UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 1sṭ March 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Yellow River
Why in News?
A recent study has noted that the Chinese practice of building embankments is one of the reasons to blame for the devastating floods occurring in the “Yellow river”.
About Yellow River:
- The Yellow River (Huang He) is the second longest river in China (after the Yangtze).
- It’s the fifth-longest river in the world.
- Source: The Bayankala Mountains on the Plateau of Tibet in western central China.
- Mouth: southern Bohai Sea
- Claims to fame: world’s muddiest major river, “China’s cradle (of civilization)”
- Provinces flowed through: Qinghai, Sichuan, Gansu, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, and Shandong
- Tributaries: Black River, White River, Tao River, Huangshui, Fen River, Luo River, Wei River.
- The name “Yellow River” comes from the huge amounts of “yellow” loess sediment it carries, which are eroded when it flows through the Loess Plateau.
- The Yellow River is not just an iconic river of China, but also the symbol of the Chinese spirit: bearing burdens (its sedimentation), adaptation (its course changes), and perseverance (its continual flow).
- Hukou Waterfall on it is the second-largest waterfall in China.
- Qinghai Lake on it is China’s biggest lake.
Source: DOWN TO EARTH
Musical instruments

Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister spoke of several musical instruments and folk artists in his Mann ki Baat address.
About musical instruments :
Sursingar:
- Sursingar is a stringed instrument made of ivory and wood.
- This traditional instrument is found in various parts of North India.
- The strings of the instrument are usually four in number and made of brass or bronze, and are plucked with a metal pick.
- The Sursingar (along with the Rudra Veena and the Surbahar) usually accompanies Dhrupad, the genre of Hindustani vocal music which has a low, deep, and thoughtful pitch.
- Noted performers: Baba Allauddin Khan, Birendra Kishore Roy Choudhury, Shaukat Ali Khan, and Radhika Mohan Maitra.
Karakattam:
- Karakattam is an ancient folk dance of Tamil Nadu in which performers in colorful saris dance with a pot (karakam) on their heads to invoke Mariamman, the goddess of the rain.
- This dance is categorized into two types: Aatta Karakam symbolizes joy and happiness and is mainly performed as entertainment.
- Sakthi Karakam is performed only in temples as a spiritual offering.
- It involves three tiers of flower arrangements of different colors sitting on top of a container filled to the brim with either water, rice, or soil.
- Other features: blowing fire, inserting needles into eyes, and keeping balance while holding a bottle parallel to the ground on the performer’s back.
- Noted performers: V Durga Devi of Salem.
Mandolin:
- It is a stringed instrument, usually with eight strings that are plucked with a pick.
- It is a moderately sized instrument, smaller than the Veena, Sitar, or guitar, and was developed in Europe in the 18th century as an evolution of the older Mandora (Mandola).
- The instrument’s modern form and proportions were strongly influenced by its maker Pasquale Vinaccia of Naples (1806-82).
- The Mandolin has long been part of the Indian film music tradition, having been used by several great composers.
- Noted Performers: late Uppalapu Srinivas, often known as ‘Mandolin’ Srinivas, Sajjad Hussain, Kishore Desai, Snehashish Mozumder, Pradipto Sengupta, and N S Prasad.
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
GS-II
What is the Anti-defection law?
Why in News?
Supreme Court recently said that legislators facing disqualification under the anti-defection law cannot participate in the floor test.
About Anti-defection law :
- It was introduced in India in 1985 through the 52nd amendment to the Constitution of India.
- This amendment added the Tenth Schedule to the Constitution, which lists out the provisions related to defection.
- It lays down the process by which legislators may be disqualified on grounds of defection by the Presiding Officer of a legislature based on a petition by any other member of the House.
- This schedule applies to both Central and State legislature.
- Aim: The main aim of this schedule was to prevent political defections and to strengthen democracy by bringing stability in politics and make members of parliament more responsible and loyal to their parties.
- Grounds of disqualification: A member of any state or central legislature can be disqualified from being a member if,
- He voluntarily gives up his membership of a political party.
- He disobeys the directions of his political party or votes or does not vote in the legislature contrary to the directions of his political
- After the election, he joins another political party.
- If a nominated member joins any political party after 6 months from the day, he becomes a member of the legislature.
- Exemptions:
- Disqualification of a member is not applied in case of a merger, provided that this merger with or into another party shall be done with the consent of at least two-thirds of its legislator In such a scenario, neither the members who decide to merge nor the ones who stay with the original party will face disqualification.
- It exempts the speaker, chairman, and deputy chairman of various legislative houses from disqualification on the ground of defection.
- Deciding authority:
- The decision to disqualify a member under the anti-defection law is taken by the presiding officer of the house. ( Speaker or Chairman accordingly).
- The law does not specify a time period for the Presiding Officer to decide on a disqualification plea.
- The decisions of the Speaker or Chairman in anti-defection cases are subject to judicial review.
- However, there can not be any judicial intervention until the Presiding Officer gives his order.
