Data Handling in Python | Computer Science for Grade 11 PDF Download
Operators
An operator is used to perform specific mathematical or logical operation on values.
Operand
- The values that the operator works on are called operands.
For example,
>>> 10 + num,
- 10 & num are operands and
- the + (plus) sign is an operator.
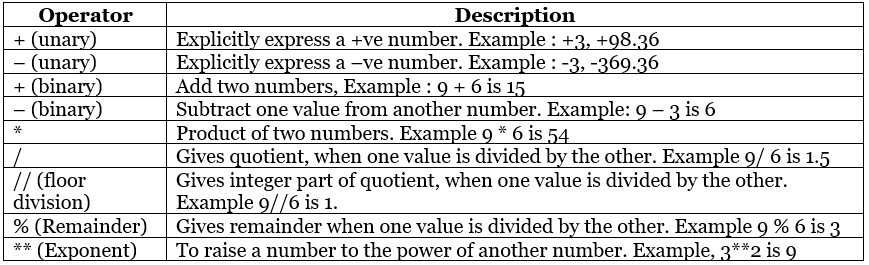
Arithmetic Operator
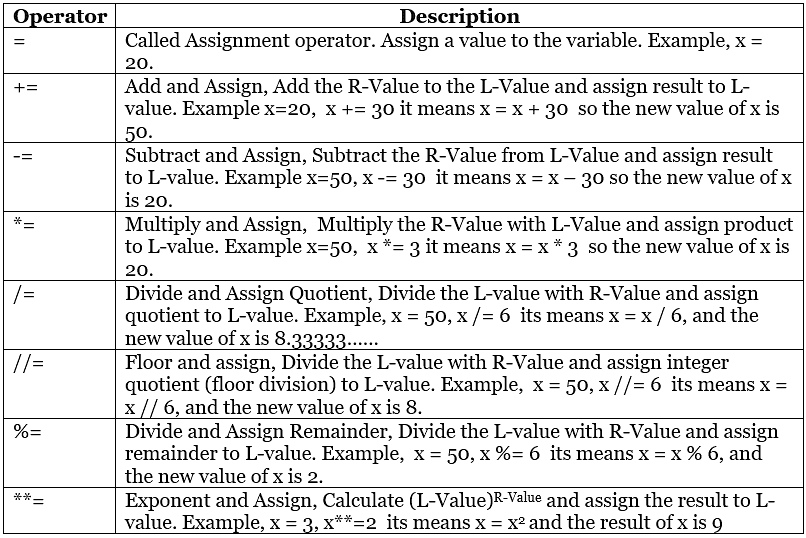
Assignment Operator
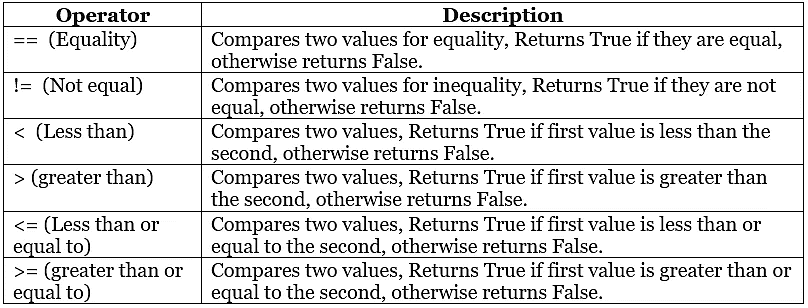
Relational Operator
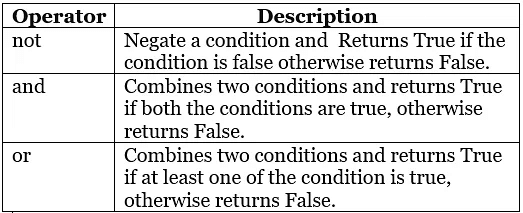
Logical Operator
 Bitwise Operator
Bitwise Operator

