Grade 10 Exam > Grade 10 Notes > Chemistry for Grade 10 > Alternative Methods of Extracting Metals
Alternative Methods of Extracting Metals | Chemistry for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Biological Methods |

|
| Phytomining |

|
| Bioleaching |

|
| Biological methods of metal extraction - Higher |

|
Biological Methods
Higher Tier Only
- Extraction of metal ores from the ground is only economically viable when the ore contains sufficiently high proportions of the useful metal, such as iron ores and aluminium ores
- For low-grade ores (ores with lower quantities of metals) other techniques are being developed to meet global demand
- This is happening in particular with nickel and copper as their ores are becoming more and more scarce
- Phytoextraction and bioleaching (bacterial) are two relatively new methods of extracting metals that rely on biological processes
- Both of these methods avoid the significant environmental damage caused by the more traditional methods of mining
- Traditional mining involves a great deal of digging, moving and disposing of large amounts of rock
- Biological methods are, however, very slow and also require either displacement or electrolysis to purify the extracted metal
- Both techniques are also used to extract metals from mining wastes, which may contain small quantities of metals or toxic metals that need to be removed from that environment
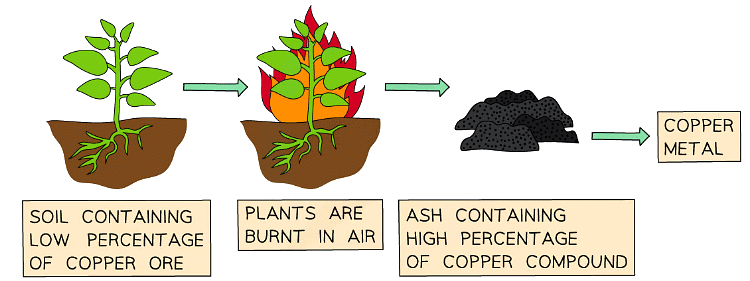
Phytomining
- This process takes advantage of how some plants absorb metals through their roots
- The plants are grown in areas known to contain metals of interest in the soil
- As the plants grow the metals are taken up through the plants vascular system and become concentrated in specific parts such as their shoots and leaves
- These parts of the plant are harvested, dried and burned
- The resulting ash contains metal compounds from which the useful metals can be extracted by displacement reactions or electrolysis
 Copper in soil can be extracted by phytoextraction
Copper in soil can be extracted by phytoextraction
Bioleaching
- Bioleaching is a technique that makes use of bacteria to extract metals from metal ores
- Some strains of bacteria are capable of breaking down ores to form acidic solutions containing metals ions such as copper(II)
- The solution is called a leachate which contains significant quantities of metal ions
- The ions can then be reduced to the solid metal form and extracted by displacement reactions or electrolysis
- This method is often used to extract metals from sulfides e.g. CuS or Fe2S
- Although bioleaching does not require high temperatures, it does produce toxic substances which need to be treated so they don't contaminate the environment
- Bioleaching is not only used for the primary extraction of metals, but it is also used in mining waste clean up operations
Exam Tip
Phytoextraction and bioleaching are principally used for copper extraction due to the high global demand for copper, but these methods can be applied to other metals.
 |
Download the notes
Alternative Methods of Extracting Metals
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Biological methods of metal extraction - Higher
The Earth's supply of metal ores is limited. For example, high-grade copper ores are becoming harder to find and mine. There are some alternative methods to extract metals from low-grade copper ores that use living organisms. These have advantages and disadvantages compared to the usual extraction methods.Phytoextraction
Plants absorb mineral ions through their roots. Phytoextraction makes use of this:- plants are grown on a low-grade ore
- the plants absorb metal ions through their roots and concentrate these ions in their cells
- the plants are harvested and burnt
- the ash left behind contains metal compounds
Phytoextraction is slow but it:
- reduces the need to obtain new ore by mining
- conserves limited supplies of high-grade ores
- reduces the amount of rock waste that must be disposed of after traditional mining
Example 1: Suggest reasons why phytoextraction reduces damage to the environment.
Mining for metal ores involves quarries, which are large holes in the ground. These create noise, dust and traffic. They also destroy natural habitats. Phytoextraction reduces the need for mining and reduces this damage.
Example 2: Give one disadvantage of phytoextraction.
It is a slow process.
Bioleaching
- Certain bacteria can break down low-grade ores to produce an acidic solution containing copper ions. The solution is called a leachate and the process is called bioleaching.
- Bioleaching does not need high temperatures but it produces toxic substances, including sulfuric acid, which damage the environment.
Processing the metal compounds
- Iron is more reactive than copper. It can displace copper from the leachate. For example:
iron + copper sulfate → iron(II) sulfate + copper
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) - Since iron is cheaper than copper, the use of scrap iron is a cost-effective way to produce copper from the leachate.
- Alternatively, the copper compounds can be dissolved and the solution electrolysed to produce copper metal.
The document Alternative Methods of Extracting Metals | Chemistry for Grade 10 is a part of the Grade 10 Course Chemistry for Grade 10.
All you need of Grade 10 at this link: Grade 10
|
78 videos|87 docs|11 tests
|
Related Searches














