Most Important Diagrams Class 12 Biology (Zoology) for NEET 2026 Biology Exam Preparation PDF Download
Diagrams are beneficial for students when it comes to understanding the topic better. This article focuses on some of the important diagrams of class 12 Zoology with an aim to aid students in preparing for the upcoming NEET exam 2023. Questions based on diagrams have become a regular feature in exams lately, so having good comprehension of diagram concepts is significant.
Diagrams of following chapters are covered:
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Evolution
- Human Health and Diseases
- Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
Diagrams of Human Reproduction
The reproductive system is responsible for the survival of species, with most animals being either female or male. Males have testes that produce sperm (male gamete) and females have ovaries that produces ovum or eggs (female gamete). The diagrams showing the male and female reproductive system and male and female gamete formation are described here.
Males have two primary sex organs, testes, and a number of accessory sex organs. These include the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, urethra and penis. Additionally, the external genital organs are the penis, scrotum and urethra, while the internal genitalia complete the anatomy.
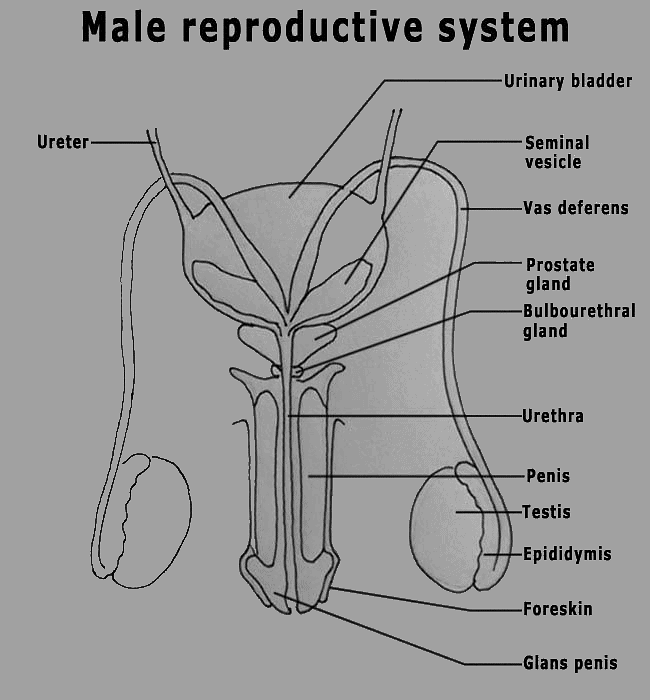
The testes (a pair) are suspended in a sac-like pouch called the scrotum. Each testis is composed of coiled tubes known as the seminiferous tubules. This seminiferous tubule continues as vas efferens which forms epididymis and continues as vas deferens. The seminiferous tubule of testis opens into vas efferens via the rete testis. The rete testis, vas efferens, epididymis and vas deferens form the accessory male sex ducts.
The vas deferens receive ducts from the seminal vesicle and open into the urethra as ejaculatory ducts. Urethra extends through the penis to its opening called the urethral meatus.
2. Sperm
Sperm is made up of four components:
(i) Head
(ii) Neck
(iii) Middle portion
(iv) Tail
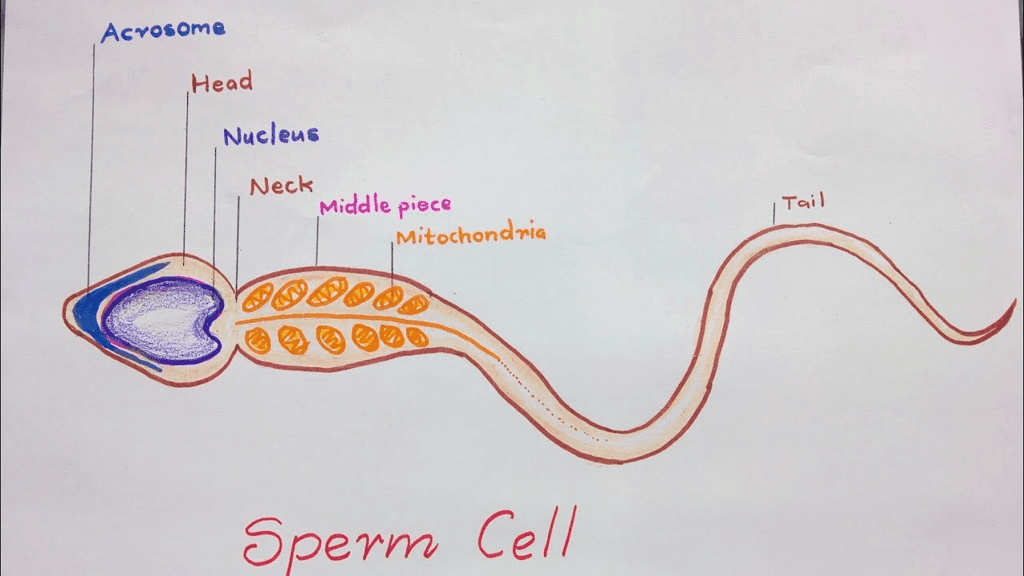
It is the only type of cell in the body that has a flagellum. The front two-thirds of the head is covered by an acrosome, which is a cap-like structure containing enzymes necessary for the sperm to penetrate and fertilize the egg. Connecting the head to the middle part is a short neck. This middle piece is where mitochondria are located, providing energy for the sperm's movement. The tail of the sperm is a long whip-like flagellum that is used to propel the sperm forward.
The primary sex organs in females are the ovaries that produce gametes (ova/egg). The secondary sex organs include a system of genital ducts like the fallopian tube, cervix, uterus and vagina and also the external genitalia like the pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris and hymen.
The fallopian tube (oviduct) or salping comprises 3 parts – the infundibulum (part closer to ovary), ampulla (wider part of the oviduct) and the isthmus (last part of the oviduct) that joins with uterus. Fimbriae are finger-like projections on the edges of the infundibulum that collects ovum after ovulation.
