Science and Technology: January 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Virovore

Why in News?
- Researchers have found the first known "Virovore," or organism that eats viruses.
- The new findings may change our understanding of the role viruses play in the food chain at a microscopic level.
What is Virovore?
- It has been identified as an actual species of protist that feasts on viruses.
- These virus-eating species of protists — which are their own kingdom on the tree of life and are not an animal, plant, or fungi — are now classified as Virovores.
- It is a species of Halteria - microscopic ciliates that populate freshwater worldwide.
- The microbe Halteria is a common genus of protist known to flit about as its hair-like cilia propel it through the water.
- They're made up of nucleic acids, nitrogen, and phosphorus. It can eat huge numbers of infectious chloroviruses that share their aquatic habitat.
- Chloroviruses are known to infect microscopic green algae.
- These organisms can sustain themselves with viruses, consuming many and growing in size.
- A virus-only diet, termed "virovory," is enough to fuel the physiological growth and even population growth of an organism.
Hybrid Immunity
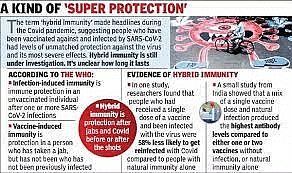
Why In News
- A recent study in the journal the Lancet Infectious Diseases held that “hybrid immunity” provides better protection against severe Covid-19.
What is Immunity?
- Immunity refers to the body’s ability to prevent the invasion of pathogens. Pathogens are foreign disease-causing substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
Types of Immunity
There are broadly two types of immunity: active and passive.
- Active Immunity: It develops from the exposure to a disease thereby triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
- Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity.
- Infection-induced immunity is defined as the immune protection in an unvaccinated individual after one or more infections.
- Vaccine-induced immunity is acquired through the introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination. For Example COVID-19 vaccine.
- Passive immunity: It is provided when a person is given antibodies to a disease rather than producing them through his or her own immune system. For example, A newborn baby acquired passive immunity from its mother through the placenta.
Hybrid Immunity
- Hybrid immunity is defined as the immune protection in individuals who have had one or more doses of a COVID-19 vaccine and experienced at least one SARS-CoV-2 infection before or after the initiation of vaccination
Antimicrobial Resistant Gonorrhea
Why in News?
Recently, a strand of antimicrobial-resistant gonorrhoea outbreak has hit Kenya.
More about the news
About:
- The outbreak of Neisseria gonorrhoeae is not just a threat to the citizens of the East African anchor state but the region as a whole, according to experts.
- The outbreak is a major concern among health practitioners, especially happening at a time WHO endeavours to end STIs as a public health concern by 2030.
More about Gonorrhoea
- About:
- Gonorrhoea is the second-most common disease to be sexually transmitted across the world after chlamydia, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The medics said the drug-resistant super gonorrhoea was first detected in samples taken from sex workers in the capital city, Nairobi, and other urban areas like Kiambu County.
- Drug resistance:
- Some of the drugs that got 100 per cent resistance included ciprofloxacin and ceftriaxone, which are in the current STI treatment algorithm in Kenya.
- The United Nations health agency blamed the drug resistance of some strands of gonorrhoea on the overuse of antibiotics, genetic mutations of the bacteria and repeated use of poor-quality drugs, in its regular reports.
- Other diseases with the concern of antimicrobial resistance:
- Other diseases that medics have expressed concern over due to total antimicrobial resistance include various strains of SARS-CoV-2, ebola virus disease, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, Lassa fever and marburg virus disease.
- The same has been reported regarding some strains of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Rift Valley fever, severe acute respiratory syndrome, Nipah and henipaviral diseases.
More about the Antimicrobial resistance
- About:
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness and death.
- Difference between Antibiotic & Antimicrobial resistance:
- Antibiotic resistance refers specifically to resistance to bacteria. Antimicrobial resistance refers to resistance to bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites.
- Issue:
- A study in 2019 found more than 1 million people a year died from infections linked to microbes that are resistant to antibiotics — more than those who died due to malaria or with HIV/AIDS.
- Experts describe antibiotic resistance as one of the greatest challenges facing humanity.
- They predict that if the problem remains unsolved, 10 million people could die as a result by 2050.
- Causes:
- Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria evolve to evade antibiotics. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics are the biggest drivers of resistance.
