Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation > Computer Fundamentals & Terminologies
Computer Fundamentals & Terminologies | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Fundamental of Computer: Basic
- As per our basic knowledge, an electronic device that accepts input/data and processes it into valuable information i.e output is named a Computer.
Functionalities of Computer
If we consider it in a very broad sense, any digital computer performs the following five operations:
- Step 1 − Accepts data as input.
- Step 2 − Saves the data/instructions in its memory and utilizes them as and when required.
- Step 3 − Execute the data and convert it into useful information.
- Step 4 − Provides the output.
- Step 5 − Have control over all the above four steps
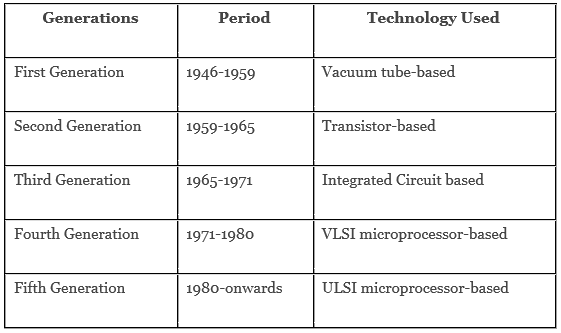
Generations of Computer
- There exist 5 computer generations till date. In the following list, approximate dates against each generation have been mentioned, which are normally accepted. These five generations of computers are based on their processing hardware.
Types of computers
- PC/Personal Computer: These are single-user computer systems having small, relatively reasonable computers designed for an individual user. This type of computer can easily be moved from one place to the other comprising a personal storage unit, input & output unit, and a Central Processing Unit.
- Workstation: Regularly a single user system is named a workstation. Workstations usually come with a high-resolution graphics screen, inbuilt network support, a large amount of RAM, and a graphical user interface. They are often designed for self-use by an individual and can be used for multiple purposes. This type of system is not convenient for carrying from one place to another.
- Mini Computer: These come under multiple user computer systems that are capable of holding hundreds of users simultaneously.
- MainFrame: Mainframe computers are also multi-user computer systems, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously; designed to be used in large firms and organizations where a lot of people have to work on the same database. Software technology is different from minicomputers.
- Supercomputer: These are extremely fast computers, which can execute hundreds of millions of instructions per second. Supercomputers are mostly used in scientific and engineering operations where processing is difficult. They are costly and complex to work on.
Advantages of Computer
High Speed
- The computer is a very fast device.
- It can perform the calculation of a very huge amount of data.
- The computer has units of speed in a microsecond, nanosecond, and even the picosecond.
- It can process millions of computational calculations in a fraction of seconds, unlike the man who may spend many months performing the same task.
Accuracy
- In addition to being very fast, computers are very accurate.
- The calculations are 100% error-free.
- Computers perform all jobs with 100% accuracy provided that the input is correct.
Storage Capability
- Memory is a very important characteristic of computers.
- A computer has much more storage capacity than human beings.
- It can store a large amount of data.
- It can store any type of data such as images, videos, text, audio, etc.
Diligence
- Unlike human beings, a computer is free from monotony, tiredness, and lack of concentration.
- It can work continuously without any error and boredom.
- It can perform repetitive tasks with the same speed and accuracy.
Versatility
- A computer is a very versatile machine.
- A computer is very flexible in performing the jobs to be done.
- This machine can be used to solve problems related to various fields.
- At one moment, it may be processing and simplifying a complex scientific problem, and the very next moment it may be running a card game.
Reliability
- A computer is a reliable machine.
- Modern electronic components have long lives.
- Computers are designed to make maintenance easy.
Automation
- A computer is an automatic machine.
- Automation is the capability due to which a machine can perform its task without the need for human consideration. Once the program is fed to the computer i.e., the program is held in the computer memory, then the program and instruction can be executed in absence of human consideration.
Reduction in Paperwork and Cost
- With the help of computers for data processing in an organization, there is a reduction of paperwork and results in speeding up the process, which in return saves trees.
- Because data saved as electronic files can be retrieved whenever required, the headache of maintaining piles of paper files gets reduced.
- While the investment at the beginning for the installation of a computer is high, it substantially reduces the cost of each of its transactions.
Disadvantages of Computer
No I.Q.
- A computer is a machine that has no intelligence to perform any task.
- Each instruction has to be given to the computer.
- A computer is not capable enough to make any decision on its own.
Dependency
- It works according to the user’s instruction, thus it is entirely dependent on humans.
- Environment
- The operating environment of the computer should be dust-free and suitable.