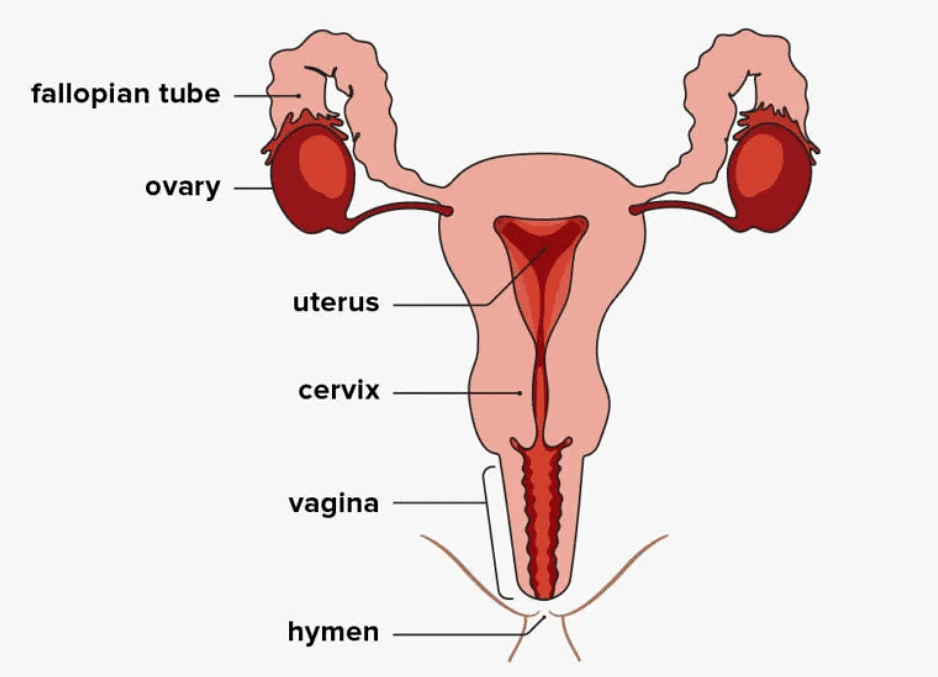
The uterus is a pear-shaped structure made of 3 layers – outer thin perimetrium, middle thick myometrium and inner glandular endometrium. The uterus opens into the vagina via a narrow cervix. Ovaries are the primary sex organs that are connected to the pelvic wall and uterus by ligaments. The structure of the ovary is discussed below with a diagram.
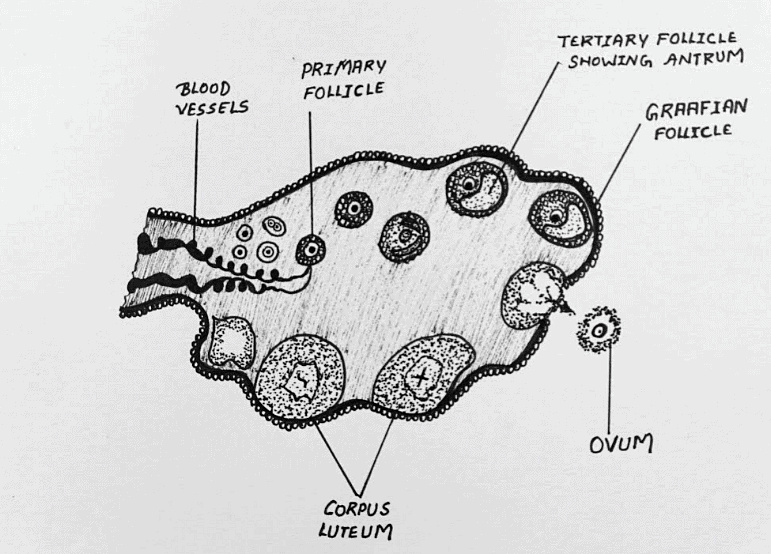
4. Sectional View of Ovary
The two ovaries are ovular-shaped organs that measure between 2 to 4 cm in length and are attached to the uterus and pelvic wall by ligaments. The two portions of the ovary are the cortex and the medulla, with the cortex containing ovarian follicles, connective tissue, and interstitial cells, and the medulla consisting of a central stroma of loose connective tissue.
The process of producing a fully developed female egg is called oogenesis. The Graafian follicle is the last mature follicle that is expelled at ovulation. This shows the role of ovaries in the female body; they release female sex hormones, mature the egg and regulate the menstrual cycle.
The immature male germ cells produce sperm through the process of spermatogenesis. The spermatogonia, located in the seminiferous tubules, reproduce by means of mitosis, resulting in an increase in their number. Each spermatagonium contains 46 chromosomes and possesses a diploid set. The last generation of mitosis progresses to the stage of growth as primary spermatocytes which then undergo meiosis, thus being divided into two growth phases.
In the first phase, the primary spermatocyte divides into 2 secondary spermatocytes. They receive only the haploid or half the number of chromosomes. During the second phase, each secondary spermatocyte undergoes 2nd meiotic division, resulting in two smaller spermatids. Each spermatid has a haploid number of chromosomes and there is no further division. These spermatids are transformed into mature sperm cells.
