Formulas play a significant role in the CAT exam preparation process. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of CAT formulae and familiarize ourselves with the essential formulas that are crucial for the exam. In particular, for the Quantitative Aptitude section of CAT 2025, it is imperative to memorize the formulas and master their application to solving problems with precision and swiftness. Being adept at the formulas will enhance our efficiency in the exam and contribute to achieving a high score.
Number Systems
- 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + … + n = n(n + 1)/2
- (12 + 22 + 32 + ….. + n2) = n ( n + 1 ) (2n + 1) / 6
- (13 + 23 + 33 + ….. + n3) = (n(n + 1)/ 2)2
- Sum of first n odd numbers = n2
- Sum of first n even numbers = n (n + 1)
Mathematical Formulas:
- (a – b)2 = (a2 + b2 – 2ab)
- (a + b)2 = (a2 + b2 + 2ab)
- (a + b)(a – b) = (a2 – b2)
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
- (a3 – b3) = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2)
- (a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2)
- (a3 + b3 + c3 – 3abc) = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ac)
- When a + b + c = 0, then a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
- (a + b)n = an + (nC1)an-1 b + (nC2)an-2 b2 + … + (nCn-1)abn-1 + bn
Profit, Loss and Discount
- Profit (or) Gain = SP – CP
- Profit % = (Profit/CP) × 100
- SP = (100 + gain % )/100 × CP
- CP = 100/(100 + gain %) × SP
- Loss = CP – SP
- Loss % = Loss/(CP) × 100
- SP = (100 – loss %)/100 × CP
- CP = 100/(100 – loss %) × SP
LCM and HCF
- LCM × HCF = Product of the numbers
- LCM of co-prime numbers = Product of the numbers
Speed, Time and Distance
- Distance = Speed × Time
- Time = Distance/Speed
- Speed = Distance/Time
Percentages
- To find what percentage of x is y: (y/x) × 100
- Increase N by S % = N( 1+ S/100 )
- Decrease N by S % = N (1 – S/100)
Time and Work
- If A can do a piece of work in n days, then A’s 1 day’s work = 1/n
- If A’s 1 day’s work =1/n, then A can finish the work in n days.
Averages
- Average = (Sum of observations/Number of observations)
Simple and Compound Interest
When interest is compounded Annually: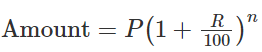
When interest is compounded, Half-yearly: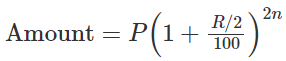
When interest is compounded Quarterly: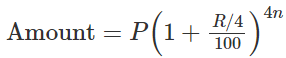
When interest is compounded annually but time is in fraction, say 3 2/5 years: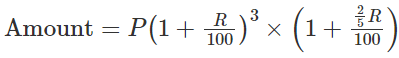
When rates are different for different years, say R1%, R2%, R3% for 1st, 2nd and 3rd year, respectively. 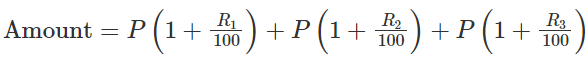
Present worth of Rs. x due n years hence is given by: 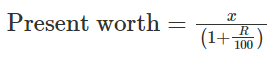
Logarithm
- loga (xy) = loga x + loga y
- logaa (x/y) = loga x – loga y
- logx x = 1
- loga 1 = 0
- loga (xn) = n(loga x)
- loga x = 1/(logx a)
- loga x = (logb x)/(logb a) = (log x)/(log a)
Probability
- Sample Space: When we perform an experiment, then the set S of all possible outcomes is called the sample space.
- Event: Any subset of a sample space is called an event.
- The probability of Occurrence of an Event:
- Let S be the sample and E be an event.
- Therefore, P(E) =n(E) / n(S)
Surds and Indices
Laws of indices:
- am × an = am+n
- am/an = am-n
- (am)n = amn
- (ab)n = anbn
- an/bn = (a/b)n
- a0 = 1
- a-m = 1/am
Surds:
Let a be the rational number and n be a positive integer such that;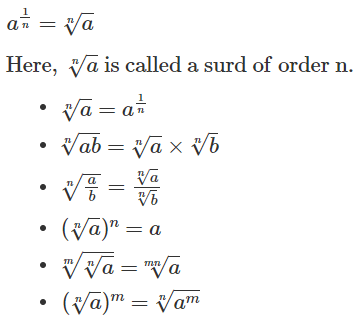
Set Theory & Function
De morgan’s Law is the basic and most important formula for sets, which is defined as
(A ? B) ‘ = A’ U B’ and (A U B)’ = A’ ? B’
The relation R ? A × A is said to be called as:
- Reflexive Relation: If aRa ? a ? A.
- Symmetric Relation: If aRb, then bRa ? a, b ? A.
- Transitive Relation: If aRb, bRc, then aRc ? a, b, c ? A.
If any relation R is reflexive, symmetric and transitive in a given set A, then that relation is known as an equivalence relation.
