The Eye | Biology for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Functions of the Eye |

|
| Structure of the Eye |

|
| Focusing the Eye |

|
| Defects of the Eye |

|
| Common Defects of the Eye and How they Can be Overcome |

|
Functions of the Eye
- The eye is a sense organ containing receptors sensitive to light intensity and colour
- Receptors are groups of specialised cells that can generate an electrical impulse in a sensory neurone
- The eye contains two types of receptor cell: rod cells which are sensitive to light intensity and cone cells which are sensitive to different wavelengths of visible light (colour)
Structure of the Eye
- The purpose the eye is to receive light and focus it onto the retina at the back of the eye
- The retina is where the rod and cone cells are located
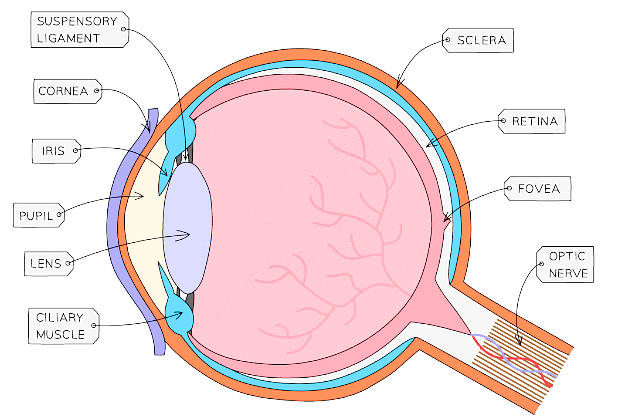 The eye is an organ made from several different types of tissue. All of the structures function together to allow light to hit the retina, which sends signals to the brain
The eye is an organ made from several different types of tissue. All of the structures function together to allow light to hit the retina, which sends signals to the brain
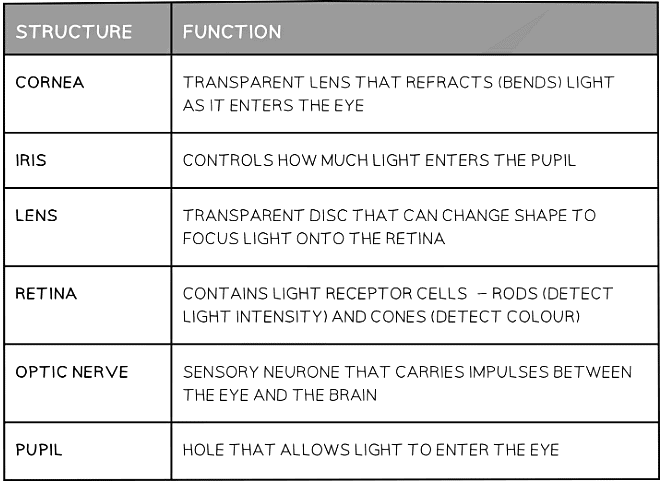
Eye structure & function table
Focusing the Eye
The pupil reflex
- This is a reflex action carried out to protect the retina from damage in bright light and protect us from not seeing objects in dim light
- It's a reflex action so it happens automatically
- The reflex action is controlled by two groups of muscle; the radial muscle and the circular muscles
- In dim light, the pupil dilates (widens) in order to allow as much light into the eye as possible
- In bright light, the pupil constricts (narrows) in order to prevent too much light entering the eye and damaging the retina