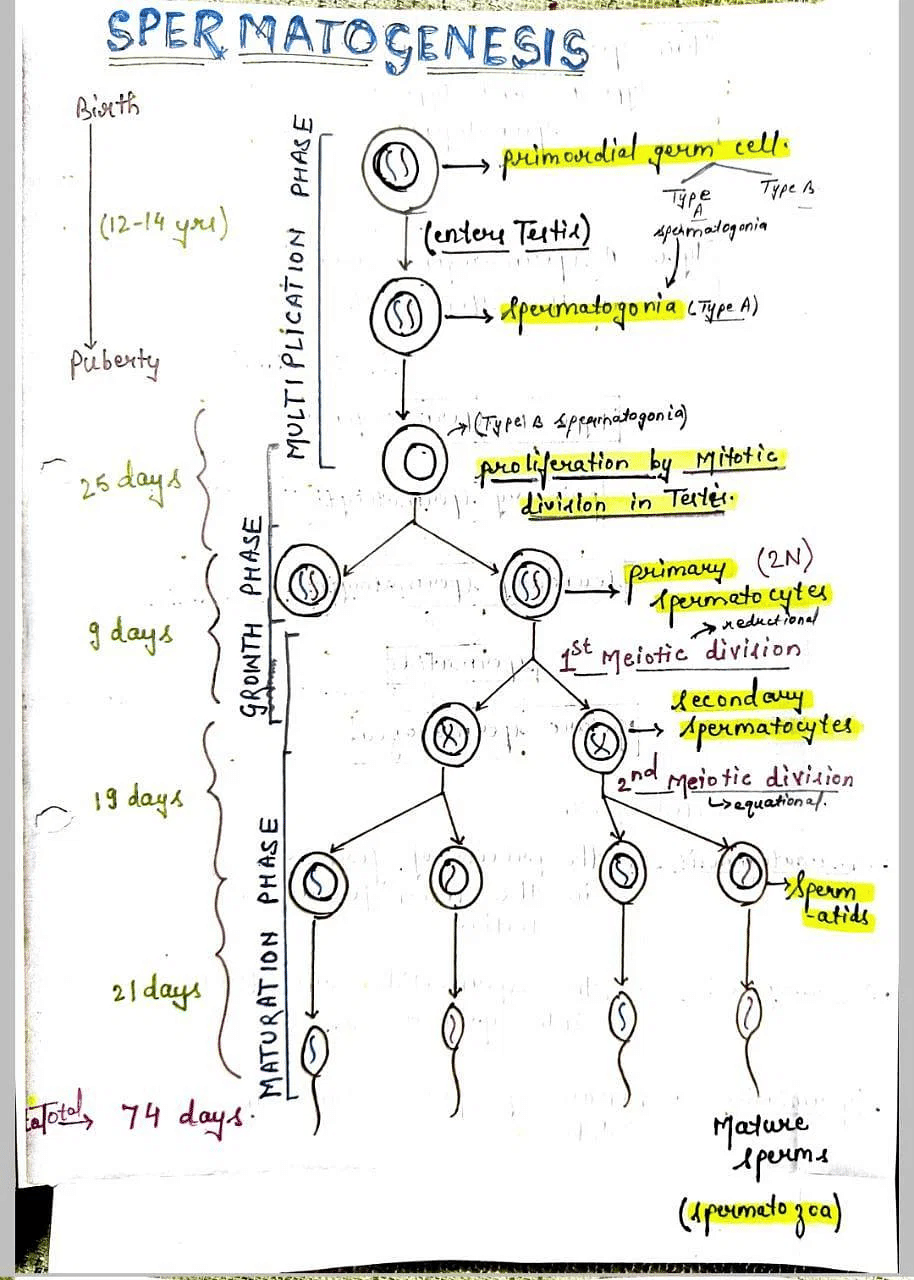
6. Seminiferous Tubule
At the onset of puberty, the transformation of spermatids into sperm is known as spermiogenesis. Following this, the sperm's head is securely held in place in the Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubule through a process called spermination. The release of GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) triggers these changes during this stage of development.
The diagrammatic sectional view of the seminiferous tubule is also important for the exam.
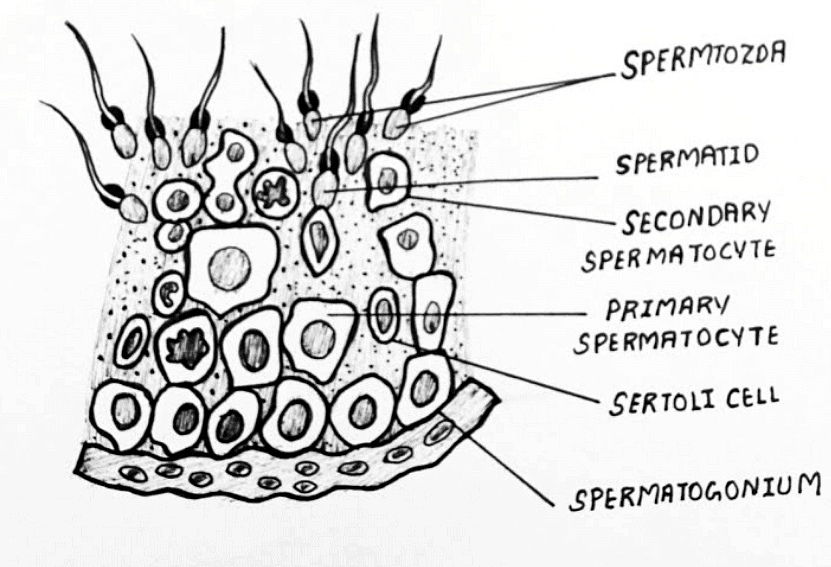 Diagrammatic sectional view of a seminiferous
Diagrammatic sectional view of a seminiferous
7. Oogenesis
The formation of a mature female gamete, known as oogenesis, begins during embryonic development when countless oogonia are produced within the fetal ovaries. This process is initiated with a germ cell called oogonia which divides through mitosis to create more cells.