Note: bin( ) returns binary representation number.
Membership Operator

Identity Operator

Operator Precedence :
Execution of operator depends on the precedence of operator.
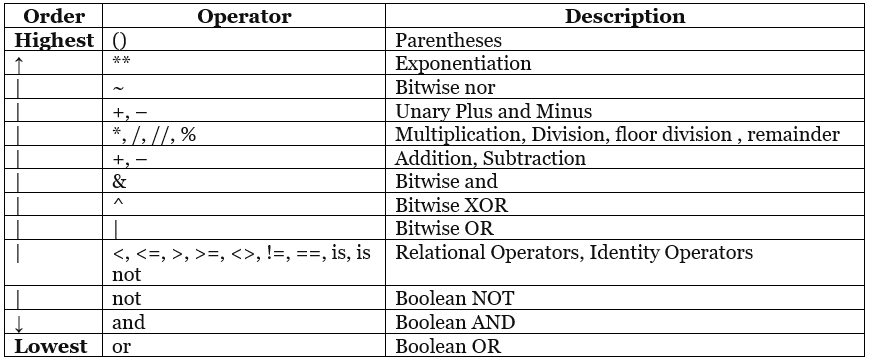
Expression
In Python, An expression is a valid combination of operators, literals and variables.
There are three types of Expression in Python, These are-
- Arithmetic Expressions :- combination of integers, floating-point numbers, complex number, and arithmetic operators. Example ; 2+9, 9.2/3
- Relational Expression :- combination of literals and/or variables of any valid type and relational operators . Example; x > y, 5 < 8, z == y
- Logical Expression:- combination of literals, variables and logical operators. Example; t and q, p or g
- String Expression :- combination of string literals and string operators ( + -> concatenate, and * -> replicate). Example;
“Hello” + “Anjeev” = “Hello Anjeev”
“Like” * 3 = “LikeLikeLike”
Types Casting / Explicit Type Conversion
The conversion of one type to specific type explicitly, called Type Casting / Explicit Type Conversion.
With explicit type conversion, there is a risk of loss of information since we are forcing an expression to be of a specific type.
Syntax: <type>( )
Example x = int ( “123”)
y = float(“5369.36”)
z = str(598698.36)
Functions in Python that are used for explicitly converting an expression or a variable to a different types are –
- int(x) – Converts x to an integer
- float(x) – Converts x to a floating-point number
- str(x) – Converts x to a string representation
- chr(x) – Converts x to a character
- unichr(x) – Converts x to a Unicode character
Program : Explicit type conversion from int to float
num1 = 10
num2 = 20
num3 = num1 + num2
print(num3)
print(type(num3))
num4 = float(num1 + num2)
print(num4)
print(type(num4))
Output:
30
<class 'int'>
30.0
<class 'float'>
Program : Explicit type conversion from float to int
num1 = 10.2
num2 = 20.6
num3 = (num1 + num2)
print(num3)
print(type(num3))
num4 = int(num1 + num2)
print(num4)
print(type(num4))
Output:
<class 'float'>
30.8
<class 'int'>
30
Implicit Conversion
Implicit conversion, also known as coercion, happens when data type conversion is done automatically by Python and is not instructed by the programmer.
Program to show implicit conversion from int to float.
num1 = 10 # num1 is an integer
num2 = 20.0 # num2 is a float
sum1 = num1 + num2
# sum1 is sum of a float and an integer
print(sum1)
print(type(sum1))
Output:
30.0
<class 'float'>
Q. Why was the float value not converted to an integer instead?
This is due to type promotion that allows performing operations (whenever possible) by converting data into a wider-sized data type without any loss of information.
Debugging (Process of Identifying and Removing Errors)
- Bug / Errors – The mistake (error) and problem found in the program is called Bug.
- Debug – Removing the bug / error from the program is called Debug.
- Debugging – The process of Identifying and removing errors from the program is called debugging.
Types of Errors
Errors occurring in programs can be categorised as:
- Syntax errors
- Logical errors
- Runtime errors
1. Syntax Errors:
- Python has its own rules that determine its syntax. The interpreter interprets the statements only if it is syntactically (as per the rules of Python) correct. If any syntax error is present, the interpreter shows error message(s) and stops the execution.
For Example : 10 = X
2. Logical Errors
- A logical error is a bug in the program that causes it to behave incorrectly. A logical error produces an undesired output but without abrupt termination of the execution of the program.
For Example : Instead of +, you writing – operator.
Total = X – Y
3. Runtime Error
- A runtime error causes abnormal termination of program while it is executing. Runtime error is when the statement is correct syntactically, but the interpreter cannot execute it. Runtime errors do not appear until after the program starts running or executing.
x = int(input(“enter number”))
You entered here 25.69. It is a run time error.
Divide by a zero is also called runtime error.
|
84 videos|19 docs|5 tests
|
