- That means that the more we use antibiotics, the worse the problem of antibiotic resistance becomes.
- Other drivers of antimicrobial resistance include the lack of access to clean water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) for both humans and animals, poor infection and disease prevention and control in healthcare facilities and farms, poor access to quality, affordable medicines, vaccines and diagnostics, lack of awareness and knowledge.
How does it work?
- Antibiotics work by binding to a specific target protein on a bacteria, then entering to kill it from the inside.
- Penicillin, for example, weakens the bacterial cell wall, causing the cell to disintegrate.
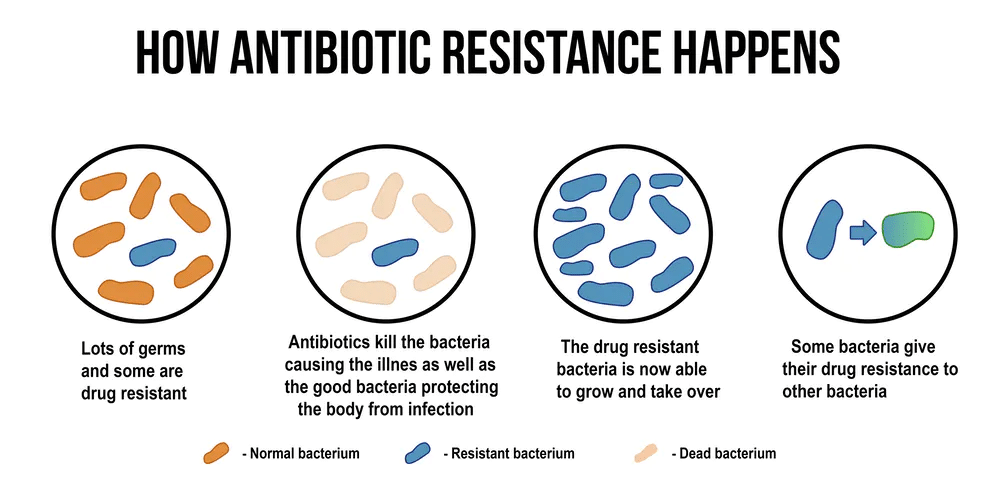
- The most common ways bacteria evade antibiotics come from mutations that allow them to stop drugs from binding to bacteria.
- It’s like the bacteria changed the locks so the antibiotic key no longer opens the cell door.
- Bacteria can also achieve resistance by producing proteins that inactivate or modify the antibiotic, so it no longer binds to the bacteria. Or the target protein is mutated so the antibiotic can no longer bind to it.
- But worst of all is when bacteria evolve many of these mechanisms in backup, so even if you overcome one, other resistances might fill the gap.
Suggestions
- Unfortunately, it isn’t as simple as developing a drug that will permanently overcome antibiotic resistance.
- Antibiotic resistance will always be with us. It’s the nature of evolution by natural selection that means bacteria will always find ways to evade antibiotics.
- Modifying existing antibiotics:
- Scientists have been working on the issue from many different angles. One approach is to modify old antibiotics so they overcome resistance.
- Developing new antibiotics:
- Another strategy is to make brand-new drugs, but this approach hasn’t been very successful in recent decades.
- But there are some signs of progress. For one, scientists are now armed with much more sophisticated drug discovery technologies, not least artificial intelligence (AI).
- But central to the issue is that antibiotic resistance develops quickly whereas antimicrobials — the basis of antibiotic drugs — are developed slowly.
- Global efforts:
- Overcoming antibiotic resistance will require tremendous international effort dedicated to the problem.
WHO Report on Global Trans Fat Elimination
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A new report from the World Health Organization (WHO) has found that 5 billion people globally remain unprotected from harmful trans fats, increasing their risk of heart disease and death.
- WHO first called for the global elimination of industrially produced trans fats in 2018, with an elimination target set for 2023.
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- According to WHO, the consumption of trans fats, which can be found in packaged foods, baked goods, cooking oils and spreads, is responsible for up to half a million premature deaths from heart disease every year.
- 43 countries have now implemented best-practice policies for tackling trans-fat in food, with 2.8 billion people protected globally. Many countries in America and Europe have phased the substance out with bans on partially hydrogenated oils.