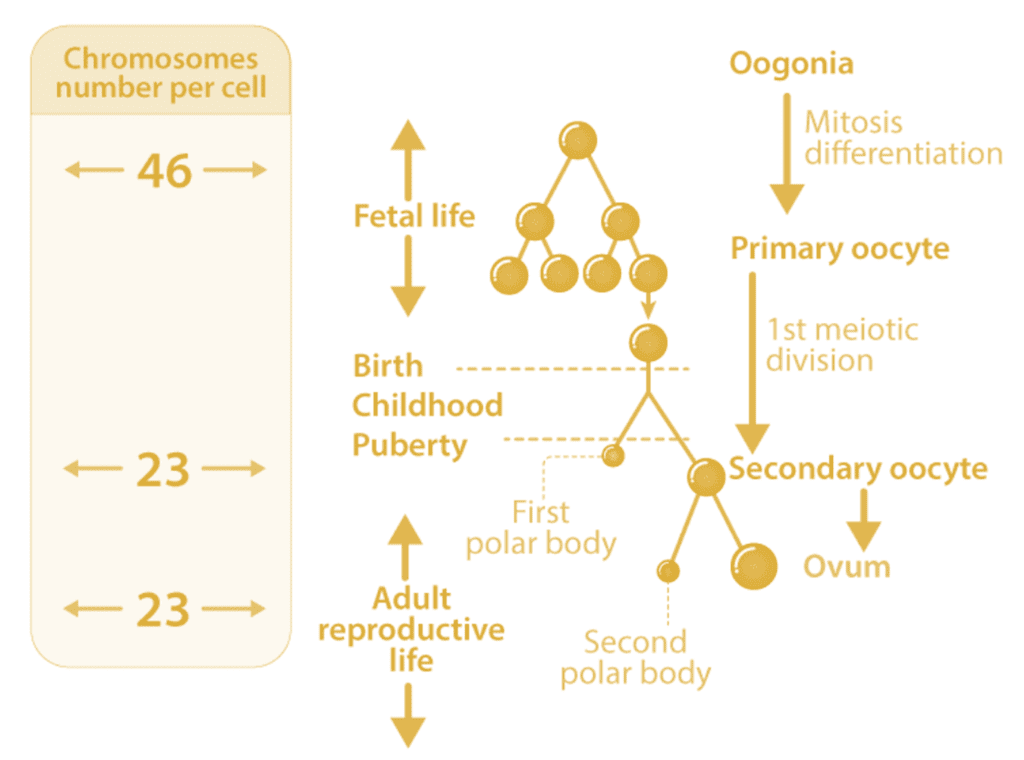
Oogonia start dividing and enter prophase-Ⅰ of meiosis and get temporarily arrested as primary oocytes. Each primary oocyte gets surrounded by primary follicles which further get surrounded by more layers to form secondary follicles and then the tertiary follicles. The primary oocyte within the tertiary follicles completes its first meiotic division to form large haploid secondary oocytes and a tiny first polar body.
The tertiary follicle further changes into a mature Graafian follicle. Now the secondary oocyte forms a zona pellucida layer surrounding the Graafian follicle and it ruptures to release the ovum by a process called ovulation.
During each menstrual cycle, a series of changes occur in the ovary and accessory sex organs. These changes are divided into 4 groups – ovarian changes, uterine changes, vaginal changes and the changes in the cervix. These changes can be divided into the following phases –
- Menstrual phase: The cycle starts with this phase by the shedding of the uterus lining and it lasts for 3 to 5 days.
- Follicular phase: Here, the primary follicle grows into a mature Graafian follicle and the endometrium regenerates through proliferation.
- Ovulatory phase: The mid-phase (13-17 days) where the LH and FSH hormones attain their peak. The LH surge ruptures the Graafian follicle and leads to the release of ovum.
- Luteal phase: The remains of the Graafian follicle form the corpus luteum. The regressed form of corpus luteum is corpus Albicans.
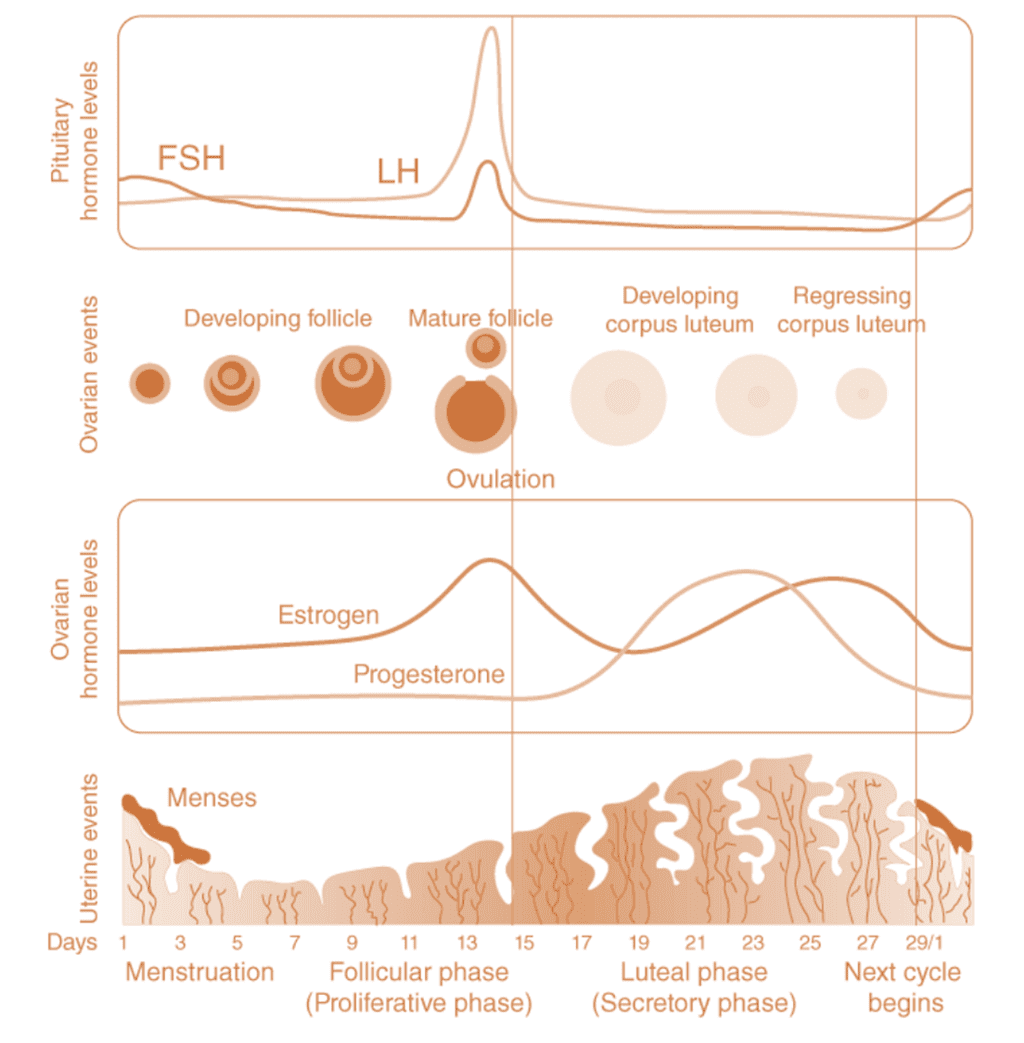 Menstrual Cycle
Menstrual Cycle
The diagram represents ovarian, hormonal and uterine events that happen during menstruation. Menstruation is repeated at an average interval of 28/29 days and the cycle of events from one menstruation to the next is termed the menstrual cycle.