No Feelings
- Computers have no feelings or emotions.
- It is not smart enough to make a judgment based on experience, feeling, taste, and knowledge just like humans.
Terminologies
- Application: An application is a set of codes designed to allow specific tasks to happen. Microsoft Windows and Internet Explorer are common examples.
- Access time: The performance of a hard drive or other storage device - how long it takes to locate a file.
- Active program or window: The application or window at the front (foreground) on the monitor.
- ALGOL: It was the first language with a formal grammar. ALGOL was created by a committee for scientific use in 1958. Its major contribution is being the root of the tree that has led to such languages as Pascal, C, C+ + and Java.
- Algorithm: In computing, an algorithm is a procedure for accomplishing some tasks which, given an initial state, will terminate in a defined end-state.
- ASCII (pronounced ask key): American Standard Code for Information Interchange. a commonly used data format for exchanging information between computers or programs.
- Amplifier: A device that takes in a weak electric signal and sends out a strong one. It is used to boost electrical Signals in many electronic devices such as radios, !elevisions and telephone.
- Analog Computer: A computer that operates on data which is in the form of continuous variable physical quantities.
- Android: It is a linux based operating system designed Primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets computer.
- Antivirus Software: Antivirus software consists of 3omputer programs that attempt to identify threat and eliminate computer virus and other malicious software ( Malware )
- API: API refers to Application Programming Interface. It’s the platform used by a program to access different services on the computer system.
- Application Software: Application software is a subclass of computer software that employs thecapabilities of a computer directly to a task that the user wishes to perform. e.g., word document, spreadsheet, etc.
- Archieve: It provides backup storage.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The arithmetic logic unit is a part of the execution unit, a core component of all CPUs. ALUs are capable of calculating the results of a wide variety of basic arithmetical and logical computations
- Artificial Intelligence: Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today.
- Array: An array is similar data saved on a computer system in a sequential form.
- Assembler: A program that translates mnemonic statement into executable instruction.
- Attribute: The characteristics of an entity are called its attributes.
- BIOS: BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. It gives the computer a platform to run the software using a floppy disk or a hard disk. BIOS is responsible for booting a PC.
- Bit: Bit is Binary Digit. It refers to a digit number, either a 0 or a 1. The binary digit is used to represent computerized data.
- Backup: A copy of a file or disk you make for archiving purposes.
- Backspace: Backspace key is used on the keyboard to delete the text. Backspace will delete the text to the left of cursor.
- Bandwidth: The maximum amount of data that can travel in a communication path in a given time, measured in bits per second (bps).
- Bar Code: A bar code is a machine-readable representation of information in a visual format on a surface. The first bar code system was developed by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver in 1952.
- Bitmap: A method of storing a graphic image as a set of bits in a computer memory. To display the image on the screen, the computer converts the bits into pixels.
- Blog: It is a discussion or informational site published on the world wide web.
- Bomb: A type of virus designed to activate at a specific date and time on your computer.
- Bluetooth: A protocol that permits a wireless exchange of information between computers. cell phone and other electronic devices within a radius about 30 feet,
- Booting: Booting is a bootstrapping process which starts the operating system when a computer is switched on
- Botnet: It is a collection of internet connected programs communicating with other similar programs in order to perform tasks.
- Boot Sequence: A boot sequence is the set of operations the computer performs when it is switched on which loads an operating system.
- Browser: A special software that enables users to read/view web pages and jump from one web page to another.
- Buffering: The process of storing data in a memory device, allowing the devices to change the data rates,perform error checking and error retransmission.
- Bug: A software bug is an error, flaw, failure, or fault in a computer program or system that produces an incorrect or unexpected result.
- Boolean: An expression, the value of which is either true or false.
- BUS: A bus is a set of wires that enables flow of data from one location of the computer to another.
- Byte: Eight bits is equal to 1 byte.
- CGI: CGI stands for Common Gateway Interface. It defines how an auxiliary program and a Web server would communicate.
- Class: A group of objects having same operations and attributes is defined as a class.
- Client: A client is a program that asks for information from other processes or programs. Outlook Express is a great example of a client.
- CD-ROM: An acronym for Compact Disc Read-Only Memory.
- Client – Server: A common form of distributed system in which software is split between server tasks and client tasks. A client sends requests to a server, according to some protocol, asking for information or action, and the server responds.
- Clipboard - A portion of memory where the Mac temporarily stores information. Called a Copy Buffer in many PC applications because it is used to hold information which is to be moved, as in word processing where text is "cut" and then "pasted".
- Clock Rate (MHz) - The instruction processing speed of a computer measured in millions of cycles per second (i.e., 200 MHz).