- However, no low-income countries have yet adopted such measures.
- Currently, 9 of the 16 countries with the highest estimated proportion of coronary heart disease deaths caused by trans-fat intake do not have a best-practice policy.
- They are Australia, Azerbaijan, Bhutan, Ecuador, Egypt, Iran (Islamic Republic of), Nepal, Pakistan and Republic of Korea.
- Best-practices in trans-fat elimination policies follow specific criteria established by WHO and limit industrially produced trans-fat in all settings. There are two best-practice policy alternatives:
- mandatory national limit of 2 grams of industrially produced trans-fat per 100 grams of total fat in all foods;
- mandatory national ban on the production or use of partially hydrogenated oils as an ingredient in all foods.
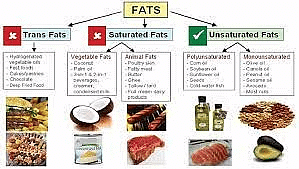
What are Trans Fats?
- About:
- Trans fat, or trans-fatty acids, are unsaturated fatty acids that come from either natural or industrial sources.
- Naturally-occurring trans-fat come from ruminants (cows and sheep).
- Industrially-produced trans-fat is formed in an industrial process that adds hydrogen to vegetable oil converting the liquid into a solid, resulting in “partially hydrogenated” oil (PHO).
- Impacts:
- Trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as they can raise bad cholesterol (LDL) levels in the blood and lower good cholesterol (HDL) levels.
- They can also contribute to the development of other health conditions such as diabetes and obesity.
- Challenges in Eliminating Trans Fat:
- Trans fats are a cheap and easy way to stabilise and extend the shelf life of food products, which is why they are widely used by food manufacturers.
- Many small and medium-sized food manufacturers may not have the resources or technical expertise to reformulate their products to remove trans fats.
- Trans fats are often used in food service and restaurant settings, which can be harder to regulate than retail food products.
- Changing consumer habits and taste preferences can be difficult, as people have become accustomed to the taste and texture of foods that contain trans fats.
- Some countries or regions may have limited infrastructure and resources to monitor and enforce the ban of trans fats.
Initiatives to Eliminate Trans Fat
- India:
- Eat Right Movement: Launched in 2018, the programme is built on two broad pillars of ‘Eat Healthy’ and ‘Eat Safe’.
- Swachh Bharat Yatra: A Pan-India cyclothon, was launched under the movement to educate citizens on issues of food safety, combating food adulteration and healthy diets.
- Heart Attack Rewind: It is a 30-second public service announcement which was broadcasted in 17 languages on social media platforms.
- The objective of the campaign was to warn citizens about the health hazards of consuming trans fats and offer strategies to avoid them through healthier alternatives.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has stated that all food items should contain less than 2% of trans fat from Jan 2022.
- Global:
- WHO released REPLACE, a step-by-step guide for the elimination of industrially-produced trans-fatty acids from the global food supply.
- REPLACE provides six strategic actions to ensure the prompt, complete, and sustained elimination of industrially-produced trans fats from the food supply:
- REview dietary sources of industrially-produced trans fats and the landscape for required policy change.
- Promote the replacement of industrially-produced trans fats with healthier fats and oils.
- Legislate or enact regulatory actions to eliminate industrially-produced trans fats.
- Assess and monitor trans fats content in the food supply and changes in trans-fat consumption in the population.
- Create awareness of the negative health impact of trans fats among policymakers, producers, suppliers, and the public.
- Enforce compliance of policies and regulations.
Way Forward
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness among the public and food industry about the dangers of trans fats and the importance of reducing their consumption can help encourage change.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Governments can establish monitoring and enforcement systems to ensure that food manufacturers are in compliance with regulations and labelling requirements.
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development of new technologies and ingredients that can replace trans fats in food products.
The Future of Metaverse and AI
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The year 2022 was not the best for tech firms, yet we may innovative technologies emerge in future related to Metaverse and AI (Artificial Intelligence), which may raise concerns and present Opportunities.
- The year 2022 saw a lot of the shift in demand during and post the Covid-induced lockdowns.
- The year 2022 ended with near mayhem across most Silicon Valley companies, especially those in the Internet business.
What will be the Future Challenges and Opportunities of Meta-AI?
