Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Chapter Notes: Rate & Extent of Chemical Change
Rate & Extent of Chemical Change Chapter Notes | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Calculating rates of reactions |

|
| Factors which affect the rates of chemical reactions |

|
| Collision theory and activation energy |

|
| Catalysts |

|
Calculating rates of reactions
- Rates of reactions can be measured using the amount of product used, or amount of product formed over time:
Rate of reaction = amount of reactant used / Time
Rate of reaction = amount of product formed / Time- Quantity of reactant or product can be measured by the mass in grams or by a volume in cm3
- Units of rate of reaction may be given as g/s or cm3/s
- You can also use quantity of reactants in terms of moles (instead of mass or volume) and therefore, units for rate of reaction in mol/s
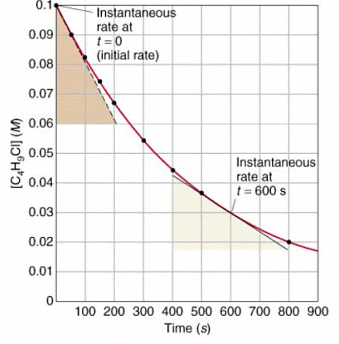
- To find the rate of reaction graphically:
- To measure the rate of reaction: draw tangents to curves and use the slope of the tangent
- Calculate the gradient of a tangent to the curve on these graphs as a measure of rate of reaction at a specific time
Factors which affect the rates of chemical reactions
- Factors:
- concentration
- pressure
- surface area
- temperature
- catalysts
Collision theory and activation energy
- Collision theory: chemical reactions can occur only when reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy
- Activation energy: the minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react
- Increasing the concentration of reactants in solution, the pressure of reacting gases, and the surface area of solid reactants increases the frequency of collisions and so increases the rate of reaction.
- Increasing the temperature increases the frequency of collisions and makes the collisions more energetic, and so increases the rate of reaction.
Catalysts
- Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions without being changed or used up during the reaction.
- Enzymes act as catalysts in biological systems
- Catalysts are not included in the equation for a reaction
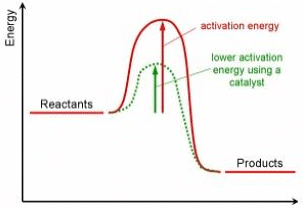
- Catalysts decrease the activation energy; this increases the proportion of particles with energy to react.
- Catalysts provide a different pathway for a chemical reaction that has a lower activation energy.
The document Rate & Extent of Chemical Change Chapter Notes | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
73 videos|87 docs|21 tests
|
Related Searches



















