Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Reaction Rates Using Moles
Reaction Rates Using Moles | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Higher Tier Only
- We have seen that the rate of reaction is a measure of a changing property per unit time
- This will frequently be expressed in units of g/s or cm3/s for a change in mass or volume, respectively
- However, it is often more useful to be able to express rate of reaction in terms of moles, in which case the unit will be mol/s
- There is no direct way to measure moles, so first it is necessary to calculate the rate using the rate formula triangle:
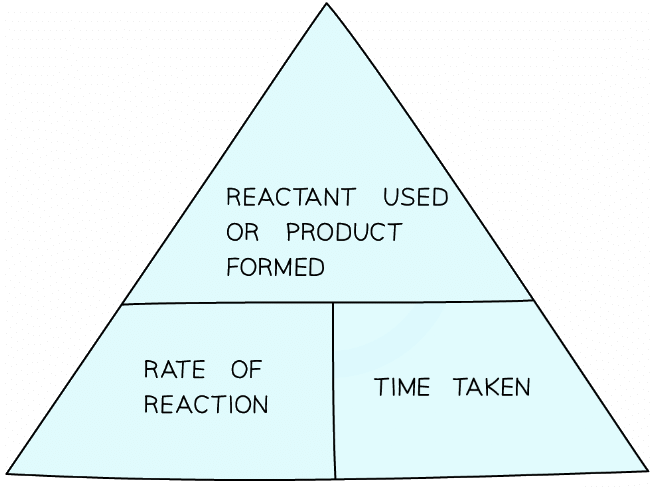 The rate formula triangle
The rate formula triangle
- After calculating the rate of reaction it can then be converted into mol/s
- If you are working in mass per unit time then the process is:
mass per unit time ÷ molar mass of the substance = moles per unit time - If you are working in volume per unit time then you have to use the molar gas volume
volume per unit time ÷ molar gas volume (24 000 cm3/mol ) = moles per unit time
Solved Examples
Example 1: Calculate the rates of reaction, in mol/s, in the following experiments:20.0 g of marble chips were added to a flask containing 100 cm3 of 2.0 mol/dm3 hydrochloric acid. The flask was placed on a balance and the mass was measured at the start of the reaction. After 2.5 minutes the mass was found to have decreased by 6.0 g.
- Convert the time into seconds
2.5 x 60 = 150 s- The rate of reaction is
6.0 g ÷ 150 s = 0.04 g/s- The loss in mass is due the carbon dioxide gas released
- The molar mass of carbon dioxide, CO2, is 44.0 g/mol
- Convert to moles
0.04 g s-1 ÷ 44.0 g/mol = 9.1 x 10-4 mol/s
Example 2: Calculate the rates of reaction, in mol/s, in the following experiments:
A piece of magnesium ribbon, 2 cm in length, was added to a flask containing 50.0 cm3 of 1.50 mol/dm3 sulfuric acid. The flask was connected to a gas syringe and the volume of gas measured every minute. 15 cm3 of gas had been collected after 6 minutes.
- Convert the time into seconds
6.0 x 60 = 360 s- The rate of reaction is
15 cm3 ÷ 360 s = 0.0417 cm3/s- Convert to moles
0.0417 cm3/s ÷ 24 000 cm3/mol = 1.7 x 10-6 mol/s
The document Reaction Rates Using Moles | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|
Related Searches