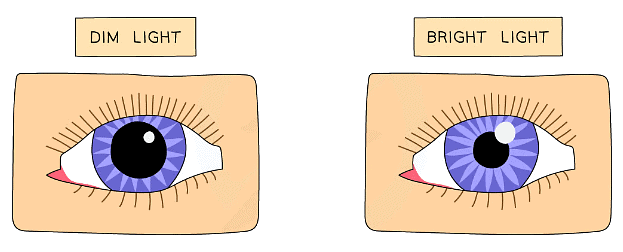 Very bright light can damage the receptor cells of the retina, the pupil reflex protects the eye by altering the diameter of the pupil
Very bright light can damage the receptor cells of the retina, the pupil reflex protects the eye by altering the diameter of the pupil
The pupil reflex in dim light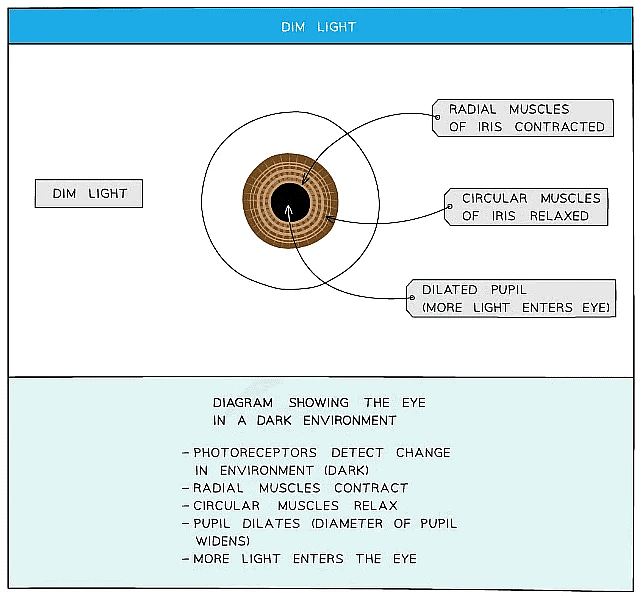
The pupil reflex in bright light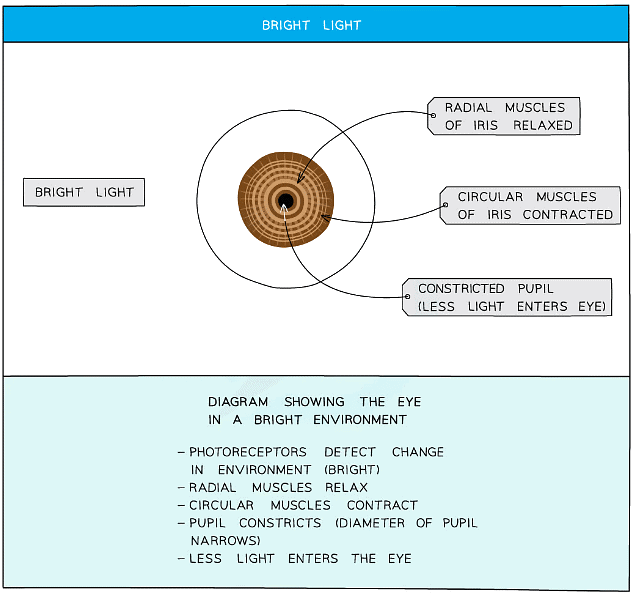
Pupil reflex table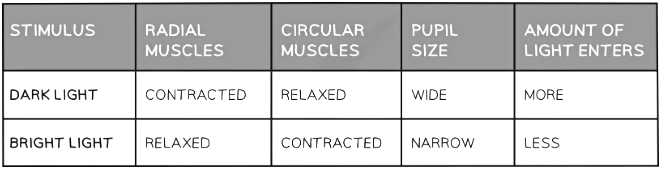
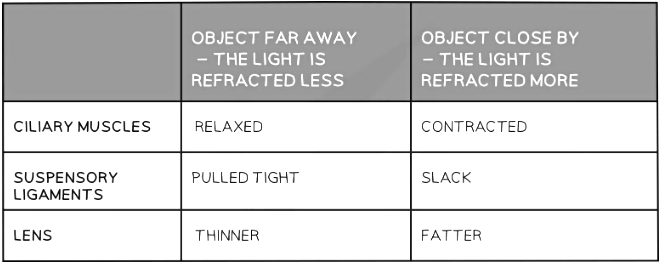
Accomodation
- Accommodation is the process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
- The lens is elastic and its shape can be changed when the suspensory ligaments attached to it become tight or loose
- The changes are brought about by the contraction or relaxation of the ciliary muscles
- To focus on a near object:
- The ciliary muscles contract
- The suspensory ligaments loosen
- The lens is then thicker and refracts light rays more strongly
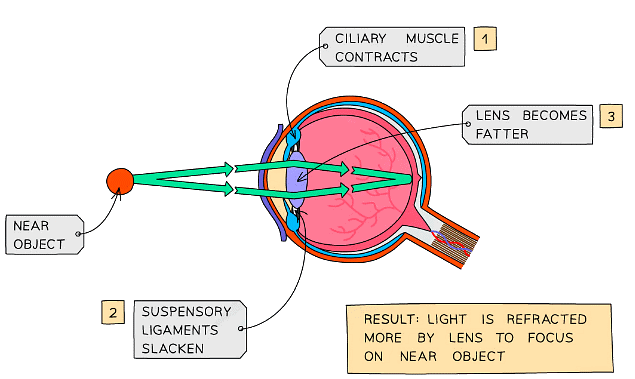 Diagram showing the eye when an object is close up
Diagram showing the eye when an object is close up
- To focus on a distant object:
- The ciliary muscles relax
- The suspensory ligaments are pulled tight
- The lens is then pulled thin and only slightly refracts light rays
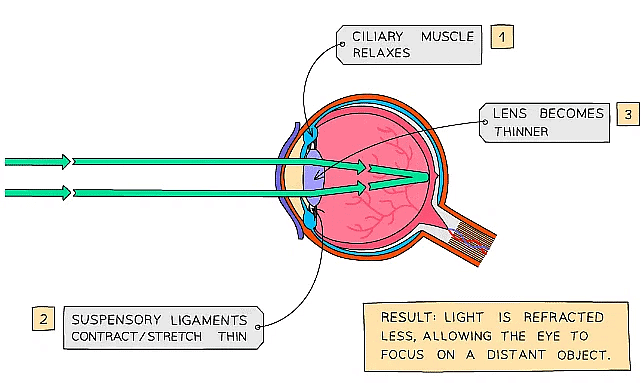 Diagram showing the eye when an object is far away
Diagram showing the eye when an object is far away
Eye Accommodation Table
Exam Tip: Accommodation is something you can work out in an exam if you have forgotten – staring at your hand right in front of your eye will make your eyes feel tight after a few seconds.This is because the ciliary muscles are contracted. Staring at an object far away feels relaxing and comfortable because the ciliary muscles are relaxed.