Source: The Hindu
What is the Windsor Framework?

Why in News?
The UK Government recently reached a landmark deal with the European Union (Known as Windsor Framework) on post-Brexit trade rules that will govern Northern Ireland.
About Windsor Framework:
- The ‘Windsor Framework’ will replace the Northern Ireland Protocol.
- What is Northern Ireland Protocol?
- Northern Ireland is a British-ruled province and part of the United Kingdom that shares a long porous border with Ireland, a member of the European Union.
- Trade over the open border when Britain left the EU was one of the most difficult parts of the Brexit negotiations which culminated in the Northern Ireland Protocol.
- The protocol is part of the Brexit deal, which sets Northern Ireland's trade rules.
- It keeps Northern Ireland inside the EU's single market for goods.
- It keeps the Irish land border open but means products arriving into Northern Ireland from the rest of the UK are subject to checks and controls.
- The checks made trade between Great Britain and Northern Ireland cumbersome.
- Features of Windsor Framework: The framework has two crucial aspects – the introduction of a two lanes system and the ‘Stormont Brake’.
- The two lanes:
- Goods from Britain destined for Northern Ireland will travel through a new "green lane", with a separate "red lane" for goods at risk of moving onto the EU.
- Products coming into Northern Ireland through the green lane would see checks and paperwork significantly reduced.
- Red lane goods would still be subject to checks.
- Bans on certain products - like chilled sausages - entering Northern Ireland from Great Britain would be removed.
- Northern Ireland would also no longer have to follow certain EU rules, for example, on VAT and alcohol duties. The new agreement reduces the proportion of EU rules applied in Northern Ireland to less than 3%.
- Stormont brake:
- Under this, the democratically elected Northern Ireland Assembly can oppose new EU goods rules that would have significant and lasting effects on everyday lives in Northern Ireland.
- The brake cannot be used for "trivial reasons" but reserved for "significantly different" rules
- Once the UK tells the EU the brake has been triggered, the rule cannot be implemented.
- It can only be applied if the UK and EU agree.
GS-III
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
Why in News?
The FATF suspended Russia’s membership over the Ukraine war recently.
About The Financial Action Task Force (FATF):
- The FATF was established in 1989 and is based in Paris.
- It is the global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog.
- The inter-governmental body sets international standards that aim to prevent these illegal activities and the harm they cause to society.
- Members: 39
- India is one of the members.
- The FATF President is a senior official appointed by the FATF Plenary from among its members.
- The terms of the FATF Presidency- two-years
- Current President: Mr. T.Raja Kumar (Singapore )
- The FATF Plenary is the decision-making body of the FATF and meets three times per year.
FATF has two lists:
- Grey List: Countries that are considered safe havens for supporting terror funding and money laundering are put on this list.
- This inclusion serves as a warning to the country that it may enter the blacklist.
- Black List: Countries known as Non-Cooperative Countries or Territories (NCCTs) are put on the blacklist.
- These countries support terror funding and money laundering activities.
Functions of FATF :
- It works to generate the necessary political will to bring about national legislative and regulatory reforms in these areas.
- It sets international standards to ensure national authorities can effectively go after illicit funds linked to drugs trafficking, the illicit arms trade, cyber fraud, and other serious crimes.
- In total, more than 200 countries and jurisdictions have committed to implementing the FATF’s Standards as part of a coordinated global response to preventing organized crime, corruption, and terrorism.
- It researches how money is laundered and terrorism is funded, promotes global standards to mitigate the risks, and assesses whether countries are taking effective action.
- It continuously monitors how criminals and terrorists raise, use, and move funds.
- It regularly publishes reports that raise awareness about the latest money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing techniques
- The FATF continuously strengthens its global standards to address new risks, such as the regulation of virtual assets, which have spread as cryptocurrencies gain popularity.
- It monitors countries to ensure they implement the FATF Standards fully and effectively.
- It holds countries to account that do not comply with the FATF Standards.
- If a country repeatedly fails to implement FATF Standards then it can be named a Jurisdiction under Increased Monitoring or a High-Risk Jurisdiction.
Source: AIR
India Municipal Bond Index

Why in News?
India’s first-ever municipal bond index has been unveiled by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) recently.
About India Municipal Bond Index:
- It is India’s firstmunicipal bond index.
- It was released by NSE Indices Ltd., an arm of the National Stock Exchange at SEBI in Bengaluru.
- It will track the performance of all municipal bondsissued by Indian municipal corporations.
- It is aimed at tracking the performance of all municipal bondsissued in the country across maturities and investment-grade credit ratings.
- The Index comprises 28 municipal bonds from 10 different issuers, all of which were in the AA credit rating category.
- In the Union Budget session 2023, the government mentioned that it will be granting incentives to urban civic bodies for the improvement of their finances and creditworthiness.
Municipal Bonds:
- It is a security issued by local governments in India or their associated bodies.
- They were first issued in India in 1997.