- More Pervasive AI:
- ChatGPT has shown the world that conversational artificial intelligence is an idea whose time has come.
- The ChatGPT can answer “follow-up questions”, and can also “admit its mistakes, challenge incorrect premises, and reject inappropriate requests.” but most such AI elements are now in standalone products, which is more play than work.
- In 2023, this intelligence will be seen coming into more products that we use every day —for instance Gmail that will not just auto-suggest but also write next mail to the boss.
- Beyond Social Media:
- Twitter and Facebook are struggling to remain relevant amid an increasingly younger and digital native audience. Their concepts of social engagement are very different, often sans text and notice-board behaviors.
- Meta, for instance, knows that it will have to think beyond its present social media platforms and wants to be the social link when users move to the Metaverse, if at all.
- But that might not be something that will shift soon. Till then, there seems to be a vacuum emerging in the social media space, for now plugged by users sticking to short videos. But that fad too shall pass and not all platforms are good in that segment.
- More Regional, Darker Social Bubbles:
- As the Internet spreads to new users, especially in countries like India, it is also becoming more localized and multilingual.
- Across the world, the English language internet seems to have plateaued, making platforms like Google focus more on opportunities to serve smaller, regional languages.
- This is a tech challenge in more ways than one, but also presents an opportunity to test out new technologies that can convert the content of the internet for these new users without much human intervention.
- Future of Metaverse:
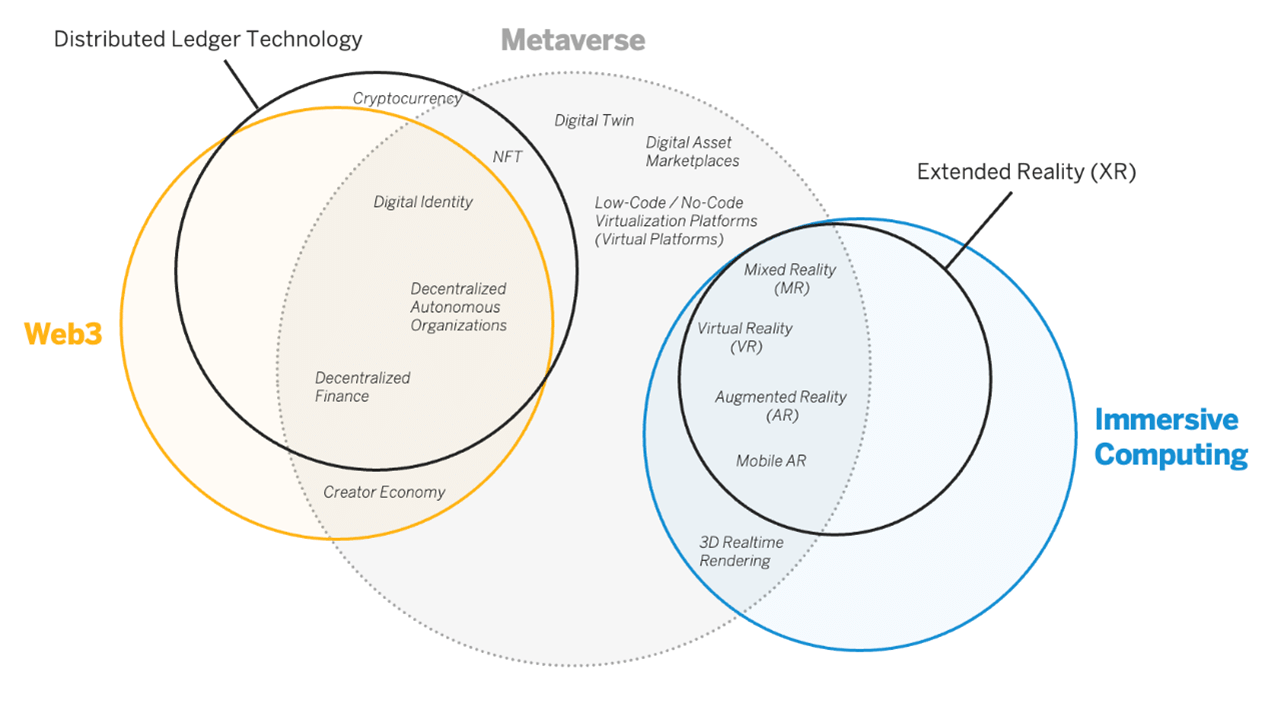
- As hybrid workforces become the norm and with travel still not as easy as earlier, extended reality (XR) could become the answer to collaborate and communicate virtually.
