UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 24th December 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Teja chilli
Why in News?
Recently export demand for Teja variety of red chilli has gone up due to its culinary, medicinal and other wide-ranging uses.
About Teja Chillies:
- Chilli was originally cultivated in North Mexico but is believed to be brought to India by the Portuguese.
- It is a fine variety of Guntur chilli.
- It is a fruit that belongs to genus Capsicum.
Health benefits of Teja Chilli:
- Rich in Vitamins and Minerals like Copper, Potassium, Vitamin C, Vitamin B, Vitamin A.
- It is a powerful anti-oxidant.
- Studies suggest that it aids in weight loss.
- Clears congestion.
- Boosts mood and reduces pain.
- It has antibacterial properties that helps in curing skin infection.
- Decreases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Protects the body against prostate problems.
Source: The Hindu
Adi Ganga Revival Plan
Why in News?
Recently, plans to revive Adi Ganga (the original channel of River Ganga passing through the city of Kolkata) have been announced.
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga has allocated around Rs 650 crore to revive the ancient river and it has been included in a multi-country South Asian River project on combating pollution.
What are the Major Issues and Developments Associated with Adi Ganga?
- Encroachment History:
- The river, which was once the main channel of the Ganga till the 17th century, has been neglected for decades and is now polluted and encroached upon. The choking of Adi Ganga severely impacted the natural drainage of the area.
- However, Adi Ganga continued to thrive till the 1970s. Since then, its water quality gradually deteriorated until it turned into a sewer and got rapidly encroached.
- In 1998, the Calcutta High Court directed the removal of all encroachments on the river within a month.
- However, another report, close to two decades after the first order, showed that the encroachments were still existing.
- Current Status:
- The river is now practically dead and has turned into a sewer with a load of faecal bacteria crossing 17 million in 100 millilitres of river water, according to the state pollution control board data and dissolved oxygen is zero.
- Rejuvenation:
- The West Bengal government has been directed by the National Green Tribunal to complete its rejuvenation “positively by September 30, 2025”.
- The river was selected for the pollution study during an international water conference organised by the non-profit Action Aid in Sylhet, Bangladesh.
- Apart from Adi Ganga, Buriganga in Bangladesh, Puyang in China, Bagmati in Nepal and Klang in Malaysia were also chosen for pollution study during the conference.
What is the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG)?
- About:
- On August 12, 2011, the NMCG was listed as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- The NMCG is implemented by the National Council for Rejuvenation, Protection and Management of River Ganga also known as the National Ganga Council.
- Objective:
- The objective of the NMCG is to reduce pollution and ensure rejuvenation of the Ganga river.
- This can be achieved by promoting intersectoral coordination for comprehensive planning & management and maintaining minimum ecological flow in the river, with the aim of ensuring water quality and environmentally sustainable development.
- Organization Structure:
- The Act envisages five tier structure at national, state and district level to take measures for prevention, control and abatement of environmental pollution in river Ganga as below:
- National Ganga Council under chairmanship of Hon’ble Prime Minister of India.
- Empowered Task Force (ETF) on river Ganga under chairmanship of Hon’ble Union Minister of Jal Shakti (Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation).
- National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG).
- State Ganga Committees
- District Ganga Committees in every specified district abutting river Ganga and its tributaries in the states.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Ganga?
- Namami Gange Programme: It is an Integrated Conservation Mission, approved as a ‘Flagship Programme’ by the Union Government in June 2014 to accomplish the twin objectives of effective abatement of pollution and conservation and rejuvenation of National River Ganga.
- Ganga was declared as the ‘National River’ of India in 2008.
- Ganga Action Plan: It was the first River Action Plan that was taken up by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change in 1985, to improve the water quality by the interception, diversion, and treatment of domestic sewage.
- The National River Conservation Plan is an extension to the Ganga Action Plan. It aims at cleaning the Ganga River under Ganga Action Plan phase-2.
- Bhuvan-Ganga Web App: It ensures involvement of the public in monitoring of pollution entering into the river Ganga.
