Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Catalysts: Rate of Reaction
Catalysts: Rate of Reaction | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
Overview of Cataysts
- Catalysts are substances which speed up the rate of a reaction without themselves being altered or consumed in the reaction
- The mass of a catalyst at the beginning and end of a reaction is the same and they do not form part of the equation
- Different processes require different types of catalysts but they all work on the same principle of providing a different pathway for the reaction to occur that has a lower activation energy
- This means a higher proportion of the reactant particles have energy greater than the activation energy and will result in more successful collisions per second
- An important industrial example is iron, which is used to catalyse the Haber Process for the production of ammonia
- Iron beads are used to increase the surface area available for catalysis
- Normally only small amounts of catalysts are needed to have an effect on a reaction
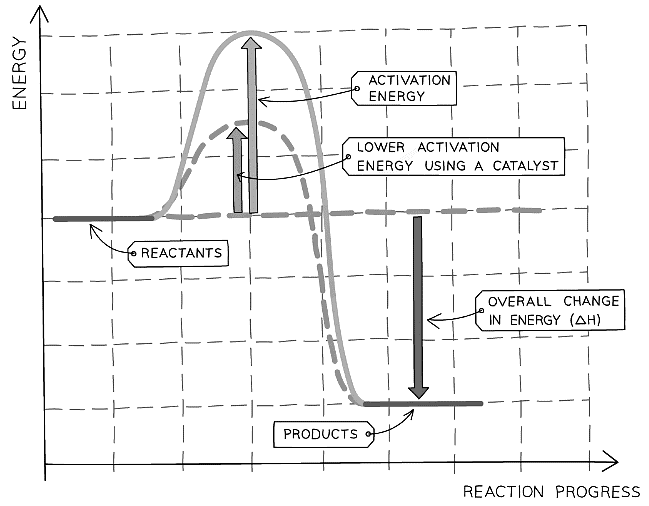 A reaction profile showing the effect of using a catalyst on the activation energy of a reaction
A reaction profile showing the effect of using a catalyst on the activation energy of a reaction
- Catalysis is a very important branch of chemistry in commercial terms as catalysts increase the rate of reaction (hence the production rate) and they reduce energy costs
- The transition metals are used widely as catalysts as they have variable oxidation states allowing them to readily donate and accept different numbers of electrons. This is key to their catalytic activity
- Enzymes act as catalysts in biological systems
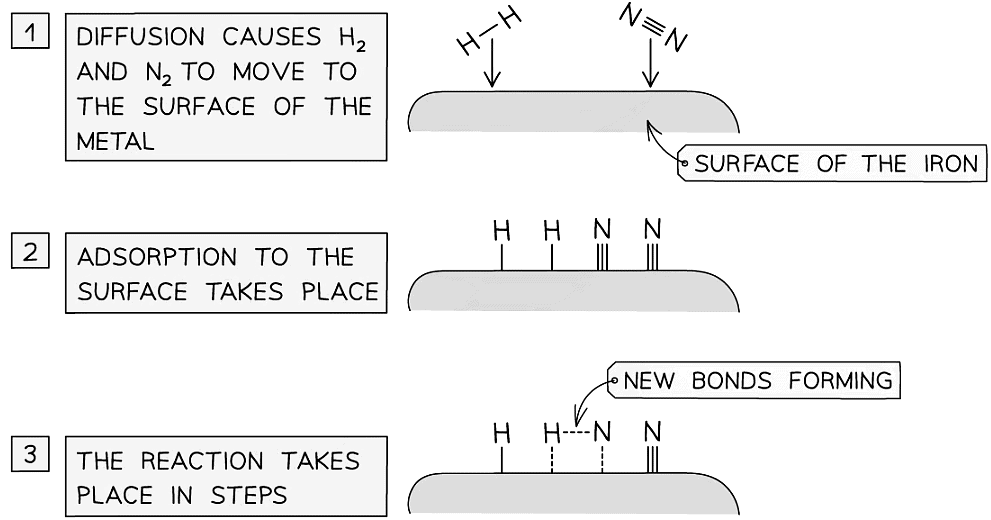
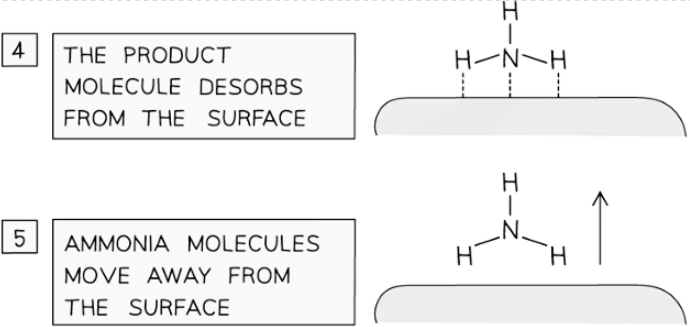 Catalysts work by attracting reactant molecules on to the surface and so providing an alternate reaction pathway of lower energy
Catalysts work by attracting reactant molecules on to the surface and so providing an alternate reaction pathway of lower energy
Exam Tip
Although catalysts are not part of the overall reaction, you may see them written over the arrow in reaction equations in the same way you can add reaction conditions above or below the arrow.
The document Catalysts: Rate of Reaction | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
73 videos|87 docs|21 tests
|
Related Searches