- Compiler - a program the converts programming code into a form that can be used by a computer.
- Compression - a technique that reduces the size of a saved file by elimination or encoding redundancies (i.e., JPEG, MPEG, LZW, etc.)
- CPU: The Central Processing Unit. The processing chip that is the "brains" of a computer.
- Cache Memory: The speed of CPU is extremely high compared to the access time of main memory Therefore, the performance of CPU decreases due to the slow speed of main memory. To decrease the mismatch in operating speed, a small memory chip is attached between CPU and main memory whose access time is very close to the processing speed of CPU It is called the Cache Memory.
- Chip: A tiny wafer of silicon containing miniature electric circuits that can store millions of bits of information.
- Client-Server: Client-server is a network architecture which separates the client from the server. Each instance of the client software can send requests to a server or application server.
- Cookie: A packet of information that travels between a browser and the web server
- Compiler: A compiler is a computer program that -translates a series of instructions written in one computer language (called the source language) into another computer language (also called the object or target language).
- Communication: The transrnission of data from one computer to another or from one device to another is called communication.
- Computer Networks: A computer network is a system or communication among two or more computers. The computer networks can be broadly classified as Homogenous' and 'Heterogeneous'.
- Computer Graphics: Computer Graphics are visual presentations on a computer screen. Examples are photographs, drawings, line arts, graphs, diagrams, typography numbers, symbols, geometric designs, maps, engineering drawings or other images.
- Cold Boot: When a computer restarts after the power cut is called cold boot
- Control Panel: Control Panel is the part of Windows menu. accessible from the start menu, which allows users to view and manipulate basic system settings and controls, such as adding hardware. adding/removing software, controlling user accounts, changing accessibility options, etc.
- Control Unit: A control unit is the part of a CPU that 'erects its operation. The outputs of this unit control The activity of the rest of the device.
- Cracker: The preferred term used to refer to a computer criminal who penetrates a computer to steal information or damage the program in some way
- Crash - a system malfunction in which the computer stops working and has to be restarted.
- Cursor - The pointer, usually arrow or cross shaped, which is controlled by the mouse.
- CMOS: CMOS is an abbreviation for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. It is the battery powered chip that is situated on the Motherboard that retains system information such as date and time.
- Data: Data refers to the information that is saved on a computer.
- DOS: DOS is an acronym for Disc Operating System. It is a command line operating system launched by Bill Gates.
- Database - an electronic list of information that can be sorted and/or searched.
- Defragment - (also - optimize) to concatenate fragments of data into contiguous blocks in memory or on a hard drive.
- Dialog box - an on-screen message box that appears when the computer requires additional information before completing a command.
- Digitise - To convert linear, or analogue, data into digital data that can be used by the computer.
- Disk - a spinning platter made of magnetic or optically etched material on which data can be stored.
- Disk drive: The machinery that writes the data from a disk and/or writes data to a disk.
- Disk window: The window that displays the contents or directory of a disk.
- Document - a file you create, as opposed to the application which created it.
- DOS - acronym for Disk Operating System - used in IBM PCs.
- Download - to transfer data from one computer to another. (If you are on the receiving end, you are downloading. If you are on the sending end, you are uploading).
- Drag - to move the mouse while its button is being depressed.
- Driver - a file on a computer that tells it how to communicate with an add-on piece of equipment (like a printer).
- DTP: Desk Top Publisher (ing) is a term that describes a program that enables users to create, design, and print items such as business cards, birthday cards, letterheads, calendars, invitations, and so on.
- Editing: The process of changing information by inserting, deleting, replacing, rearranging and reformation.
- E-mail: Electronic mail, abbreviated e-mail is a method of composing, sending, storing and receiving messages over electronic communication systems.
- Encapsulation: It is a mechanism that associates the code and the data it manipulates into a single unit and keeps them safe from external interference.
- Encryption: In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding messages (or information) in such a way that hackers cannot read it, but the authorised users can access it.
- End User: Any individual who uses the information oefierated by a computer based system.
- Entity: An entity is something that has certain attributes or properties which may be assigned values.
- Entity-relationship diagram: It’s a diagram that represents entities and how they are related to each other.
- Ethernet - a protocol for fast communication and file transfer across a network.
- Execution Time: The total time required to executela program on a particular system.
- Expansion slot: A connector inside the computer that allows one to plug in a printed circuit board that provides new or enhanced features.
- Environment: Environment refers to the interaction among all factors external to a physical platform. An environment is made of specific software, hardware, and network protocols that allow communication with the system.