Defects of the Eye
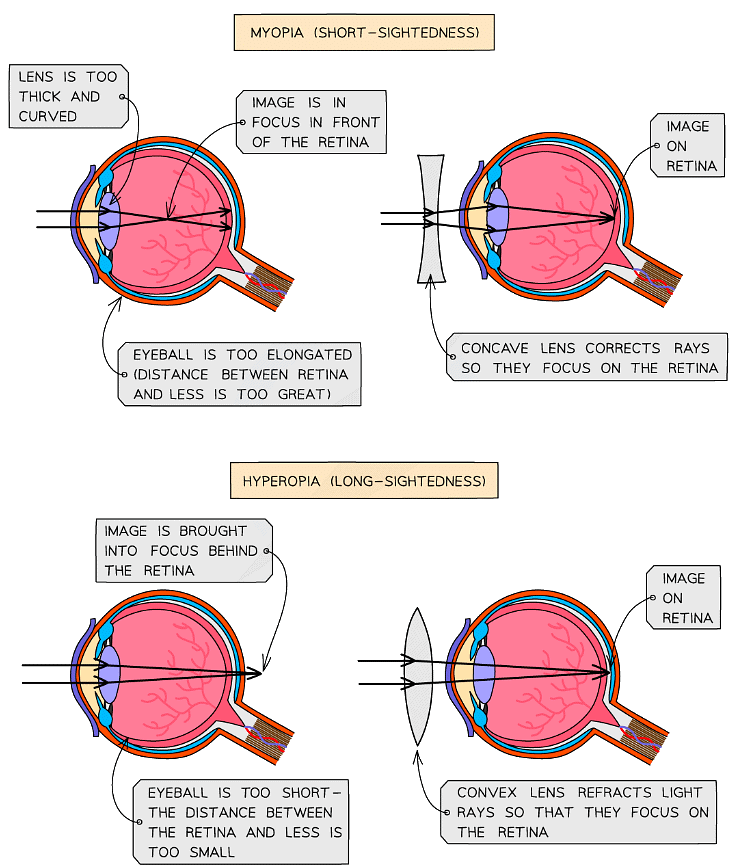
- Two common defects of the eyes are myopia (short-sightedness) and hyperopia (long-sightedness) in which rays of light do not focus on the retina
- Generally, these defects are treated with spectacle lenses (glasses) which refract the light rays so that they do focus on the retina
 Myopia (short-sightedness) and hyperopia (long-sightedness)
Myopia (short-sightedness) and hyperopia (long-sightedness) - New technologies are now available which can treat both of these defects rather than using spectacle lenses
- Treatments include:
- Hard and soft contact lenses: these sit on the surface of the eye and are almost invisible, making them ideal for activities like sports. Soft lenses are more comfortable but carry a higher infection risk
- Laser surgery: lasers can be used to change the shape of the cornea (changing how it refracts light onto the retina) although like all surgical procedures there is risk of unexpected damage occurring during the procedure which could lead to worse vision or an infection
(i) For myopia: the cornea is slimmed down, reducing the refractive power
(ii) For hyperopia: the cornea shape is changed so the refractive power is increased - Lens replacement surgery completely replaces the lens of the eye with a plastic artificial lens (rather than changing the shape of the cornea during laser eye surgery) but this procedure is more invasive than laser surgery and carries a risk of damage occurring to the retina leading to complete sight loss
Exam Tip: You should expect to see ray diagrams, showing myopia and hyperopia of the eye and be able to demonstrate how spectacle lenses can correct them.