9. Mammary Gland
Mammary glands are paired structures that contain a variable amount of fat and glandular tissue. The glandular tissues of each gland have 15-20 mammary lobes which comprise clusters of cells called alveoli. The alveoli are lined with milk-secreting epithelial cells which further open into the mammary tubules. The tubules of each mammary lobe join to form a mammary duct. Likewise, many mammary ducts join to form the ampulla which is connected to the lactiferous duct via which milk is sucked out.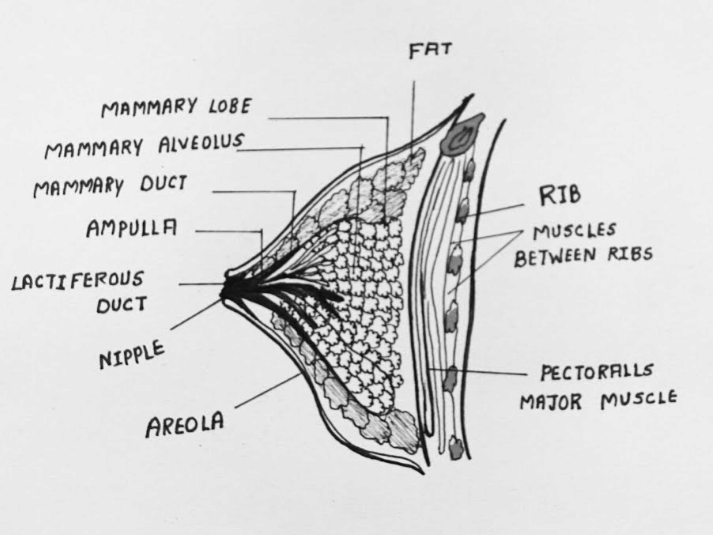
Diagrams of Reproductive Health
One way to keep population growth in check is through the use of contraception. This includes a variety of different birth control devices, such as diaphragms, IUDs, condoms, and implants. Other methods include oral contraceptives and surgical procedures. All of these can help to prevent unwanted pregnancies and reduce population growth.
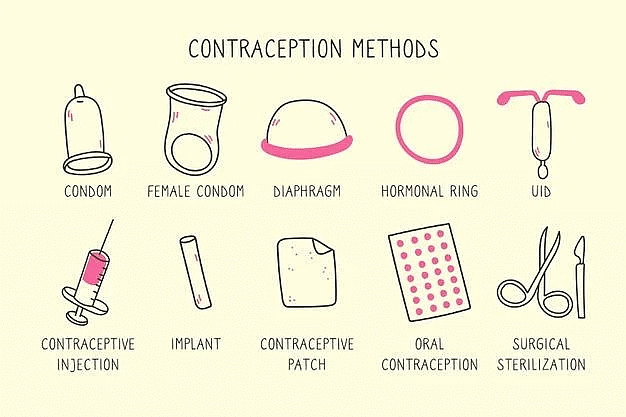
- Condoms are barrier contraceptives that are made of latex or rubber sheath. Male condom covers the penis and the female condom (femidom) covers the cervix or vagina during copulation.
- Dome-shaped diaphragms or cervical caps or vaults can also be used as barriers. They have higher efficiency due to the usage of spermicide in them.
- The IUDs (intrauterine devices) are inserted in the female reproductive tract to prevent pregnancy. They can be classified into non-medicated IUDs (Lippes loop), copper-releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and hormonal IUDs (LNG-20 and progestasert).
- The surgical methods include vasectomy (male sterilisation) and tubectomy (female sterilisation). Vasectomy includes tying up or cutting and removal of vas deferens. Likewise, tubectomy includes tying or removal of the fallopian tube.
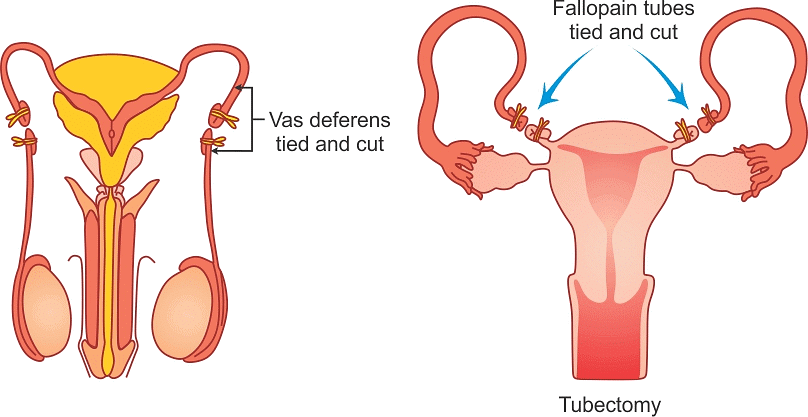 Surgical Contraception
Surgical Contraception
Diagrams of Evolution
This chapter looks at diagrams that might be asked on the NEET exam, centering around the origin of life, adaptive radiation, the mechanism of evolution, and the evolution of mankind. It also includes schematic representations. Examples of important diagrams included are the origin of life, adaptive radiation, mechanism of evolution, and evolution of mankind.
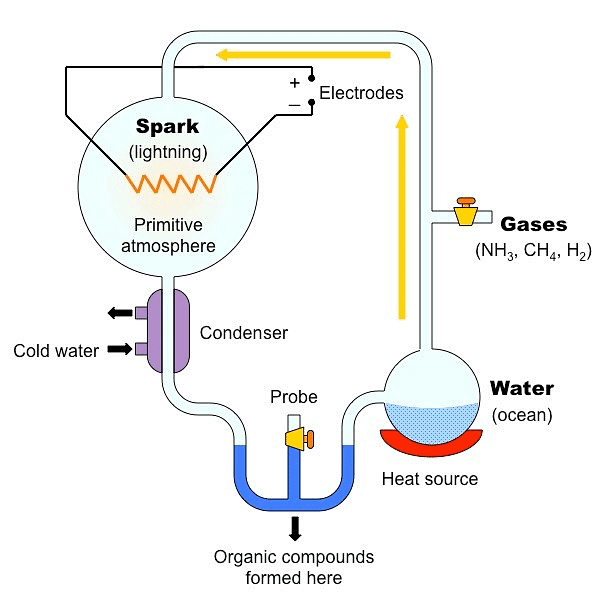
Urey and Miller did an experiment to prove how life forms could have emerged from non-living organic molecules like proteins, RNA, etc. They designed a spark discharge apparatus to perform a simulation experiment. The experimental model contained a half-filled flask with water and another flask with a pair of electrodes and gases like methane, ammonia, hydrogen (in the ratio of 2:1:2 respectively) and water vapour to imitate the primitive earth’s atmosphere. They created electric discharge in the flask containing these gases at 800°C and observed the formation of amino acids like glycine, alanine and aspartic acid.