Source: DTE
GS-II
60% of Voters Linked Aadhaar to Voter ID
Why in News?
According to the Election Commission (EC), over 60% of India's 94.5 crore voters have linked their Aadhaar number to their voter IDs.
What is the Status of Aadhaar Linking in India?
- Tripura has the highest rate of Aadhaar linking, with over 92% of voters in the state providing their Aadhaar details to the EC.
- Lakshadweep and Madhya Pradesh have the second and third highest rates of Aadhaar linking, with over 91% and 86% of voters having provided the number respectively.
- Southern states have lower proportions of Aadhaar registration compared to the national average, with Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka falling shy of 71%, and Tamil Nadu and Kerala standing around 63% and 61%.
- Gujarat has the lowest Aadhaar registration by voters, with only 31.5% of voters linking the document to their voter registration.
- Also, less than 34% of voters in Delhi had their Aadhaar linked.
Why is the Government Pushing to Link Voter ID with Aadhaar?
- Update Database:
- The linking project would help the Election Commission, which conducts regular exercises to maintain an updated and accurate record of the voter base.
- Remove Duplication:
- To weed out duplication of voters, such as migrant workers who may have been registered more than once on the electoral rolls in different constituencies or for persons registered multiple times within the same constituency.
- Pan India Voter ID:
- As per the government, linkage of Aadhaar with voter IDs will assist in ensuring that only one Voter ID is issued per citizen of India.
What are the Issues Related to Linking Aadhaar with Voter ID?
- Unclear Constitutional Status:
- In the Puttaswamy case(Right to Privacy), one of the questions that the Supreme Court explored was whether the mandatory linking of Aadhaar with bank accounts was constitutional or not.
- Different Purpose:
- The preference for Aadhaar for the purposes of determining voters is puzzling as Aadhaar is only proof of residence and not proof of citizenship.
- Therefore, verifying voter identity against this will only help in tackling duplication but will not remove voters who are not citizens of India from the electoral rolls.
Conclusion
Along with pursuing the Aadhaar-Voter ID integration, the government shall also look forward to enacting the Digital Personal Data Protection(DPDP) Bill, 2022. The DPDP regime must also apply to government entities and require them to obtain an individual's explicit consent before sharing their data across various government institutions.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
New policy to help Indian communities displaced by coastal erosion
Why in News?
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) received the final inputs on the draft of India’s first national policy for the mitigation and rehabilitation of the people affected by river and coastal erosion.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs has directed NDMA to draft a policy based on the 15th Finance Commission’s report.
About Disaster and its classification:
- Disaster is an undesirable catastrophe resulting from the forces that are largely beyond human control, strikes quickly with little or no warning, and causes or threatens serious disruption of life and property. For example, earthquake, tsunami, cyclone, flood, etc.
Categories of Natural Disaster:
- Natural Disasters are broadly categorized as − Atmospheric Disasters, Terrestrial Disasters, Aquatic Disasters and Biological Disasters.
- Atmospheric disasters include blizzard, thunderstorm, lightning, tropical cyclone, tornado, drought, hailstorm, frost, heat wave, cold waves, etc.
- Terrestrial disasters include earthquake, volcanic eruption, landslide, avalanches, subsidence, etc.
- Aquatic disasters include flood, tidal waves, storm surge, tsunami, etc.
- Biological disasters include fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases (e.g. bird flu, dengue, etc.).
About NDMA:
- National Disaster Management Authority is an apex body for disaster management in India.
- It is headed by the Prime Minister of India and has a Vice-Chairman, nine members, and a CEO.
- It was established under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 and provides guidelines for disaster management to various agencies.
- It is responsible for preparing and implementing disaster management plans at national, state, and district levels.
Major highlights of the policy:
Allocations:
- 15th Finance Commission’s report allocates Rs 1,500 crore for 2021-26 for mitigation measures to prevent erosion under NDMF.
- Rs 1,000 crore allocated for resettlement of displaced people affected by erosion under NDRF for the same period.
