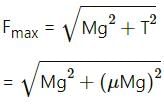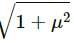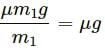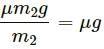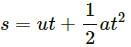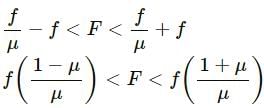Short Answers
Q.1. For most of the surfaces used in daily life, the friction coefficient is less than 1. Is it always necessary that the friction coefficient is less than 1?
It is not necessary that the friction coefficient is always less than 1. When the friction is stronger than the normal reaction force, the coefficient of friction is greater than 1. For example, silicon rubber has the coefficient of friction greater than 1.
Q.2. Why is it easier to push a heavy block from behind than to press it on the top and push?
It is easier to push a heavy block from behind than from the top because when we try to push a heavy block from the top, we increase the normal reaction force, which, in turn, increases the friction between the object and the ground (see the figure).
Q.3. What is the average friction force when a person has a usual 1 km walk?
The person started with zero initial velocity, covered a 1 km distance and ended with zero velocity, so the acceleration is zero. Hence, the average friction force is zero.
Q.4. Why is it difficult to walk on solid ice?
It is difficult to walk on solid ice because the coefficient of friction between our foot and ice is very less; hence, a person trying to walk on solid ice may slip.
Q.5. Can you accelerate a car on a frictionless horizontal road by putting more petrol in the engine? Can you stop a car going on a frictionless horizontal road by applying brakes?
No, we cannot accelerate or stop a car on a frictionless horizontal road. The car will not move on a frictionless surface because rolling is not possible without friction.
Q.6. Spring fitted doors close by themselves when released. You want to keep the door open for a long time, say for an hour. If you put a half kg stone in front of the open door, it does not help. The stone slides with the door and the door gets closed. However, if you sandwitch a 20 g piece of wood in the small gap between the door and the floor, the door stays open. Explain why a much lighter piece of wood is able to keep the door open while the heavy stone fails.
In the first case, the normal reaction force is equal to the weight of the stone, hence the stone slides easily because the friction force is very less. However, in the second case, a small piece of wood is sandwiched, which increases the normal reaction force on the wood due to the weight of the door. Hence, greater the normal reaction force on the wood, the greater will be the frictional force between wood and the floor.
Q.7. A classroom demonstration of Newton's first law is as follows : A glass is covered with a plastic card and a coin is placed on the card. The card is given a quick strike and the coin falls in the glass. (a) Should the friction coefficient between the card and the coin be small or large? (b) Should the coin be light or heavy? (c) Why does the experiment fail if the card is gently pushed?
(a) The coefficient of friction between the card and the coin should be small.
(b) The coin should be heavy.
(c) If the card is pushed gently, the experiment fails because the frictional force gets more to time to act and it may gain some velocity and move with the card.
Q.8. Can a tug of war be ever won on a frictionless surface?
No, a tug of war cannot be won on a frictionless surface because the tension in the rope on both the sides of both the teams will be same. So, to win, one of the teams must apply some greater force, which is the force of friction.
Q.9. Why do tyres have a better grip of the road while going on a level road than while going on an incline?
The normal reaction force on a level road is mg, whereas on an inclined plane it is mg cos θ, which means that on an incline road the friction force between the tyre and the road is less. Hence, tyres have less grip on an incline plane and better grip on a level road.
Q.10. You are standing with your bag in your hands, on the ice in the middle of a pond. The ice is so slippery that it can offer no friction. How can you come out of the ice?
By throwing the bag in one direction, we gain some velocity in the opposite direction as per the law of conservation of linear momentum. In this way we can come out of the ice easily.
Q.11. When two surfaces are polished, the friction coefficient between them decreases. But the friction coefficient increases and becomes very large if the surfaces are made highly smooth. Explain.
The coefficient of friction increases between two highly smooth surfaces because the atoms of both the materials come very closer to each and the number of bonds between them increase.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
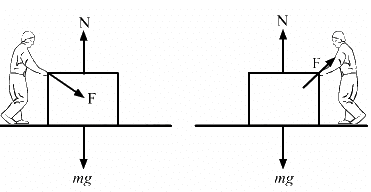
Try yourself:In a situation the contact force by a rough horizontal surface on a body placed on it has constant magnitude. If the angle between this force and the vertical is decreased, the frictional force between the surface and the body will
Explanation
According to the first law of limiting friction,
f = μN
where f is the frictional force
N is the normal reaction force
μ is the coefficient of static friction
and
N = mg - Fcosθ
where m is the mass of the body
F is the contact force acting on the body
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:While walking on ice, one should take small steps to avoid slipping. This is because smaller steps ensure
Explanation
According to the first law of the limiting friction,
f = μN
where f is the frictional force
μ is the coefficient of friction
N is the normal reaction force
When we take smaller steps on ice, the normal reaction force exerted by the ice is small. Therefore, the smaller steps ensure smaller friction.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
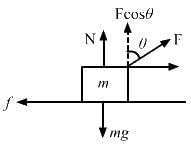
Try yourself:A body of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface (friction coefficient = μ). A person is trying to pull the body by applying a horizontal force but the body is not moving. The force by the surface on A is F, where
Explanation
Let T be the force applied on an object of mass M.
If T = 0, Fmin = Mg.
If T is acting in the horizontal direction, then the body is not moving.
∴ T = μ(mg)
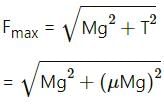
Thus, we have:
Mg ≤ F ≤ Mga 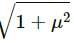
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:A scooter starting from rest moves with a constant acceleration for a time ∆t1, then with a constant velocity for the next ∆t2 and finally with a constant deceleration for the next ∆t3 to come to rest. A 500 N man sitting on the scooter behind the driver manages to stay at rest with respect to the scooter without touching any other part. The force exerted by the seat on the man is
Explanation
During the time interval ∆t2, the scooter is moving with a constant velocity, which implies that the force exerted by the seat on the man is 500 N (for balancing the weight of the man).