Permutation and Combination
Permutation Formula: A permutation is the choice of r things from a set of n things without replacement. Order matters in permutation.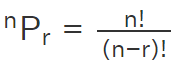
Combination Formula: A combination is the choice of r things from a set of n things without replacement. The order does not matter in combination.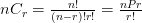
Mixtures and Alligations
Alligation: It is the rule that enables us to find the ratio in which two or more ingredients at the given price must be mixed to produce a mixture of the desired price.
Mean Price: The cost of a unit quantity of the mixture is called the mean price.
Rule of Alligation:
If two ingredients are mixed, then
(Quantity of cheaper / Quantity of dearer) = (C.P. of dearer – Mean Price / Mean price – C.P. of cheaper)
Trigonometry
Trigonometric Identities:
- Sine = Opposite/Hypotenuse
- Secant = Hypotenuse/Adjacent
- Cosine = Adjacent/Hypotenuse
- Tangent = Opposite/Adjacent
- Co?Secant = Hypotenuse/Opposite
- Co?Tangent = Adjacent/Opposite
The reciprocal identities are given as:
- cosec ? = 1/sin ?
- sec ? = 1/ cos ?
- cot ? = 1/tan ?
- sin ? = 1/cosec ?
- cos ? = 1/sec ?
- tan ? = 1/cot ?
Coordinate Geometry
The Distance Between two Points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2):
AB² = (x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²
The Midpoint of a Line Joining Two Points
The midpoint of the line joining the points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is:
[(x1 + x2)/1, (y1 + y2)/2]
The Equation of a Line Using One Point and the Gradient
The equation of a line which has gradient m and which passes through the point (x1, y1) is:
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
Mensuration
Rectangle
- Area = lb
- Perimeter = 2(l+b)
Square
- Area = a × a
- Perimeter = 4a
Triangle
- Area = (1/2) × b × h
- or
- ?[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], where s = (a + b + c)/2
Circle
- Area = ?r² or ?d²/4
- Circumference = 2?r or ?d
- Area of sector of a circle = (??r² )/360
Cube
- Volume: V = a3
- Lateral surface area = 4a²
- Surface Area: S = 6a2
- Diagonal (d) = ?3 a
Cuboid
- Volume of cuboid: lbh
- Total surface area = 2 (lb + bh + hl) or 6l2
- Length of diagonal =?(l² + b² + h²)
CAT 2023 Important Formulas by EduRev
The QA section of CAT 2023 exam comprises questions from diverse topics, including Profit, Loss and Discount, Number System, Time and Work, LCM and HCF, Logarithm, Averages, Set theory & Function, Probability, Permutation & Combination, Trigonometry, Geometry, Coordinate Geometry, and more. In this context, mastering the important formulas is an indispensable part of CAT revision tips, which can help aspirants excel in the quantitative section of the exam.
Indeed, the knowledge of essential formulas serves as a vital elixir for CAT preparation, and candidates must familiarize themselves with them to perform well in the QA section. Therefore, as candidates embark on their CAT 2023 preparation, it is crucial to prioritize learning the critical formulas and practising their application to crack the Common Admission Test with a high score.
You should also practise sectional mock tests of quant as it will familiarise you with the format and types of questions which are typically asked. EduRev provides you with sectional mock tests along with chapter-wise mock tests.
EduRev also provides you with previous 10 year papers of CAT so that you can analyse the level of Quantitative Aptitude Section.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to CAT Important Formulas
What are the profit and loss important formulas for CAT?
The formula to calculate the profit percentage is: Profit%=Profit / costprice×100. The formula to calculate the loss percentage is: Loss%=Loss / Costprice×100. Answer: Loss = Cost price – selling price.
Is maths in CAT difficult?
Though the topics of this section are based on the fundamental mathematics, the questions are tricky and complex enough to baffle anyone. The major areas of Quantitative Aptitude are: Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry and Advanced/Modern Mathematics.
What are some important formulas for CAT?
There are many important formulas for CAT, including those for arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry. Here are a few examples:
Arithmetic: Average = (sum of terms) / (number of terms)
Algebra: Quadratic equation = (-b ± ?(b2 - 4ac)) / 2a
Geometry: Area of a triangle = (1/2) * base * height
Trigonometry: sin2? + cos2? = 1
How can I remember all of these formulas?
One way to remember formulas is to practice applying them to problems. The more you use a formula, the more likely you are to remember it. You can also make flashcards or mnemonic devices to help you remember the formulas.
Are there any shortcuts or tricks for solving CAT problems using these formulas?
Yes, there are many shortcuts and tricks that can help you solve problems more quickly and efficiently. For example, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to quickly find the hypotenuse of a right triangle or use the distributive property of multiplication to simplify expressions.
How can I improve my problem-solving skills for CAT?
The best way to improve your problem-solving skills is to practice solving problems. You can find practice problems online or in CAT preparation books. Try to solve problems on your own before looking at the answer, and make note of the types of problems you struggle with so you can focus on improving those areas.
How important is it to memorize formulas for CAT?
Memorizing formulas is important, but it's not the only thing that matters. It's also important to understand how and when to use the formulas. Some CAT problems may require you to combine multiple formulas or use them in a creative way. Therefore, it's important to have a deep understanding of the concepts behind the formulas.