- XR is an emerging umbrella term for all the immersive technologies, including augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) plus those that are still to be created.
- All immersive technologies extend the reality we experience by either blending the virtual and “real” worlds or by creating a fully immersive experience.
- Since the headsets and other paraphernalia to facilitate these virtual interactions are still very expensive, it might be up to companies to make these available to their employees for regular XR meetings. The first experience of this could end up looking like an upgraded version of video conferencing, but with the ability to interact with objects in the virtual space.
- A few more commercial versions of the Metaverse is expected to be accessible to regular users during the year. However, the challenge will be with the hardware that lets people access these virtual worlds without making people bankrupt in the real world. The big disruptor could be an affordable device that logs users into the Metaverse easily — maybe it will just be a smartphone.
What are the Ethical Concerns related to AI?
- The legal and ethical issues that confront society due to AI include privacy and surveillance, bias or discrimination, and potentially the philosophical challenge is the role of human judgment. Concerns about newer digital technologies becoming a new source of inaccuracy and data breaches have arisen as a result of its use.
- The other side of this technological revolution is a growing apprehension on the socio-political and economic implications of AI, specifically, the concerns about co-existence of these emerging technologies and core principles of modern democracies.
- Consequently, AI ethics and the safe and responsible application of AI are becoming front and centre of the technology revolution.
- Constitutional morality was envisioned as the cornerstone for AI ethics’ principles in India, thus, propelling our constitutional rights and ethos to the paramount consideration for deploying AI in a responsible manner.
What are the Principles of a Responsible AI?
- Safety and Reliability: AI systems must ensure reliability regarding their intended functions and must have built-in safeguards to ensure the safety of stakeholders.
- Equality: AI systems must be built keeping in mind that similar people in similar circumstances are treated equally.
- Inclusivity and Non-Discrimination: AI systems must be developed to be inclusive of all stakeholders, and must not discriminate through bias between stakeholders on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth or residence in matters of education, employment, access to public spaces etc.
- Privacy and Security: AI systems must ensure that the personal data of data subjects must be safe and secure, such that only authorised persons must access personal data for specified and necessary purposes, within a framework of sufficient safeguards to ensure this process.
- Principle of Transparency: The design and training of AI systems is key for its functioning. The system must be audited and be capable of external scrutiny to ensure that the deployment of the AI system is impartial, accountable and free from bias or inaccuracies.
- Principle of Accountability: Since there are various actors in the process of developing, deploying and operationalizing an AI system, the accountability structures for any effects, harms or damages by the AI system must be clearly set out in a publicly accessible and understandable manner.
- Protection and Reinforcement of Positive Human Values: This principle focuses on the possible deleterious effects of AI systems through collection of personal data for profiling, the use of AI systems in manners contrary to fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution of India.
Hyderabad: Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has chosen Hyderabad, Telangana for establishing its Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR).
- The C4IR Telangana will be an autonomous, non-profit organisation with a thematic focus on healthcare and life sciences.
What is the Fourth Industrial Revolution?
- About:
- It is characterised by the use of technology to blur the boundaries between the digital, physical, and biological worlds, and is driven by data.
- Key technologies include cloud computing, big data, autonomous robots, cybersecurity, simulation, additive manufacturing, and the internet of things (IoT).
- The term 4IR was coined by Klaus Schwab, executive chairperson of the WEF, in 2016.
- Major Examples of its Application:
- Pacemaker: The pacemaker is a near-perfect example of the ongoing fourth industrial revolution (4IR).
- The four wireless sensors of the pacemaker monitor vitals such as temperature, oxygen levels and the heart’s electrical activity.
- The device then analyses the vitals and decides when to pace the heart and at what rate. Doctors can wirelessly access the information on a tablet or smartphone.
- Xenobots: Xenobots, which are less than a millimetre long, are known to be the first living robot, were created in 2020 from the stem cells of the African clawed frog and can be programmed using artificial intelligence.
- It has a reproductive ability demonstrated in October 2021 by a team of US scientists.
