Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Cellular Respiration |

|
| Respiration: Principles |

|
| Aerobic Respiration |

|
| Anaerobic Respiration in Animals |

|
| Anaerobic Respiration in Plants & Yeast |

|
| Comparing Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration |

|
Cellular Respiration
Releasing energy
Respiration releases energy – it is an exothermic process.
Don't confuse respiration with photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, and some bacteria, synthesise food molecules – which they then use, in addition to other things, for respiration. The process of photosynthesis requires energy – it is endothermic.
Don't confuse respiration with breathing, which is ventilation. Respiration happens in cells.
Why organisms need energy
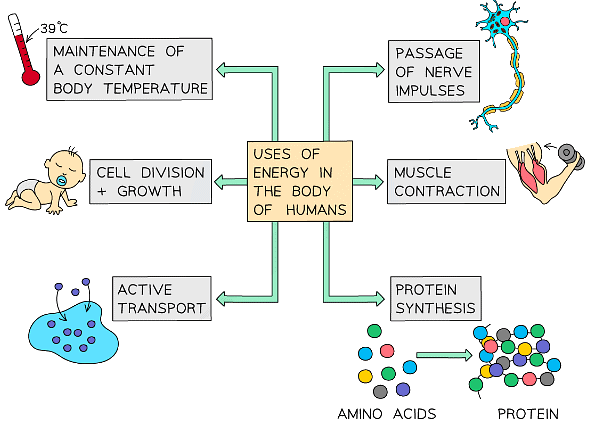
All organisms need energy to live. This energy is used:
- to drive the chemical reactions needed to keep organisms alive – the reactions to build complex carbohydrates, proteins and lipids from the products of photosynthesis in plants, and the products of digestion in animals, require energy
- movement – in animals, energy is needed to make muscles contract, while in plants, it is needed for transport of substances in the phloem
Respiration is only around 40 per cent efficient. As animals respire, heat is also released. In birds and mammals, this heat is distributed around the body by the blood. It keeps these animals warm and helps to keep a constant internal temperature.
Energy is also used:
- for cell division
- to maintain constant conditions in cells and the body – homeostasis
- to move molecules against concentration gradients in active transport
- for the transmission of nerve impulses
Respiration: Principles
- Cellular respiration is an exothermic reaction which is continuously occurring in living cells
- The chemical process of cellular respiration releases energy
- The energy transferred supplies all the energy needed for living processes to occur within cells and organisms as a whole
- Organisms need energy for:
- Chemical reactions to build larger molecules from smaller molecules
- Muscle contraction to allow movement
- Keeping warm (to maintain a constant temperature suitable for enzyme activity)
 Uses of the energy released from respiration
Uses of the energy released from respiration
Aerobic Respiration
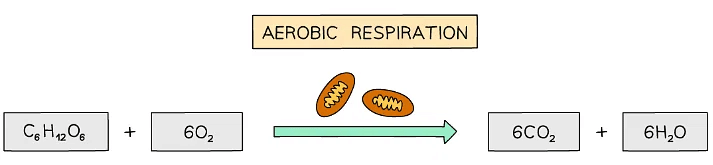
- Respiration in cells can take place aerobically (using oxygen) to transfer energy; glucose is reacted with oxygen in this process
- The equations that summarise the chemical reactions of respiration that release energy from glucose are:
 Word equation for aerobic respiration
Word equation for aerobic respiration Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration
Balanced symbol equation for aerobic respiration - Aerobic respiration uses oxygen and most of the reaction takes place in the mitochondria (these are shown above the arrow in the equations)
Anaerobic Respiration in Animals
- Respiration in cells can take place anaerobically (without oxygen), to transfer energy; it simply involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose into lactic acid
- This occurs when the body can’t supply enough oxygen for aerobic respiration, such as during vigorous exercise
- Anaerobic respiration is represented by the equation:
 Word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals – some bacterial cells respire in this way too
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in animals – some bacterial cells respire in this way too - As the oxidation of glucose is incomplete in anaerobic respiration much less energy is transferred than in aerobic respiration
- Anaerobic respiration takes place without the need of oxygen
 |
Download the notes
Aerobic & Anaerobic Respiration
|
Download as PDF |
Anaerobic Respiration in Plants & Yeast
- Plants and yeast can respire without oxygen as well, breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide
- Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation
- Fermentation is economically important in the manufacture of bread (where the production of carbon dioxide makes dough rise) and alcoholic drinks (as ethanol is a type of alcohol)
 The process outlined above is the same in plants
The process outlined above is the same in plants
Comparing Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration
You need to be able to compare the processes of aerobic and anaerobic respiration with regard to the need for oxygen, the differing products and the relative amounts of energy transferred:
Exam Tip: Remember that cellular respiration is not breathing; it is a chemical process of transferring energy from glucose in all living cells.
|
110 videos|93 docs|9 tests
|