- FAT: FAT is an acronym for File Allocation Table. It resembles a table of contents so that files can be located on a computer.
- Fault: Hardware or software failure.
- Fax: It stands for 'Facsimile machine'. It is used to transmit a copy of a document electronically.
- Field: The attributes of an entity are written as fields in the table representation.
- File - the generic word for an application, document, control panel or other computer data.
- Floppy - a 3.5-inch square rigid disk which holds data. (so named for the earlier 5.25 and 8 inch disks that were flexible).
- Folder - an electronic subdirectory that contains files.
- Font - a typeface that contains the characters of an alphabet or some other letterforms.
- Fragmentation - The breaking up of a file into many separate locations in memory or on a disk.
- Freeze - a system error, which causes the cursor to lock in place
- Front End: It is an interface through which a program can be accessed by common users.
- Gateway: A device that is used to joint together two networks having different base protocols.
- Groupware: It is software that allows networked individual to form groups and collaborate on documents, programs or database.
- Hardware: Hardware is a set of physical objects such as monitor, keyboard, mouse, and so on.
- Hard drive - a large capacity storage device made of multiple disks housed in a rigid case.
- Head crash - a hard disk crash caused by the heads coming in contact with the spinning disk(s).
- High density disk: a 1.4 MB floppy disk.
- Hub: A network device that connects multiple computers on a LAN, so that they can communicate with one another.
- Hyperlink: An image or portion of text on a web page that is linked to another web page.
- Highlight: To select by clicking once on an icon or by highlighting text in a document.
- Hit rate - The fraction of all memory reads which are satisfied from the cache.
- Hz - Abbreviation for hertz, the number of cycles per second, used to measure clock speed
- Icon: Icon is a small visual display of an application which can be activated by clicking on it.
- IDE: It stands for Integrated Development Environment. IDE is a programming system that combines several tools of programming to provide an integrated platform for programming. For instance, Visual Basic provides an IDE.
- Initialise - to format a disk for use in the computer; creates a new directory and arranges the tracks for the recording of data.
- Insertion point - in word processing, the short flashing marker that indicates where your next typing will begin.
- Installer - software used to install a program on your hard drive.
- Interrupt button - a tool used by programmers to enter the debugging mode. The button is usually next to the reset button
- Instance: It is an object described by its class.
- Internet: Internet is a network that accommodates several computers to facilitate exchange and transfer of data.
- Joystick: A joystick is a computer peripheral or general control device consisting of a handheld stick that pivots about one end and transmits its angle in two or three dimensions to a computer.
- Kernel: It is a program called when a computer system is started. Kernel is responsible for setting up system calls in order to manage hardware and system services, and allocate resources to applications.
- Kilobyte - 1024 bytes.
- LIGHT Pen: A light sensitive style for forming graphics by touching coordinates on a display screen. There by seeming to draw directly on the screen.
- Loop: A sequence of instructions that is executed repeatedly until a terminal condition occurs.
- LAN: LAN is an acronym for Local Area Network that spans small area. A LAN can be connected to another LAN to accommodate more computers.
- Landscape: In printing from a computer, to print sideways on the page.
- Launch - start an application.
- Memory: Memory is the internal storage location where data and information is stored on a computer.
- Modem: Modem is a term created from the beginning letters of two other words viz. MOdulation and DEModulation. The term implies changing of data from digital to analog and then back to digital.
- Morphing: The transformation of one image into another image
- Multitasking: Multitasking can simultaneously work with several programs or interrelated tasks that share memories, codes, buffers and files.
- Multithreading: It is a facility available in an operating system that allows multiple functions from the same application packages.
- Multiuser: The term describing the capability of a computer system to be operated at more than one terminal at the same llf 11°
- Multiplexer: It is a device That combines multiple input signals into an aggregate signal for transmission.
- Memory - the temporary holding area where data is stored while it is being used or changed; the amount of RAM a computer has installed.
- Menu - a list of program commands listed by topic.
- Menu bar: The horizontal bar across the top of the screen that lists the menus.
- MHz - Abbreviation for megahertz, or millions of cycles per second.
- Multi-tasking: Running more than one application in memory at the same time.
- Nibble: A sequence of four adjacent bits , or a half byte . A hexadecimal or BCD coded digit can be represented by a nibble.
- Network: A Network is a group of computers connected to each other in order to send and receive data.
- Operating System: An Operating System provides the software platform required for various applications to run on. Its responsibility is to manage memory storage and security of Data.
- Optical disk: A high-capacity storage medium that is read by a laser light.
- Packet: Sections in which message or data are divided to transfer it over a network.
