of password and similar other techniques, it prevents unauthorized access to programs and data.
- Control over system performance − Recording delays between request for a service and response from the system.
- Job accounting − Keeping track of time and resources used by various jobs and users.
- Error detecting aids − Production of dumps, traces, error messages, and other debugging and error detecting aids.
- Coordination between other softwares and users − Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, assemblers and other software to the various users of the computer systems.
Types of Operating System
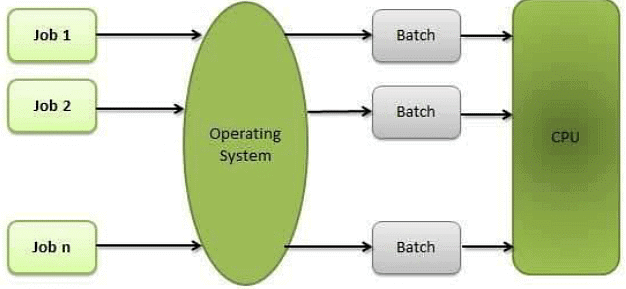
- Batch operating system: The users of a batch operating system do not interact with the computer directly. Each user prepares his job on an off-line device like punch cards and submits it to the computer operator. To speed up processing, jobs with similar needs are batched together and run as a group. The programmers leave their programs with the operator and the operator then sorts the programs with similar requirements into batches.
- Time-sharing operating systems: Time-sharing is a technique which enables many people, located at various terminals, to use a particular computer system at the same time. Time-sharing or multitasking is a logical extension of multiprogramming. Processor's time which is shared among multiple users simultaneously is termed as time-sharing.
- Multiprogramming Operating System: Multiprogramming is an extension to the batch processing where the CPU is kept always busy. Each process needs two types of system time: CPU time and IO time. In multiprogramming environment, for the time a process does its I/O, The CPU can start the execution of other processes. Therefore, multiprogramming improves the efficiency of the system.
- Multiprocessing Operating System: In Multiprocessing, parallel computing is achieved. There are more than one processors present in the system which can execute more than one process at the same time. This will increase the throughput of the system.
- Distributed operating System: Distributed systems use multiple central processors to serve multiple real-time applications and multiple users. Data processing jobs are distributed among the processors accordingly. The processors communicate with one another through various communication lines (such as high-speed buses or telephone lines). These are referred as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems.
- Network operating System: A Network Operating System runs on a server and provides the server the capability to manage data, users, groups, security, applications, and other networking functions. The primary purpose of the network operating system is to allow shared file and printer access among multiple computers in a network, typically a local area network (LAN), a private network or to other networks.
- Real Time operating System: A real-time system is defined as a data processing system in which the time interval required to process and respond to inputs is so small that it controls the environment. The time taken by the system to respond to an input and display of required updated information is termed as the response time. So in this method, the response time is very less as compared to online processing. There are two types of real-time operating systems.
- Hard real-time systems: Hard real-time systems guarantee that critical tasks complete on time. In hard real-time systems, secondary storage is limited or missing and the data is stored in ROM. In these systems, virtual memory is almost never found.
- Soft real-time systems: Soft real-time systems are less restrictive. A critical real-time task gets priority over other tasks and retains the priority until it completes. Soft real-time systems have limited utility than hard real-time systems. For example, multimedia, virtual realities, Advanced Scientific Projects like undersea exploration and planetary rovers, etc.
- Batch processing: Batch processing is a technique in which an Operating System collects the programs and data together in a batch before processing starts
- Multitasking: Multitasking is when multiple jobs are executed by the CPU simultaneously by switching between them. Switches occur so frequently that the users may interact with each program while it is running. A program that is loaded into memory and is executing is commonly referred to as a process.
- Spooling: Spooling is an acronym for simultaneous peripheral operations on line. Spooling refers to putting data of various I/O jobs in a buffer. This buffer is a special area in memory or hard disk which is accessible to I/O devices.
- Booting: When the computer starts, the operating system is first loaded (as it is essential for running all other programs), this process is known as booting.
- Cold Boot: Turn ON the computer from an OFF position is called Cold Booting.
- Warm Boot: A computer system starts up/reset from a complete powerless state is called Warm Booting.
- Firmware: Firmware is a software program that is written to a hardware device. It allows the hardware to be updated. The contents are saved when a hardware device is turned off or loses its external power source.
- Middleware: Middleware is a software layer situated between applications and operating systems. It enables communication and data management for distributed applications.
The document Operating System | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
647 videos|1019 docs|305 tests
|
Related Searches





















