Standard Nornam Distribution | Applied Mathematics for Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
The standardized normal distribution is a type of normal distribution, with a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1. It represents a distribution of standardized scores, called z-scores, as opposed to raw scores (the actual data values). A z-score indicates the number of standard deviation a score falls above or below the mean. Z-scores allow for comparison of scores, occurring in different data sets, with different means and standard deviations. It would not make sense to compare apples and oranges. Likewise, it does not make sense to compare scores from two different samples that have different means and standard deviations. Z-scores can be looked up in a Z-Table of Standard Normal Distribution, in order to find the area under the standard normal curve, between a score and the mean, between two scores, or above or below a score. The standard normal distribution allows us to interpret standardized scores and provides us with one table that we may use, in order to compute areas under the normal curve, for an infinite number of data sets, no matter what the mean or standard deviation.
A z-score is calculated as z = x-μ/σ. The score itself can be found by using algebra and solving for x. Multiplying both sides of the equation by σ gives: (z)(σ) = x − μ. Adding μ to both sides of the equation gives μ + (z)(σ) = x.
Suppose we have a data set with a mean of 5 and standard deviation of 2. We want to determine the number of standard deviations the score of 11 falls above the mean. We can find this answer (or z-score) by writing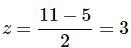
or
5 + (z)(2) = 11,
we can solve for z.
2z = 6
z = 3
We have determined that the score of 11 falls 3 standard deviations above the mean of 5.
With a standard normal distribution, we indicate the distribution by writing Z ~ N(0, 1) which shows the normal distribution has a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1. This notation simply indicates that a standard normal distribution is being used.
Z-Scores
As described previously, if X is a normally distributed random variable and X ~ N(μ, σ), then the z-score is 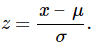
The z-score tells you how many standard deviations the value x is above, to the right of, or below, to the left of, the mean, μ. Values of x that are larger than the mean have positive z-scores, and values of x that are smaller than the mean have negative z-scores. If x equals the mean, then x has a z-score of zero.
When determining the z-score for an x-value, for a normal distribution, with a given mean and standard deviation, the notation above for a normal distribution, will be given.
Example 1: Suppose X ~ N(5, 6). This equation says that X is a normally distributed random variable with mean μ = 5 and standard deviation σ = 6. Suppose x = 17. Then,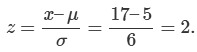
This means that x = 17 is two standard deviations (2σ) above, or to the right, of the mean μ = 5.
Notice that 5 + (2)(6) = 17. The pattern is μ + zσ = x.
Now suppose x = 1. Then, 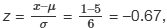 rounded to two decimal places.
rounded to two decimal places.
This means that x = 1 is 0.67 standard deviations (–0.67σ) below or to the left of the mean μ = 5. This z-score shows that x = 1 is less than 1 standard deviation below the mean of 5. Therefore, the score doesn't fall very far below the mean.
Summarizing, when z is positive, x is above or to the right of μ, and when z is negative, x is to the left of or below μ. Or, when z is positive, x is greater than μ, and when z is negative, x is less than μ. The absolute value of z indicates how far the score is from the mean, in either direction.
Example 2: Some doctors believe that a person can lose five pounds, on average, in a month by reducing his or her fat intake and by consistently exercising. Suppose weight loss has a normal distribution. Let X = the amount of weight lost, in pounds, by a person in a month. Use a standard deviation of two pounds. X ~ N(5, 2). Fill in the blanks.
Q.1. Suppose a person lost 10 pounds in a month. The z-score when x = 10 pounds is z = 2.5 (verify).
This z-score tells you that x = 10 is ________ standard deviations to the ________ (right or left) of the mean _____ (What is the mean?).
This z-score tells you that x = 10 is 2.5 standard deviations to the right of the mean five.
Q.2. Suppose a person gained three pounds, a negative weight loss. Then z = __________. This z-score tells you that x = –3 is ________ standard deviations to the __________ (right or left) of the mean.
z = –4. This z-score tells you that x = –3 is four standard deviations to the left of the mean.
Q.3. Suppose the random variables X and Y have the following normal distributions: X ~ N(5, 6) and Y ~ N(2, 1). If x = 17, then z = 2. This was previously shown. If y = 4, what is z?
where µ = 2 and σ = 1.
The z-score for y = 4 is z = 2. This means that four is z = 2 standard deviations to the right of the mean. Therefore, x = 17 and y = 4 are both two of their own standard deviations to the right of their respective means.
The z-score allows us to compare data that are scaled differently. To better understand the concept, suppose X ~ N(5, 6) represents weight gains for one group of people who are trying to gain weight in a six-week period and Y ~ N(2, 1) measures the same weight gain for a second group of people. A negative weight gain would be a weight loss. Since x = 17 and y = 4 are each two standard deviations to the right of their means, they represent the same, standardized weight gain relative to their means.
The Empirical Rule
If X is a random variable and has a normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ, then the Empirical Rule states the following:
- About 68 percent of the x values lie between –1σ and +1σ of the mean µ (within one standard deviation of the mean).
- About 95 percent of the x values lie between –2σ and +2σ of the mean µ (within two standard deviations of the mean).
- About 99.7 percent of the x values lie between –3σ and +3σ of the mean µ (within three standard deviations of the mean). Notice that almost all the x values lie within three standard deviations of the mean.
- The z-scores for +1σ and –1σ are +1 and –1, respectively.
