Developing the Atmosphere | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Earth’s early atmosphere |

|
| How oxygen increased |

|
| How carbon dioxide decreased |

|
| Uptake by living organisms |

|
The early atmosphere was mainly carbon dioxide and water vapour. Water vapour condensed to form the oceans. Photosynthesis caused the amount of carbon dioxide to decrease and oxygen to increase.
The Earth’s early atmosphere
The Earth formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago. Scientists cannot be certain about what gases made up the Earth’s early atmosphere. Ideas about how the atmosphere was produced and has changed have developed over time as new evidence has been discovered. There is still not enough evidence for scientists to be certain.Where did the atmosphere come from?
One theory suggests that the early atmosphere came from intense volcanic activity, which released gases that made the early atmosphere very similar to the atmospheres of Mars and Venus today. These atmospheres have:- a large amount of carbon dioxide
- little or no oxygen
- small amounts of other gases, such as ammonia and methane
Volcanic activity also released water vapour, which condensed as the Earth cooled to form the oceans. Nitrogen was probably also released by volcanoes which gradually built up in the atmosphere because it is unreactive. A volcano in iceland
A volcano in iceland
The modern atmosphere
For approximately 200 million years, the proportions of different gases in the atmosphere have been relatively stable. The pie chart below shows the percentages of gases that make up the atmosphere.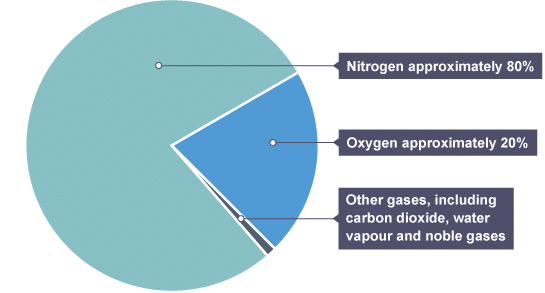 The composition of the modern atmosphere
The composition of the modern atmosphere
Example: Name the most abundant gas in the modern atmosphere.
Nitrogen.
How oxygen increased
Plants make their own food by photosynthesis. In this process, carbon dioxide is reacted with water to produce glucose, with oxygen as a by-product:carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)
Scientists think that algae first evolved approximately 2.7 billion years ago, and soon after this oxygen began to exist in the atmosphere. Photosynthesis by primitive plants and algae released oxygen, which gradually built up in the atmosphere. Eventually, the amount of oxygen present in the atmosphere enabled animals to evolve. Green algae cells viewed using an electron microscope
Green algae cells viewed using an electron microscope
How carbon dioxide decreased
Formation of sedimentary rocks
Carbon dioxide is a very soluble gas. It dissolves readily in water. As the oceans formed, carbon dioxide dissolved to form soluble carbonate compounds so its amount in the atmosphere decreased. Carbonate compounds were then precipitated as sedimentary rocks, eg limestone.
Uptake by living organisms
- Carbon dioxide was also absorbed from the oceans into photosynthetic algae and plants. Many of these organisms, and the simple organisms in the food chains that they supported were turned into fossil fuels, eg crude oil, coal and natural gas, which all contain carbon.
- Coal is a fossil fuel which was formed from trees which were in dense forests in low-lying wetland areas. Flooding caused the wood from these forests to be buried in a way that prevented oxidation taking place. Compression and heating over millions of years turned the wood into coal.
- Crude oil and natural gas were formed from simple plants and tiny animals which were living in oceans and lakes. These small organisms died and their remains sank to the bottom where they were buried under sediments. The lack of oxygen prevented oxidation from occurring.
- Over millions of years, heat and pressure turned the remains of the organisms into crude oil and natural gas. Natural gas contains the smallest molecules and is often found on top of crude oil, trapped under sedimentary rock.
Example: Describe two reasons why the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere decreased over time.
Carbon dioxide dissolved in the oceans, and primitive plants used it for photosynthesis.
|
75 videos|131 docs|24 tests
|




