- It is issued to raise money to finance projects such as bridges, schools, hospitals, and the provision of household amenities that aim to achieve socio-economic development.
- The Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urbanization Transformation (AMRUT) and the Smart Cities Mission are two projects which have been funded by municipal bonds.
Source: THE HINDU
National Science Day and the Raman Effect
Why in News?
In 1986, the Government of India, under then Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi, designated February 28 as National Science Day to commemorate the announcement of the discovery of the “Raman Effect”.
- This year’s edition is being celebrated under the theme of “Global Science for Global Wellbeing”, in light of India’s G20 presidency.
About Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman:
- Raman was born on 7 november 1888 in Tirucirapalli, Madras Presidency to Tamil Parents.
- He joined Indian Financial Service in Calcutta as Assistant Accountant General at the age of 19.
- In 1926, he established the Indian Journal of Physics as the first editor.
- In February 1928, Raman led an experiment with K.S. Krishnan, on the scattering of light, when he discovered what is called Raman Effect.
- He was the president of the 16th session of the Indian Science Congress in 1929.
- He won the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics for his Raman Scattering and for the discovery of Raman Effect.
- He founded the Indian Academy of Sciences in 1934 and started publishing the proceedings of the Academy.
- He retired from IISc Bangalore in 1948 and established the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore in 1949.
- He was against the control of research programmes by the government such as the establishment of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR).
About Raman Effect:
- Raman is the inelastic scattering of a photon by molecules which are excited to higher vibrational or rotational energy levels. It is also called Raman scattering.
- In simpler words, it is a change in the wavelength of light that occurs when a light beam is deflected by molecules.
- When a beam of light traverses a dust-free, transparent sample of a chemical compound, a small fraction of the light emerges in directions other than that of the incident (incoming) beam.
- Most of this scattered light is of unchanged wavelength.
- A small part, however, has wavelengths different from that of the incident light and its presence is a result of the Raman Effect.
- The Raman effect forms the basis for Raman spectroscopy which is used by chemists and physicists to gain information about materials.
- Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation.
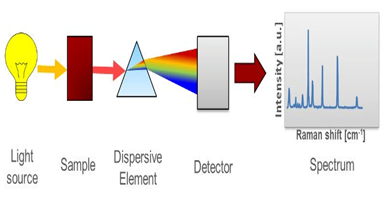
Raman Spectroscopy:
- Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique which provides detailed information about chemical structure, phase and polymorphy, crystallinity and molecular interactions.
- It is based upon the interaction of light with the chemical bonds within a material.
- In this, a molecule scatters incident light from a high intensity laser light source.
- Most of the scattered light is at the same wavelength (or colour) as the laser source and does not provide useful information which is called Rayleigh Scatter.
- However, a small amount of light (typically 0.0000001%) is scattered at different wavelengths (or colours), which depend on the chemical structure of the analyte which is called Raman Scatter.
Significance of the discovery:
- CV Raman’s discovery took the world by storm as it had deep implications far beyond Raman’s original intentions.
- As Raman himself remarked in his 1930 Nobel Prize speech, “The character of the scattered radiations enables us to obtain an insight into the ultimate structure of the scattering substance.”
- For quantum theory, in vogue in the scientific world at the time, Raman’s discovery was crucial.
- The discovery would also find its use in chemistry, giving birth to a new field known as Raman spectroscopy as a basic analytical tool to conduct non-destructive chemical analysis for both organic and inorganic compounds.
- With the invention of lasers and the capabilities to concentrate much stronger beams of light, the uses of Raman spectroscopy have only ballooned over time.
- This method has a wide variety of applications, from studying art and other objects of cultural importance in a non-invasive fashion to finding drugs hidden inside luggage at customs.
Source: Indian Express
QR-Code based Coin Vending Machine (QCVM)
Why in News?
RBI recently announced its plan to launch a pilot project to assess the functioning of QR-code based coin vending machines (QCVM).
About QR-Code based Coin Vending Machine (QCVM):
- QCVM is a cashless coin dispensation machine that would dispense coins with the requisite amount being debited from the customer’s account using United Payments Interface (UPI).
- It will eliminate the need for physical tendering of banknotes and their authentication.
- It will be launched with an aim to promote the distribution of coins and enhance the accessibility to coins.
- Customers will also have the option to withdraw coins in required quantity and denominations in QCVMs.
- The pilot project is planned to be initially rolled out at 19 locations in 12 cities across the country.
- These vending machines are intended to be installed at public places such as railway stations, shopping malls, and marketplaces to enhance ease and accessibility.
Source: The Hindu
|
39 videos|4283 docs|904 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 1sṭ March 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I, GS-II, and GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered under GS-I in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. What does GS-II in the UPSC exam focus on? |  |
| 4. What are the main subjects covered under GS-III in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare effectively for the General Studies papers in the UPSC exam? |  |
|
39 videos|4283 docs|904 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
