- The z-scores for +2σ and –2σ are +2 and –2, respectively.
- The z-scores for +3σ and –3σ are +3 and –3, respectively.
So, in other words, this is that about 68 percent of the values lie between z-scores of –1 and 1, about 95% of the values lie between z-scores of –2 and 2, and about 99.7 percent of the values lie between z-scores of -3 and 3. These facts can be checked, by looking up the mean to z area in a z-table for each positive z-score and multiplying by 2.
The empirical rule is also known as the 68–95–99.7 rule.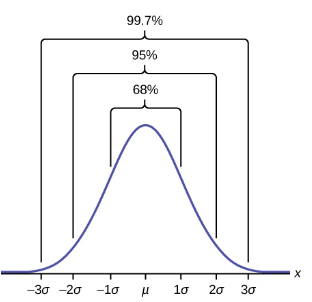
Example 1: The mean height of 15-to 18-year-old males from Chile from 2009 to 2010 was 170 cm with a standard deviation of 6.28 cm. Male heights are known to follow a normal distribution. Let X = the height of a 15-to 18-year-old male from Chile in 2009–2010. Then X ~ N(170, 6.28).
Q.1. Suppose a 15-to 18-year-old male from Chile was 168 cm tall in 2009–2010. The z-score when x = 168 cm is z = _______. This z-score tells you that x = 168 is ________ standard deviations to the ________ (right or left) of the mean _____ (What is the mean?).
The z-score when x = 168 cm is z = -0.32. This z-score tells you that x = 168 is 0.32 standard deviations to the left (right or left) of the mean 170 (What is the mean?).
Q.2. Suppose that the height of a 15-to 18-year-old male from Chile in 2009–2010 has a z-score of z = 1.27. What is the male’s height? The z-score (z = 1.27) tells you that the male’s height is ________ standard deviations to the __________ (right or left) of the mean. What is the male’s height?
The z-score (z = 1.27) tells you that the male’s height is 177.98 cm standard deviations to the 1.27, right (right or left) of the mean.
Example 2: From 1984 to 1985, the mean height of 15-to 18-year-old males from Chile was 172.36 cm, and the standard deviation was 6.34 cm. Let Y = the height of 15-to 18-year-old males from 1984–1985, and y = the height of one male from this group. Then Y ~ N(172.36, 6.34).
The mean height of 15-to 18-year-old males from Chile in 2009–2010 was 170 cm with a standard deviation of 6.28 cm. Male heights are known to follow a normal distribution. Let X = the height of a 15-to 18-year-old male from Chile in 2009–2010, and x = the height of one male from this group. Then X ~ N(170, 6.28).
Q.1. Find the z-scores for x = 160.58 cm and y = 162.85 cm. Interpret each z-score. What can you say about x = 160.58 cm and y = 162.85 cm as they compare to their respective means and standard deviations?
The z-score for x = 160.58 cm is z = –1.5.
The z-score for y = 162.85 cm is z = –1.5.
Both x = 160.58 and y = 162.85 deviate the same number of standard deviations from their respective means and in the same direction.
Example 3: Suppose x has a normal distribution with mean 50 and standard deviation 6.
- About 68 percent of the x values lie within one standard deviation of the mean. Therefore, about 68 percent of the x values lie between –1σ = (–1)(6) = –6 and 1σ = (1)(6) = 6 of the mean 50. The values 50 – 6 = 44 and 50 + 6 = 56 are within one standard deviation from the mean 50. The z-scores are –1 and +1 for 44 and 56, respectively.
- About 95 percent of the x values lie within two standard deviations of the mean. Therefore, about 95 percent of the x values lie between –2σ = (–2)(6) = –12 and 2σ = (2)(6) = 12. The values 50 – 12 = 38 and 50 + 12 = 62 are within two standard deviations from the mean 50. The z-scores are –2 and +2 for 38 and 62, respectively.
- About 99.7 percent of the x values lie within three standard deviations of the mean. Therefore, about 95 percent of the x values lie between –3σ = (–3)(6) = –18 and 3σ = (3)(6) = 18 of the mean 50. The values 50 – 18 = 32 and 50 + 18 = 68 are within three standard deviations from the mean 50. The z-scores are –3 and +3 for 32 and 68, respectively.
Example 4: From 1984–1985, the mean height of 15-to 18-year-old males from Chile was 172.36 cm, and the standard deviation was 6.34 cm. Let Y = the height of 15-to 18-year-old males in 1984–1985. Then Y ~ N(172.36, 6.34).
(i) About 68 percent of the y values lie between what two values? These values are ________________. The z-scores are ________________, respectively.
(ii) About 95 percent of the y values lie between what two values? These values are ________________. The z-scores are ________________ respectively.
(iii) About 99.7 percent of the y values lie between what two values? These values are ________________. The z-scores are ________________, respectively.
(i) About 68 percent of the values lie between 166.02 cm and 178.7 cm. The z-scores are –1 and 1.
(ii) About 95 percent of the values lie between 159.68 cm and 185.04 cm. The z-scores are –2 and 2.
(iii) About 99.7 percent of the values lie between 1153.34 cm and 191.38 cm. The z-scores are –3 and 3.
|
59 videos|101 docs|63 tests
|

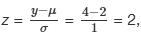 where µ = 2 and σ = 1.
where µ = 2 and σ = 1.



















