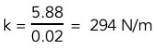Force-Extension Graphs | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
Linear & Non-Linear Extension
- Hooke’s law is the linear relationship between force and extension
- This is represented by a straight line on a force-extension graph
- Materials that do not obey Hooke's law, i.e they do not return to their original shape once the force has been removed, have a non-linear relationship between force and extension
- This is represented by a curve on a force-extension graph
- Any material beyond its limit of proportionality will have a non-linear relationship between force and extension
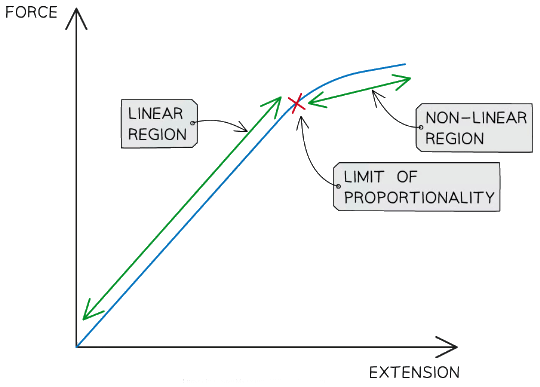 Linear and non-linear regions of a force-extension graph
Linear and non-linear regions of a force-extension graph
Calculating Spring Constant
- The spring constant can be calculated by rearranging the Hooke's law equation for k:
k = F/e - Where:
- k = spring constant in newtons per metres (N/m)
- F = force in newtons (N)
- e = extension in metres (m)
- This equation shows that the spring constant is equal to the force per unit extension needed to extend the spring, assuming that its limit of proportionality is not reached
- The stiffer the spring, the greater the spring constant and vice versa
This means that more force is required per metre of extension compared to a less stiff spring
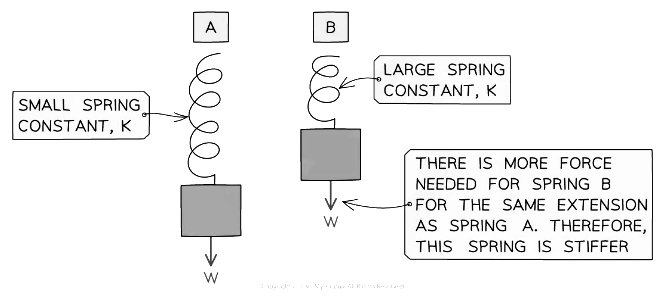 A spring with a larger spring constant needs more force per unit extension (it is stiffer)
A spring with a larger spring constant needs more force per unit extension (it is stiffer)
The spring constant is also used in the equation for elastic potential energy
Tip: Remember the unit for the spring constant is Newtons per metres (N/m). This is commonly forgotten in exam questions
Example: A mass of 0.6 kg is suspended from a spring, where it extends by 2 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring.
Step 1: List the known quantities
Mass, m = 0.6 kg
Extension, e = 2 cmStep 2: Write down the relevant equation
k = F/eStep 3: Calculate the force
The force on the spring is the weight of the mass
g is Earth's gravitational field strength (9.8 N/kg)
W = mg = 0.6 × 9.8 = 5.88 NStep 4: Convert any units
The extension must be in metres
2 cm = 0.02 mStep 5: Substitute values into the equation
Interpreting Graphs of Force v Extension
- The relationship between force and extension is shown on a force-extension graph
- If the force-extension graph is a straight line, then the material obeys Hooke's law
- Sometimes, this may only be a small region of the graph, up to the material's limit of proportionality
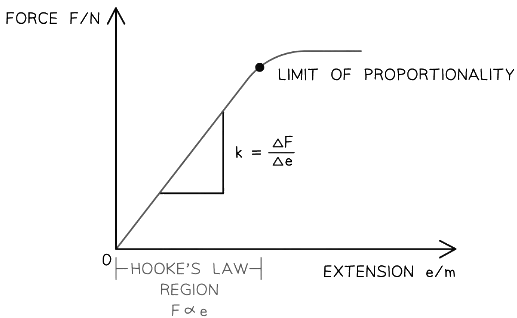 The Hooke's law region on a force-extension graph is where the graph is a straight line
The Hooke's law region on a force-extension graph is where the graph is a straight line
- Sometimes, this may only be a small region of the graph, up to the material's limit of proportionality
- The symbol Δ means the 'change in' a variables
- For example, ΔF and Δe are the 'change in' force and extension respectively
- This is the same as rise ÷ run for calculating the gradient
- The '∝' symbol means 'proportional to'
- i.e. F ∝ e means the 'the force is proportional to the extension'
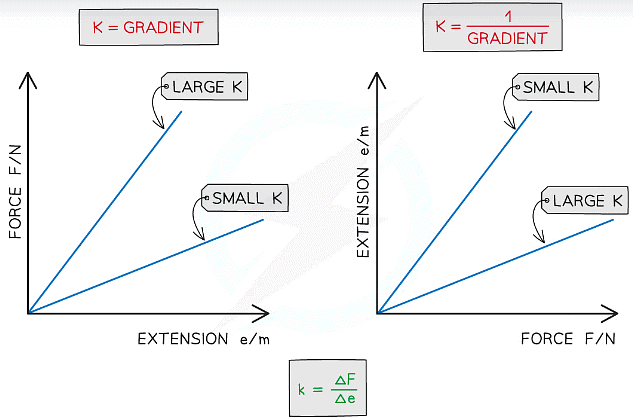 The spring constant is the gradient, or 1 ÷ gradient of a force-extension graph depending on which variable is on which axis
The spring constant is the gradient, or 1 ÷ gradient of a force-extension graph depending on which variable is on which axis
- i.e. F ∝ e means the 'the force is proportional to the extension'
- If the force is on the y axis and the extension on the x axis, the spring constant is the gradient of the straight line (Hooke's law) region of the graph
- If the graph has a steep straight line, this means the material has a large spring constant
- If the graph has a shallow straight line, this means the material has a small spring constant
- If the force is on the x axis and the extension on the y axis, the spring constant is 1 ÷ gradient of the straight line (Hooke's law) region of the graph
- If the graph has a steep straight line, this means the material has a small spring constant
- If the graph has a steep straight line, this means the material has a large spring constant
Tip: Make sure to always check which variables are on which axes to determine which line has a larger or smaller spring constant, as well as the units for calculations
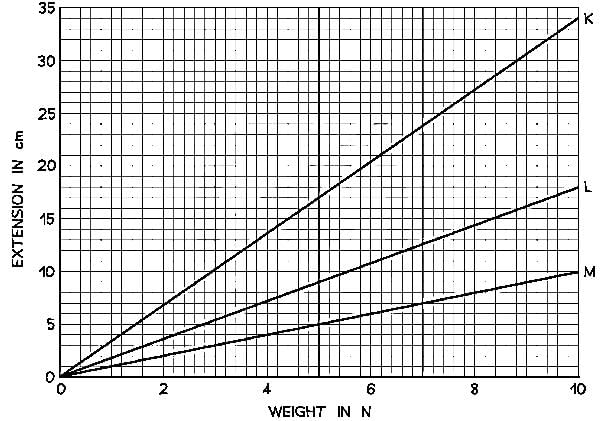
Which of the statements is correct?
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|