- Both funds require state governments to contribute 25% of costs on a cost-sharing basis, except Northeastern states which only need to contribute 10% of state funds.
- NDMA to coordinate allocations and expenses under NDRF and NDMF for mitigation and rehabilitation.
Implementation and institutional mechanisms:
- District disaster management authorities (DDMAs) to implement measures, aided by other district agencies and a specific panchayat-level committee.
- DDMA to prepare mitigation and rehabilitation plans and submit them to SDMAs for appraisal by NDMA and approval by home ministry’s high-level committee for disbursal of funds.
- DDMAs will be responsible for organizing, monitoring, and evaluating efforts under supervision of state and national counterparts.
- NDMA to consultant and emphasize the need for qualified disaster management professionals in all teams.
Challenges and recommendations
- Policy addresses erosion-linked displacement but not displacement caused by deposition of eroded materials and soil piping.
- Financial allocation under policy not yet clear; funds currently allocated on first-come, first-serve basis for states.
- Population density should be considered during allocation.
- Hazard assessments carried out by central agencies should be made available to SDMAs in GIS formats.
- Policy recommends mapping of fallow areas for rehabilitation with input from affected and vulnerable communities.
Significance of disaster management in India:
- Human lives are at stake: Disaster management can help reduce the loss of life and minimize the impact of disasters which leads to loss of life and property, and long-term health consequences.
- Climate change: Effective disaster management can help in mitigating the effects of climate change which has led to more frequent and severe natural disasters.
- Economic impact: Disaster management can help minimize the economic impact of disasters which have a significant impact on the economy, including loss of property and infrastructure, decreased productivity, and disrupted supply chains.
- Humanitarian assistance: Disaster management can help in coordinating relief efforts and ensuring that assistance reaches those who need it the most.
- Infrastructure: It can help in improving the resilience of infrastructure which are vulnerable to natural disasters such as roads, bridges, and buildings.
Challenges of disaster management:
- Lack of preparedness: Despite frequent disasters, there is still a lack of preparedness at all levels of governance and society leading to delays in response time and inadequate resources to deal with disasters effectively.
- Population density: India is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, which can make evacuations and relief efforts more difficult during disasters.
- Climate change: With the increasing threat of climate change, India is experiencing more frequent and intense disasters, such as floods, droughts, and cyclones putting pressure on the country’s disaster management systems to adapt and respond effectively.
- Funding: Despite the increasing frequency and severity of disasters, funding for disaster management is often inadequate which often limit the resources available for preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
- Lack of coordination: There is often a lack of coordination between different agencies involved in disaster management, such as the government, NGOs, and international organizations leading to duplication of efforts and inefficiencies.
- Poor infrastructure: Many areas in India lack basic infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and communication networks, making it difficult to reach affected areas during disasters.
Way Forward:
Disaster management in India faces various challenges, such as inadequate resources, poor infrastructure, limited awareness and education, weak institutional capacity, inadequate coordination and communication, and inadequate research and innovation.
Therefore, steps such as continuous improvement and innovation in disaster management, based on the best available science, technology, and practices, and involving all stakeholders in a participatory and inclusive manner can go a long way in changing the scenario.
Source: DownToEarth
K- 9 Vajra- T howitzers

Why in News?
The Indian Army recently ordered 100 additional K9 Vajra self-propelled howitzers.
About K- 9 Vajra- T howitzers :
- It is a 155 mm, 52-caliber tracked self-propelled artillery system.
- It is built by Larsen & Toubro with technology transferred from South Korean defence major Hanwha Defense based on its K9 Thunder.
- Features:
- It has all-welded steel armour up to 19mm thick.
- The main weapon is the 155mm / 52 calibre gun.
- It has a burst rate of fire of three rounds per 15 seconds and a maximum rate of fire of six to eight rounds a minute for three minutes.
- Range: 40 km
- The K9 uses a digital fire control system, by which it can fire multiple rounds that can impact a given area at the same time.