During the time interval ∆t1 and ∆t3, the scooter is moving with constant acceleration and deceleration, which implies that a frictional force is also applied. Therefore, the net force exerted by the seat on the man should be >500 N.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
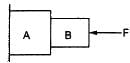
Try yourself:Consider the situation shown in figure. The wall smooth but the surface of A and B in contact are rough. The friction on B due to A in equilibrium
Explanation
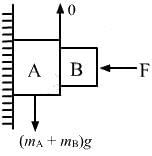
Since the wall is smooth and the surface of A and B in contact are rough, the net vertical force on the system is in the downward direction. Hence, the system cannot remain in equilibrium.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:Suppose all the surface in the previous problem are rough. The direction of friction of B due to A
Explanation
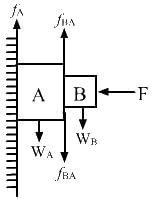
The normal reaction force on the system (comprising of wall and contact surface of Aand B) is provided by F. As can be seen from the figure, the weight of A and B is in the downward direction. Therefore, the frictional force fA and fBA (friction on B due to A) is in upward direction.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:Two cars of unequal masses use similar tyres. If they are moving at the same initial speed, the minimum stopping distance
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:In order to stop a car in shortest distance on a horizontal road, one should
Explanation
When we apply hard brakes just enough to prevent slipping on wheels, it provides optimum normal reaction force, which gives the maximum friction force between tyres of the car and the road.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:A block A kept on an inclined surface just begins to slide if the inclination is 30°. The block is replaced by another block B and it is found that it just begins to slide if the inclination is 40°.
Explanation
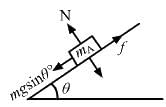
We know that
N = mg cos θ˚
fmax = μN = μmg cos θ
where N = normal reaction force
fmax = frictional force
θ = angle of inclination
μ = coefficient of friction
When the block just begins to slide, it means
mg sin θ = fmax
mg sin θ = μmg cos θ
μ = tan θ
and the coefficient of friction depends on the angle of inclination (θ) and does not depend on mass.
Now consider the block sliding condition:
mg sin θ − fmax = ma
mg sin θ − μmg cos θ = ma
∴ a = g(sin θ − μ cos θ)
From the above equation it is clear that acceleration does not depend on the mass but depends on θ and μ.
Report a problem
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
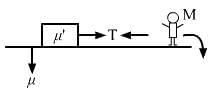
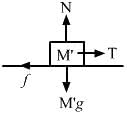
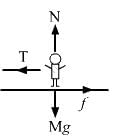
Try yourself:A boy of mass M is applying a horizontal force to slide a box of mass M' on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the shoes of the boy and the floor is μ and that between the box and the floor is μ'. In which of the following cases it is certainly not possible to slide the box?
Explanation
Report a problem
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:Let F, FN and f denote the magnitudes of the contact force, normal force and the friction exerted by one surface on the other kept in contact. If none of these is zero.
Explanation
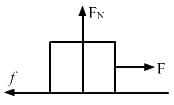
The system is in equilibrium condition when F = f.
Hence, the net horizontal force is zero.
f = μFN
F > FN
f = FN and 0 ≤ μ ≤ 1
Therefore, we can say that F > f. So the net horizontal force is nonzero.
F > f, and so the net horizontal force is zero.
FN > f ⇒ FN > μFN ⇒ μ < 1
Here, the given relation between F and f i.e
F > f and f = μFN will not be satisfied So it cannot be said that the net horizontal force is zero or nonzero.
FN − f < F < FN + f
∵ f = μFN
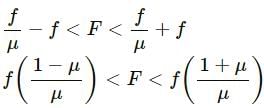
For the above relation, we can say that F ≠ f and so the net horizontal force is nonzero.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:The contact force exerted by a body A on another body B is equal to the normal force between the bodies We conclude that
Explanation
The contact force exerted by a body A on another body B is equal to the normal force between the bodies. Therefore, we can conclude that the force of friction between the bodies is zero or the bodies may be rough but they don't slip on each other.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:Mark the correct statements about the friction between two bodies.
Explanation
All the above statements are correct. The static friction is sometimes less than the kinetic friction.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:A block is placed on a rough floor and a horizontal force F is applied on it. The force of friction f by the floor on the block is measured for different values of F and a graph is plotted between them.
Explanation
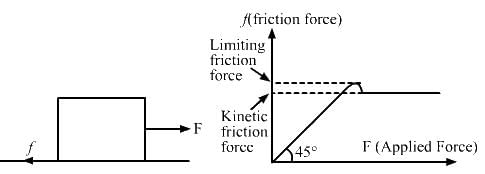
When force F is applied on the block, the force of friction f comes into play. As we increase the applied F, the static friction force adjusts itself to become (equal) to the applied force F and goes upto its maximum value equal to limiting friction force.After this ,it is treated as a constant force (i.e . now its value does not change until and unless the body starts moving). If the applied force F is greater than the limiting friction force, then the kinetic friction force comes into play at that time. The kinetic friction force is always less than the limiting friction force.
*Multiple options can be correct
Question for HC Verma Questions and Solutions: Chapter 6- Friction- 1
Try yourself:Consider a vehicle going on a horizontal road towards east. Neglect any force by the air. The frictional force on the vehicle by the road
Explanation
When the vehicle is accelerating, the force is applied (by the tyre on the road) in west direction .That causes a net resultant frictional force acting in east direction. Due to this force of friction only ,the car is moving in east direction.
When the vehicle is moving with a uniform velocity, the force of friction on the wheels of the vehicle by the road is zero.