Common Defects of the Eye and How they Can be Overcome
Correcting vision defects
- Two common defects of the eyes are myopia (short-sightedness) and hyperopia (long-sightedness). In both cases rays of light do not focus on the retina so a clear image is not formed.
- These two defects are treated with spectacle lenses, which refract (bend) the light rays so that they do focus on the retina.
Short sight
Someone with short-sight can see near objects clearly, but cannot focus properly on distant objects.
Short sight is caused by one of the following:
- The eyeball being elongated - so that the distance between the lens and the retina is too great.
- The lens being too thick and curved - so that light is focused in front of the retina.
Short-sightedness can be corrected by placing a concave lens in front of the eye, as shown in the diagrams below.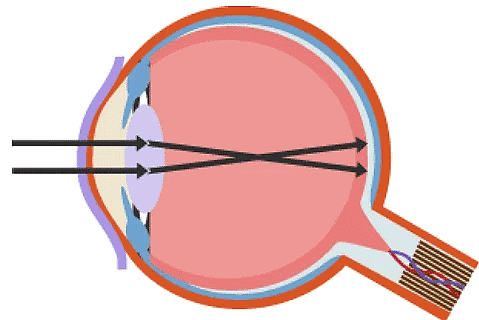
Myopia - short-sightedness
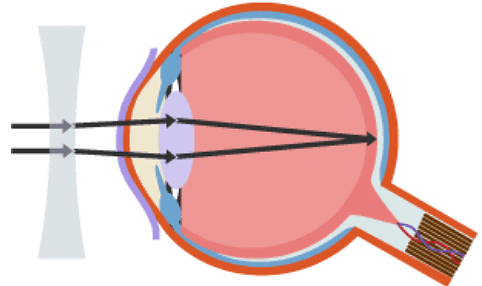
Concave lens cures short-sightedness
Long-sight
Someone who is long-sighted can see distant objects clearly, but they cannot focus properly on near objects.
Long-sightedness is caused by one of the following:
- the eyeball being too short - so the distance between the lens and retina is too small
- a loss of elasticity in the lens - meaning it cannot become thick enough to focus (which is often age-related)
As a result, the lens focuses light behind the retina instead of onto it. Long-sightedness is corrected by putting a convex lens in front of the eye, as shown in the diagrams below.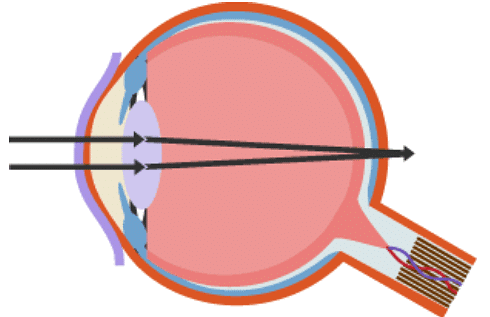
Long-sightedness (Hyperopia)
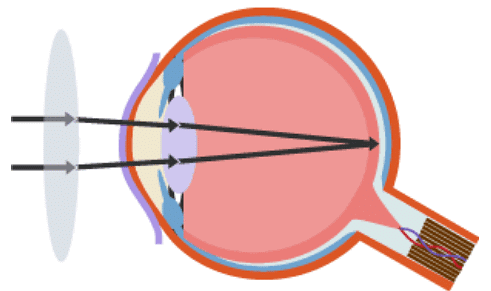
A convex lens corrects long-sightedness, allowing an image to focus on the retina
New technologies have provided alternatives to wearing spectacle lenses: the hard and soft contact lenses, laser surgery to change the shape of the cornea and a replacement lens in the eye. Contact lenses – work by being in 'contact' with your eye. They float on the surface of the cornea. They work like spectacle lenses, by focusing and refracting the light.
- Laser surgery – reshapes the cornea surgically. Common for myopia but can be used for some hyperopia conditions.
- Replacement lens – implanting artificial lenses is a recent development, and can placed in front of the original lens, through a small cut in the cornea, to correct an eye defect.
|
102 videos|100 docs|15 tests
|