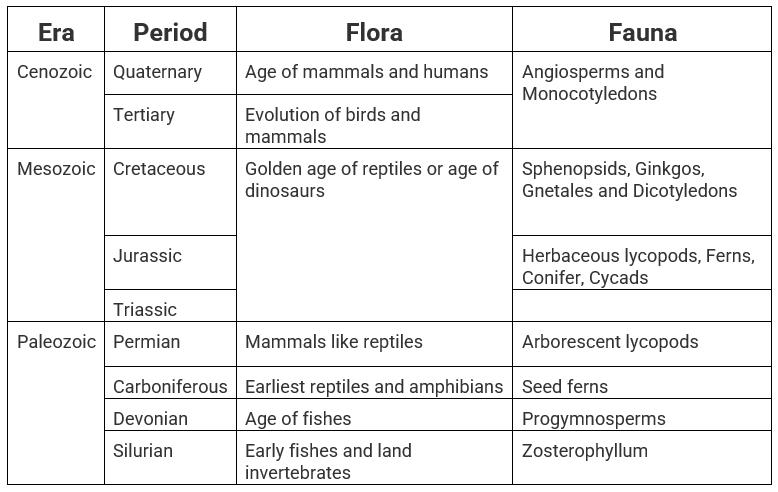
2. Evolution of Plants and Animals through Ages
The evolutionary sequence of Palaeozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic are to be remembered along with the significant happenings during each period.
3. Operation of Natural Selection on Different Traits
Natural Selection is a process by which physically, physiologically and behaviourally well-adapted organisms survive and reproduce. The three types of selection that can occur are:
- Stabilising selection
- Directional selection
- Disruptive selection
When two extreme traits are competing and the natural selection favours an intermediate trait then it is called the stabilising selection. When the selection process favours one extreme trait then it is called directional selection. Disruptive selection is an uncommon process where both extreme traits are favoured against the intermediate one.
4. Adaptive Radiation of Marsupials of Australia
Similar to the adaptive radiation in Darwin’s finches, there is another example given in NCERT called the adaptive radiation of marsupials in Australia. The diagram represents various marsupials like Kangaroo, Tasmanian wolf, Koala, Bandicoot, etc., arising from an ancestral stock but within the Australian island. The Australian placental mammals also exhibit similar adaptive radiation.
Also Check: NEET Flashcards of Evolution
Diagrams of Human Health and Diseases
This chapter contains some of the most important diagrams of the class 12 syllabus. The chapter discusses infectious and non-infectious diseases and also the concept of immunity and vaccination.
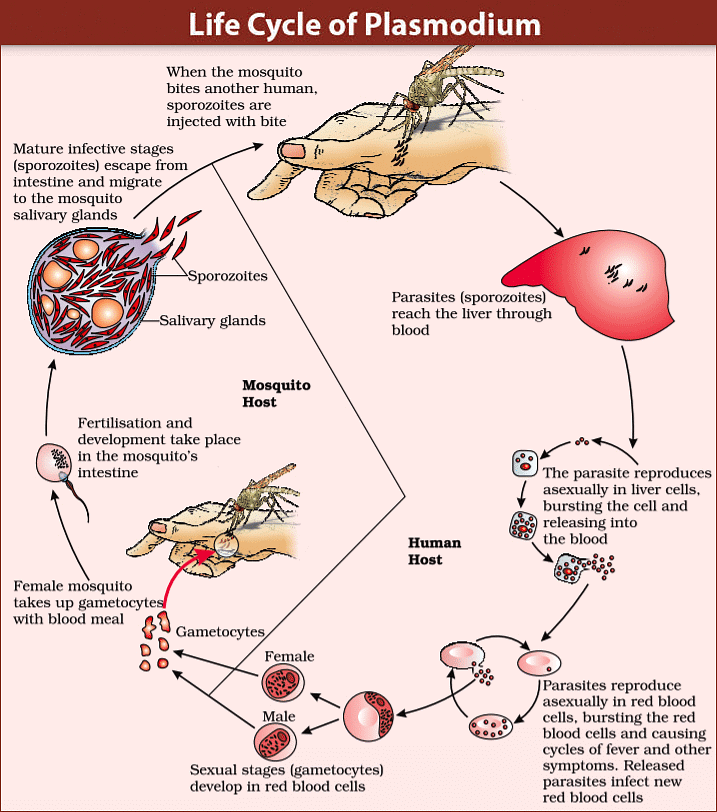
The life cycle of plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its cycle. The first host is an Anopheles mosquito, which transmits the parasite in the form of infectious sporozoites to a human host when it bites them. The parasite typically grows in the liver before entering the bloodstream, where it attacks and ruptures red blood cells, releasing a toxic substance known as haemozoin. This can cause high fever and chills. When the mosquito bites an infected person, the parasite is stored in its salivary gland and when it bites another human, the parasite is injected, continuing the cycle.
Each antibody has 4 peptide chains – two long heavy chains and two small light chains. These chains are bound together by disulfide bonds to form a Y shape and the structure is represented as H2L2. Both heavy and light chains have variable and constant regions. The structure also comprises the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) present on the N terminus and the crystallisable fragment (Fc) on the C terminus of the chain.
The antibodies or immunoglobulins (Ig) produce IgA, IgE, IgM and IgG in our body.