- Pixel: Pixel is formed by combining the two words viz. Picture Element. It represents one point within an image.
- Palette - a small floating window that contains tools used in a given application.
- Partition - a subdivision of a hard drives surface that is defined and used as a separate drive.
- Paste: To insert text, or other material, from the clipboard or copy buffer.
- PC - acronym for personal computer commonly used to refer to an IBM or IBM clone computer that uses DOS.
- PCI: Acronym for Peripheral Component Interchange - the newer, faster bus architecture.
- Peripheral - an add-on component to your computer.
- Pop-up menu: Any menu that does not appear at the top of the screen in the menu bar. (May pop up or down)
- Power PC - a processing chip designed by Apple, IBM and Motorola (RISC based).
- Power Mac - a family of Macs built around the PowerPC chip.
- Print spooler - a program that stores documents to be printed on the hard drive, thereby freeing the memory up and allowing other functions to be performed while printing goes on in the background.
- Port: Port is a connecting component mainly a hardware that enables two computers to allow data sharing physically. Examples are USB and HDMI.
- Process: It’s a series of commands that changes data values.
- Protocol: Protocol refers to a set of rules that are followed by two devices while interacting with each other.
- Query: Query is a request made by a computer from a database residing in the same system or aremotely located system.
- RAM: RAM is an acronym for Random Access Memory. It is a configuration of storage cells that hold data so that it can be processed by the central processing unit. RAM is a temporary storage location.
- Router: A network device that enables the network to reroute messages it receives that are intended for other networks. The network with the router receives the message and sends it on its way exactly as received. In normal operations. they do not store any of the messages that they pass through.
- Routing: The process of choosing the best path throughout the LAN.
- Root directory - the main hard drive window.
- ROM: ROM is an acronym for Read-Only Memory. It is semiconductor-based storage system that saves information permanently.
- Software: Software is a program (coding) that the computer reads. The system then carries out functions as directed by the code. Adobe Photoshop is software.
- Save - to write a file onto a disk.
- Save as: To save a previously saved file in a new location and/or with a new name.
- Scroll: To shift the contents of a window to bring hidden items into view.
- Swapping: Storing programs on disk and then transferring these programs into main storage as and when they are needed.
- Synchronisation: This method ensures that the receiving end can recognise characters in order, in which the transmitting end sends them in a serial data transmission.
- Scroll bar - a bar at the bottom or right side of a window that contains the scroll box and allows scrolling.
- Scroll box - the box in a scroll bar that is used to navigate through a window.
- SCSI: Acronym for Small Computer System Interface.
- Serial port: A port that allows data to be transmitted in a series (one after the other), such as the printer and modem ports on a Mac.
- Server - a central computer dedicated to sending and receiving data from other computers (on a network).
- Shut down - the command from the Special menu that shuts down the computer safely.
- Spreadsheet - a program designed to look like an electronic ledger.
- Startup disk - the disk containing system software and is designated to be used to start the computer.
- Surge suppressor - a power strip that has circuits designed to reduce the effects of surge in electrical power. (Not the same as a UPS)
- TCP/IP: TCP/IP is an acronym for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. It’s a set of communication protocols used to connect host computers on the Internet.
- Title bar - the horizontal bar at the top of a window that has the name of the file or folder it represents.
- URL: URL stands for Universal Resource Locator. It’s a way of accessing the Internet.
- Upload - to send a file from one computer to another through a network.
- Uninterruptible Power Source (UPS): A constantly charging battery pack that powers the computer. A UPS should have enough charge to power your computer for several minutes in the event of a total power failure, giving you time to save your work and safely shut down.
- UPS - acronym for Uninterruptible Power Source.
- Virtual Memory: Virtual Memory is the unused memory on the hard disk used when certain applications require more RAM than is available on the machine.
- Virus: Virus is a program that is loaded onto your computer without you knowing about it and it runs to hinder the normal functioning of the computer.
- WWW: WWW stands for World Wide Web. It’s a term used to define the Internet.
- WAN: WAN is an acronym for Wide Area Network. Such a network spans over an area larger than a LAN.
- WORM - acronym for Write Once-Read Many; an optical disk that can only be written to once (like a CDROM).
- Zoom box - a small square in the upper right corner of a window which, when clicked, will expand the window to fill the whole screen.
- ZIP: ZIP is an acronym for Zone Information Protocol. ZIP application enables transfer of data using compression of files.
The document Computer Fundamentals & Terminologies | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
647 videos|1019 docs|305 tests
|
Related Searches
















