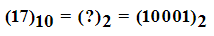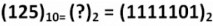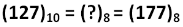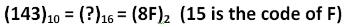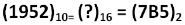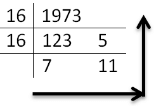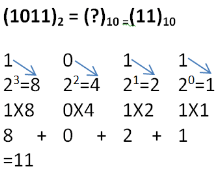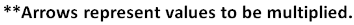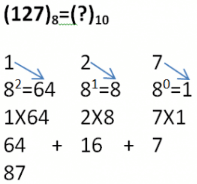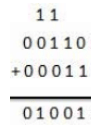Number System | Computer Science for Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction
Number system is the way to represent everything in the form of digits. There are four types of number system.
Binary Number System
Binary number system can contain two digits 0 and 1. So base of binary number system is 2. Binary numbers are represented with 2 as subscript to the value.
Examples of binary numbers are:
- (1101)2
- (1110.011)2
Decimal Number System
Decimal number system can contain digits from 0 to 9. So base of decimal number system is 10. Decimal numbers are represented with 10 as subscript to the value.
Examples of decimal numbers are:
- (1234)10
- (55.34)10
Octal Number System
Octal number system can contain digits from 0 to 7. So base of octal number system is 8. Octal numbers are represented with 8 as subscript to the value.
Examples of octal numbers are:
- (561)8
- (17.54)8
Hexadecimal Number System
Hexadecimal number system can contain digits from 0 to 9 and alphabets from A to F where
A=10
B=11
C=12
D=13
E=14
F=15
So base of hexadecimal number system is 16. Hexadecimal numbers are represented with 16 as subscript to the value.
Examples of hexadecimal numbers are:
- (A74)16
- (91.B3)16
Number System Conversions
Decimal to Binary Conversion
To obtain binary equivalent of a decimal number, decimal number should be repeatedly divided by 2 writing remainder obtained at every step.
This should continue until last quotient is 1. The remainders should be written bottom to upwards to get binary equivalent of decimal number.
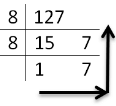
Decimal to octal Conversion
To obtain octal equivalent of a decimal number, decimal number should be repeatedly divided by 8 writing remainder obtained at every step.
This should continue until last quotient is less than 8. The remainders should be written bottom to upwards to get octal equivalent of decimal number.
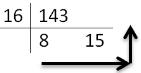
Decimal to hexadecimal Conversion
To obtain hexadecimal equivalent of a decimal number, decimal number should be repeatedly divided by 16 writing remainder obtained at every step.
This should continue until last quotient is less than 16. The remainders should be written bottom to upwards to get hexadecimal equivalent of decimal number.
Binary to Decimal Conversion
To obtain decimal equivalent of a binary number, individual digits of binary number should be multiplied by powers of 2 starting with rightmost digit multiplied by 20, second last digit multiplied by 21, third last digit multiplied by 22 and so on upto the leftmost digit.
- Example:
Octal to Decimal Conversion
To obtain decimal equivalent of an octal number, individual digits of octal number should be multiplied by powers of 8 starting with rightmost digit multiplied by 80, second last digit multiplied by 81, third last digit multiplied by 82, and so on upto the leftmost digit.
Example:
**Arrows represent values to be multiplied.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion
To obtain decimal equivalent of a hexadecimal number, individual digits of hexadecimal number should be multiplied by powers of 16 starting with rightmost digit multiplied by 160, second last digit multiplied by 161, third last digit multiplied by 162 and so on upto the leftmost digit.
In case of alphabets A to F, codes of alphabets should be multiplied by power of 16.
Example:
**Arrows represent values to be multiplied.
Octal to Binary Conversion
To obtain binary equivalent of an octal number, individual digits of octal number should be converted to binary in groups of three digits.
For example, to get binary equivalent of octal number 127 we can take following steps:
Binary equivalent of 7 is 111
Binary equivalent of 2 is 010
Binary equivalent of 1 is 001
So Binary equivalent of (127)8 is:
Hexadecimal to Binary Conversion
To obtain binary equivalent of a hexadecimal number, individual digits of hexadecimal number should be converted to binary in groups of four digits.
For example, to get binary equivalent of hexadecimal number A27 we can take following steps:
Binary equivalent of 7 is 0111
Binary equivalent of 2 is 0010
Binary equivalent of A(10) is 1010
So Binary equivalent of (A27)16 is:
Binary to octal Conversion
To obtain octal equivalent of a binary number, digits of binary number should be divided into groups of three digits starting from the right most digit. Then these groups should be converted into corresponding decimal numbers.
For example, to get octal equivalent of binary number 101011 we can take following steps:
101011 is divided into groups of three digits as:
(101)(011)
Decimal equivalent of 011 is 3
Decimal equivalent of 101 is 5
Octal equivalent of 1010112 is:
Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
To obtain hexadecimal equivalent of a binary number, digits of binary number should be divided into groups of four digits starting from the rightmost digit. Then these groups should be converted into corresponding decimal numbers.
For example, to get octal equivalent of binary number 1011101011 we can take following steps:
1011101011 is divided into groups of four digits as:
(0010)(1110)(1011)
Note: zeros are filled at the beginning of left most group of binary digits if there are lesser number of digits than four.
Decimal equivalent of 1011 is 11 (B)
Decimal equivalent of 1110 is 14 (E)
Decimal equivalent of 0010 is 2
Hexadecimal equivalent of 10111010112 is: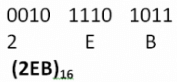
Binary Addition
Binary numbers can be added just like normal numbers but in case of binary numbers sum is always 0 or 1. Rules of adding binary numbers are:
- 0+0=0
- 0+1=1
- 1+0=1
- 1+1=0 with carry 1
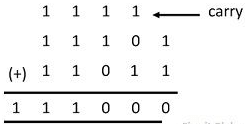
Example 1:
Sum in above example is performed by following steps:
1 + 1 = 10 = 0 with carry 1.
1+0+1 = 10 = 0 with carry 1
1+1+0 = 10 = 10 = 0 with carry 1
1+1+1= 10+1 = 11= 1 with carry 1
1 +1 +1 = 11
Example 2:
|
84 videos|19 docs|5 tests
|