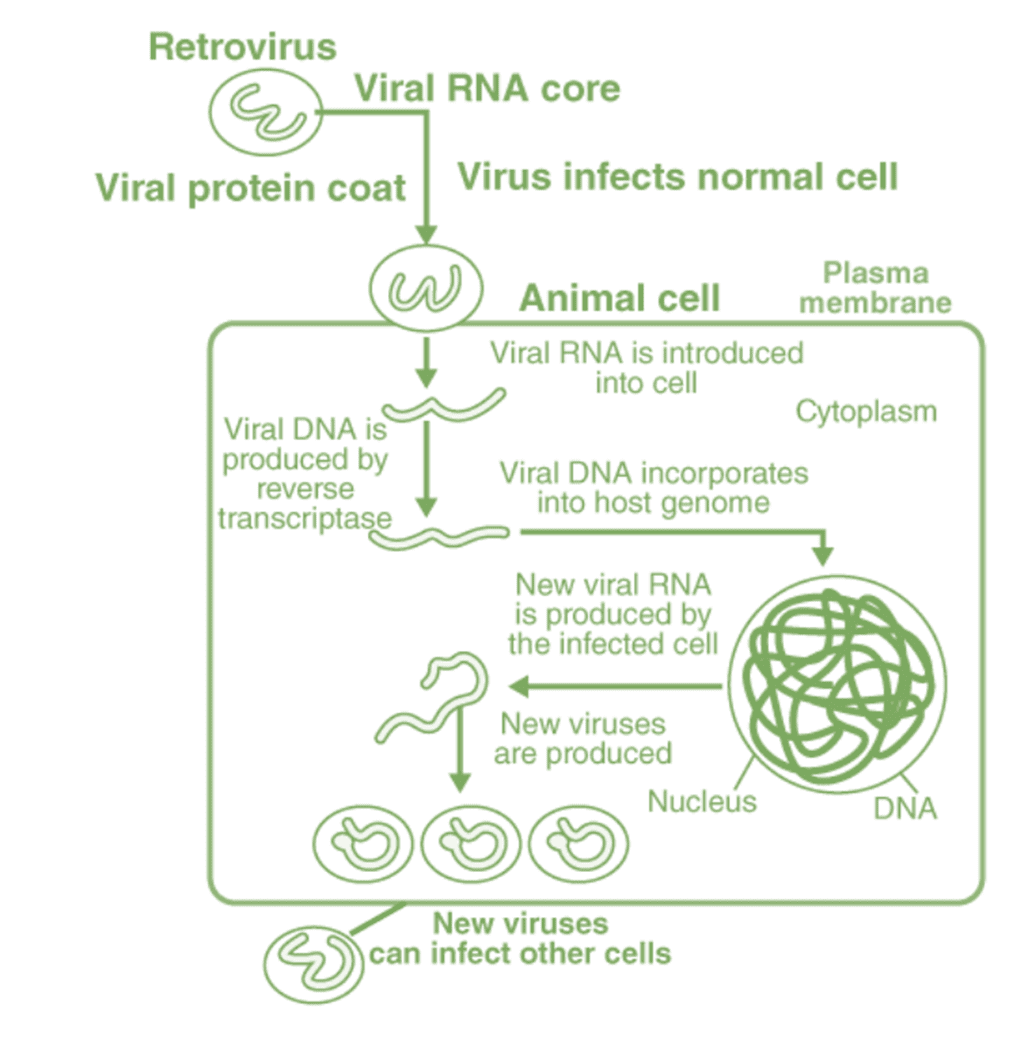
Retrovirus (Eg., HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is an enveloped structure that includes the RNA genome. Once a retrovirus infects a normal cell, the viral RNA is introduced into the host cell. This undergoes reverse transcription and thus results in viral DNA. Now, the viral DNA is introduced into the host cell’s DNA, where it starts replicating.
The viral DNA is transcribed and translated, which further results in new viruses that can infect other cells. The sequential step is well explained in the diagram given below.
Diagrams of Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
This chapter examines different cutting-edge biotechnological methods and explains the ideas behind recombinant DNA technology and cloning vectors with the help of diagrams. Additionally, the following chapter goes into detail about how biotechnology is used in practice.
This technique involves the selection of the desired gene which needs to be inserted into the host cell. The process also involves a suitable cloning vector in which the desired gene has to be integrated. Thus, the host consumes the vector with desired DNA and becomes the final tool of recombinant DNA technology. The sequential process of rDNA technology is described below in the diagram.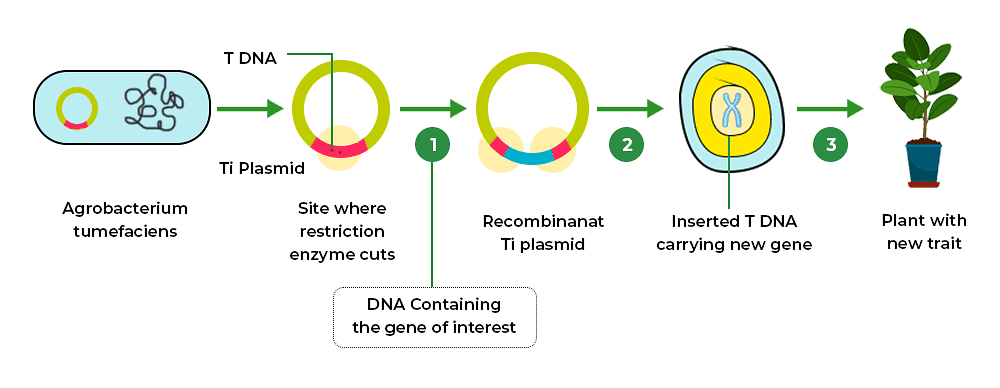 Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant DNA Technology
2. E.coli Cloning Vector pBR322
We talked about cloning vectors in the previous concept. These vectors are small DNA fragments that can easily replicate and integrate with the host. Plasmids are also a type of cloning vector. Here, let us look at the E.coli cloning vector pBR322 and its characteristic features.
- It has Ori or the origin of replication from where the replication begins.
- It has restriction sites like BamH Ⅰ, EcoR Ⅰ, Sal Ⅰ, Cla Ⅰ, Pvu Ⅰ, Pst Ⅰ, Pvu Ⅱ and Hind Ⅲ.