Source: The Hindu
Dark galaxy

Why in News?
Recently, Italian researchers have discovered a Dark Galaxy or Invisible Galaxy using Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA).
About Dark Galaxy:
- It is termed invisible because the light emitted couldn’t be seen from the earth.
- The presence of the galaxy has been discovered using the gravitational lensing technique.
Gravitational lensing technique:
- It is an effect of Einstein’s theory of general relativity – simply put, mass bends light.
- The gravitational field of a massive object will extend far into space, and cause light rays passing close to that object to be bent and refocused somewhere else.
- It is discovered as compact.
- It is young and has interstellar dust.
- It is forming new stars at the rate of 1000 times the Milky Way.
Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA):
- It is an international partnership of the European Southern Observatory (ESO), with U.S., Japan, Canada, Taiwan, Korea and Chile.
- It is the world’s largest ground-based facility for observations in the millimeter/submillimetre regime.
- It is a single telescope composed of 66 high precision antennas.
- It is located on the Chajnantor plateau, 5000 meters altitude in northern Chile.
- It allows scientists to unravel longstanding and important astronomical mysteries, in search of our Cosmic Origins.
Source: Livescience
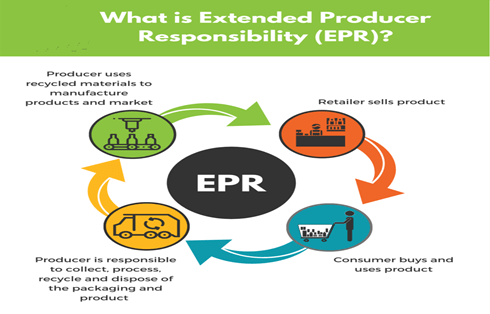
Extended Producer Responsibility
Why in News?
India’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework for used tyres, batteries, and revised rules for e-waste and plastics kindled interest among the G20 countries.
About Extended Producer Responsibility:
- Extended producers’ Responsibilities is a globally recognized policy used as an effective tool to put the onus on the producers for efficient end of life waste management of the plastic, electronic and electrical equipment.
- The concept of EPR responsibility is based on three foundation principles:
- Pollution prevention approach
- Life cycle thinking,
- Polluter pay principle
- EPR responsibility makes it the responsibility of the producers not only to take back products for recycling but also to design better and longer life products to minimize the amount of waste generated.
EPR in India:
EPR responsibility Certificate:
- EPR responsibility Certificate is authorized by Central Pollution Control Board which is mandatory for Producers/Importers of the Electronic products.
- Under these rules, the producers have a responsibility to delegate this responsibility to the third party or specialized organizations which manufacturers can financially aid for proper waste management.
EPR Responsibility Policies under E-Waste Management Rules:
- E-Waste (management and handling) Rules, 2016 adopted Extended Producers Responsibility for the first time in India.
- EPR responsibility under E-Waste (management) Rules, 2016 stipulates collection targets of E–Waste for producers.
- The producers are responsible for setting up collection centres for e-waste and financing and organizing a system for environmentally sound management of e-waste.
- The producers are required to have an arrangement with dismantlers and recyclers through either the Producers responsibility organization or the E-Waste exchange system.
- Marketing or selling any electronic equipment without EPR responsibility Authorization is considered a violation of the rules.
EPR responsibility Policy under Plastic Waste Management Rules:
- The Plastic Waste Management (Amendment) Rules, 2022 provide guidelines for strengthening the circular economy of plastic packaging waste as well as promoting alternatives to plastic.
- Producers of waste are mandated to ensure that generation of plastic waste is minimized, and plastic waste is not littered and stored at the source, which is then handed over to local bodies or authorized agencies.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 24th December 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I in UPSC exams? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered under GS-II in UPSC exams? |  |
| 3. What is the role of GS-III in UPSC exams? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of daily current affairs in UPSC preparation? |  |
| 5. How can I effectively prepare for UPSC exams with daily current affairs? |  |




