- When the researchers put the xenobots into a petri dish, they were able to gather hundreds of tiny stem cells inside their mouths and create new xenobots a few days later.
- Once perfected, xenobots could be useful for tasks like cleaning up microplastics and regrowing or replacing dead cells and tissues inside human bodies.
- Smart Railway Coaches: In November 2020, the Modern Coach Factory (MCF) at Raebareli, Uttar Pradesh, rolled out smart railway coaches that are fitted with a battery of sensors to provide a comfortable experience to passengers.
- The sensors monitor odour levels in toilets, check if the doors are safely closed, avoid fire outbreaks and stop unauthorised travel using CCTV cameras with face recognition capabilities, among other technologies.
- Challenges Associated with 4IR:
- Job Displacement: As automation and artificial intelligence become more prevalent, there is a concern that many jobs will be replaced by machines, leading to widespread job loss and unemployment.
- Privacy Concern: The increasing connectivity of devices and systems in Industry 4.0 increases the risk of cyber-attacks, which can have significant consequences for both businesses and individuals.
- Ethical Concerns: As artificial intelligence and automation become more advanced, there are also concerns about ethical issues such as accountability, bias, and transparency.
- Lack of Digital Infrastructure: Not all countries have the digital infrastructures for Industry 4.0, leading to digital divide and uneven economic growth.
What are the Other Industrial Revolutions?
- First Industrial Revolution (1800s): It used water and steam power to mechanise production. Example: Steam engine.
- Second Industrial Revolution (early 1900s): It used electric power to create mass production. Example: Electricity.
- Third Industrial Revolution (late 1900s): It used electronics and information technology to automate production. Example: Computer and Internet.
BharOS Software
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, an IIT Madras-incubated company has developed the BharOS.
What is BharOS?
- About:
- It is an indigenous mobile operating system (OS), like Android or iOS. It is focused on privacy and security.
- A mobile operating system is a software that is the core interface on a smartphone like Android by Google and iOS by Apple, which help smartphone users interact with their device and access its features, while ensuring safety.
- BharOS is a contribution towards the idea of a self-reliant India or ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ by creating a secure OS environment for India-based users.
- BharOS Services are currently being provided to organisations that have stringent privacy and security requirements and whose users handle sensitive information that requires confidential communications on restricted apps on mobiles.
- Such users require access to private cloud services through private 5G networks.
Features
- Native Over the Air:
- BharOS would offer Native Over the Air (NOTA) updates, meaning that security updates and bug fixes will be automatically installed rather than users having to check for updates and implementing them on their own.
- No Default Apps:
- No Default Apps (NDA) setting, means that users do not have to keep or use pre-installed apps in this mobile operating system.
- NDA is key as many pre-installed apps that currently ship with other smartphones can slow down the device or take a toll on battery life by acting as bloatware.
- Going with an NDA design for BharOS was intentional as it will let users have more control over the apps on their mobile phones based on the user’s trust in the app and the kind of data they store on their phone.
- Private App Store Services:
- It will use a system known as Private App Store Services (PASS), which will examine and curate the apps that are safe for the users.
- Users will be able to use other apps, as long as they meet BharOS’ PASS standards.
- Significance:
- The project aims to reduce the dependence on foreign OS in smartphones and promote the use of locally developed technology.
- It is a huge leap forward to create an indigenous ecosystem and a self-reliant future.
- It aspires to put India on par with those few countries that currently possess such capabilities.
How BharOS is Different from Google Android?
- BharOS is based on Android Open-Source Project (AOSP) and is somewhat similar to Google Android. However, it does not come preloaded with Google services like in regular Google Android phones. So BharOS users are free to download only those apps that they like or prefer rather than being forced.
- Android phone with stock OS usually have Chrome set up as default browser. BharOS makers are looking to partner with DuckDuck Go for its default browser.
- DuckDuck Go is a privacy-focused browser with several privacy-centric features like anonymous browsing mode and Privacy Grade.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Science and Technology: January 2023 UPSC Current Affairs - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is Virovore? |  |
| 2. What is Hybrid Immunity? |  |
| 3. What is Antimicrobial Resistant Gonorrhea? |  |
| 4. What is the WHO Report on Global Trans Fat Elimination? |  |
| 5. What is the Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in Hyderabad? |  |





