- It contains selectable markers like antibiotic resistance genes for tetracycline (tetR) and ampicillin (ampR)
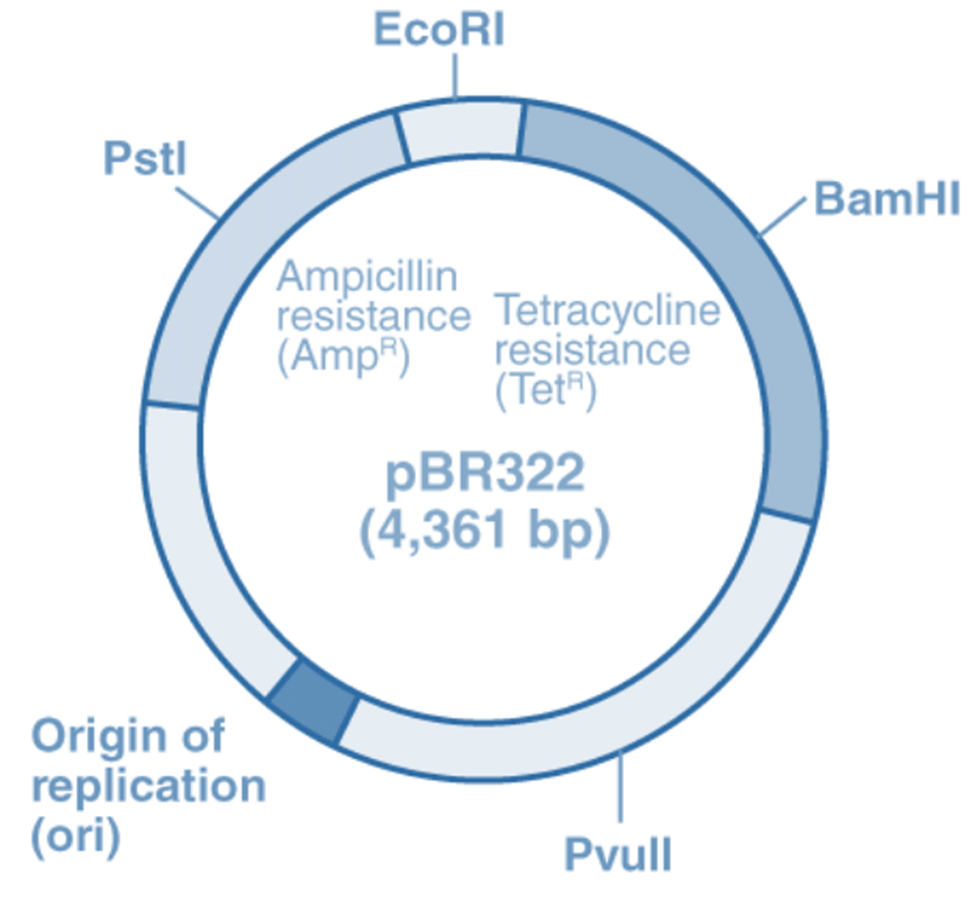 PBR322
PBR322
Diagrams of Biotechnology and its Applications
The biotechnological techniques can be used in agriculture, farming, medicine and research.
PCR: Polymerase Chain Reaction
In the PCR technique, multiple copies of the desired gene or DNA are synthesised in vitro using DNA polymerase and 2 sets of primers (oligonucleotide primers). The following are 3 important steps in the polymerase chain reaction which are also represented in the diagram.
- The double-stranded DNA is turned into single-stranded DNA by the process of denaturation. Here, the hydrogen bonds are broken at a high temperature.
- Then the oligonucleotide primers undergo annealing at an optimum temperature (40 – 65°C). Here, the primers cohere with the complementary sequence on the DNA template.
- In the elongation process, the DNA polymerase extends the primers using genomic DNA and the nucleotides provided in the reaction as templates. This process of continuous amplification is better achieved by a thermostable DNA polymerase called the Taq polymerase.
Finally, the amplified DNA fragment can be ligated with a vector to proceed with further cloning.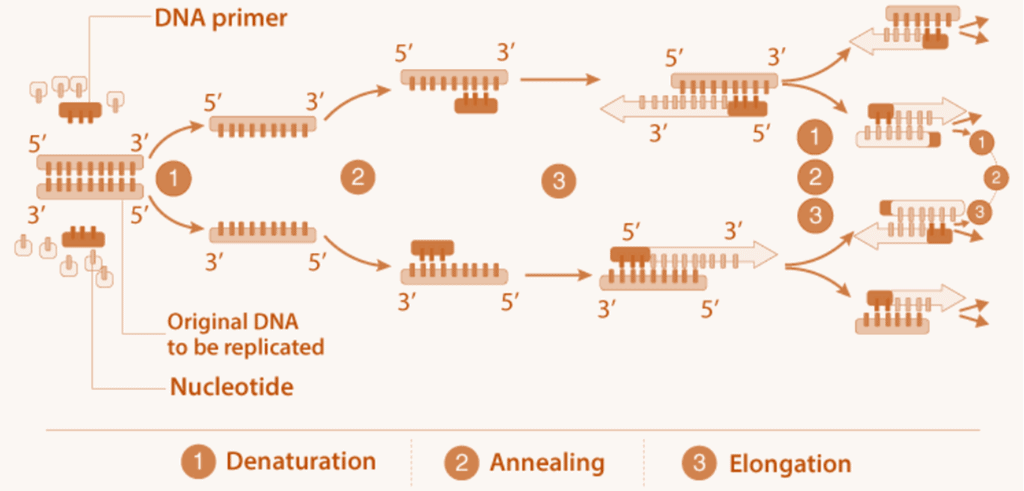 Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase Chain Reaction
FAQs on Most Important Diagrams Class 12 Biology (Zoology) for NEET 2026 Biology Exam Preparation
| 1. What are the key diagrams related to human reproduction? |  |
| 2. What diagrams are essential for understanding reproductive health? |  |
| 3. Which diagrams are important for studying evolution? |  |
| 4. What diagrams are useful for learning about human health and diseases? |  |
| 5. Which diagrams are important in the field of biotechnology? |  |




















