Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > The Mole
The Mole | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Higher Tier Only
The Mole
- Chemical amounts are measured in moles
- The symbol for the unit mole is mol
- One mole of a substance contains the same number of the stated particles, atoms, molecules, or ions as one mole of any other substance
- The number of atoms, molecules or ions in a mole (1 mol) of a given substance is the Avogadro constant. The value of the Avogadro constant is 6.02 x 1023 per mole
For example:
- One mole of sodium (Na) contains 6.02 x 1023 atoms of sodium
- One mole of hydrogen (H2) contains 6.02 x 1023 molecules of hydrogen
- One mole of sodium chloride (NaCl) contains 6.02 x 1023 formula units of sodium chloride
Exam Tip
You need to appreciate that the measurement of amounts in moles can apply to atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, formulae and equations. E.g. in one mole of carbon (C) the number of atoms is the same as the number of molecules in one mole of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Linking the Mole and the Atomic Mass
- One mole of any element is equal to the relative atomic mass of that element in grams
- This is called the molar mass
- If you had 6.02 x 1023 atoms of carbon in your hand, that number of carbon atoms would have a mass of 12 g (because the Ar of carbon is 12)
- So one mole of helium atoms would have a mass of 4 g (Ar of He is 4), one mole of lithium would have a mass of 7 g (Ar of Li is 7) and so on
- To find the mass of one mole of a compound, we add up the relative atomic masses
- So one mole of water would have a mass of (2 x 1) + 16 = 18 g
Exam Tip
Remember the key link between moles and mass: one mole of any element is equal to that elements atomic mass in grams.
Calculating Moles & Masses
- Although elements and chemicals react with each other in molar ratios, in the laboratory we use digital balances and grams to measure quantities of chemicals as it is impractical to try and measure out moles
- Therefore, we have to be able to convert between moles and grams
- We can use the following formula to convert between moles, mass in grams and the molar mass:
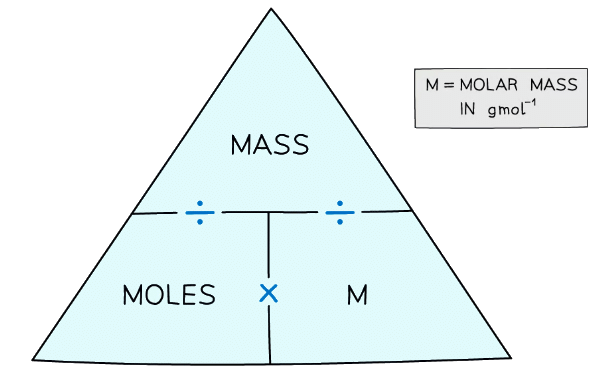 Formula triangle for moles, mass and molar mass
Formula triangle for moles, mass and molar mass
Solved Example
Example 1: What is the mass of 0.250 moles of zinc?
- From the Periodic Table, the relative atomic mass of Zn is 65
- So, the molar mass is 65 g / mol
- The mass is calculated by moles x molar mass
- This comes to 0.250 mol x 65 g / mol = 16.25 g
Example 2: How many moles are in 2.64 g of sucrose, C12H22O11 (Mr = 342.3)?
- The molar mass of sucrose is 342.3 g / mol
- The number of moles is found by mass ÷ molar mass
- This comes to
= 7.71 x 10-3 mol
Exam Tip
Always show your workings in calculations as its easier to check for errors and you may pick up credit if you get the final answer wrong.
The document The Mole | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|
Related Searches
















