UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 21st March 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| GS-I |

|
| GS-II |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| GS-III |

|
GS-I
Climate Change: Mission Adaptation A Comprehensive Measure
Why in News?
The budget for 2023-24 in India includes some measures towards climate change mitigation, but adaptation has not been given adequate attention. The government needs to adopt a Mission Adaptation to create a supportive ecosystem for all entities to come together and work towards developing locally-sound adaptation solutions.
Climate Change Mitigation Measures
- Allocation for green transition: The budget for 2023-24 in India has allocated funds towards climate change mitigation, with a focus on green growth initiatives targeted at reducing the carbon intensity of the economy such as green mobility, energy efficiency, and the green hydrogen mission announcement.
- Promoting nature based initiatives: Nature-based solutions such as the mangrove plantation initiative and the community-based wetland conservation scheme also promise to have potentially positive impacts in mitigating climate change.
Lack of Attention to Climate Change Adaptation
- Climate change is addressed indirectly: While climate change mitigation has received attention in the budget, climate change adaptation has been addressed only indirectly.
- No measures towards enhancing resilience: The budget does not include measures towards enhancing the resilience of communities and habitations to climate change’s impact, despite India’s high vulnerability to climate change.
- For instance: Measures to account for climate change-induced risks, such as the recent example of Joshimath, do not find explicit mention in the budget.
Funding for Adaptation
- Adaptation has traditionally received far less attention than mitigation in the global climate discourse, resulting in lower funding for adaptation.
- In India, the ratio of funding for climate adaptation to mitigation stands at 1:10. While funding for mitigation is also underfunded, with only 25% of the requirement met, the gap for adaptation stands much higher, at only 7.9% of the needed funds.
Challenges in Funding Adaptation
- Adapting to climate change often requires highly local and nature-based solutions that do not have a classically-measured ROI. Consequently, mainstream, interest-seeking capital flowing into adaptation is scant.
- Climate adaptation has largely remained a publicly-funded endeavor in India, with nearly 100% of the funding for adaptation coming from public sources. International funding has also remained scarce due to the skewed discourse on climate change.
The Need for a Strategic Investment
- Climate shocks are anticipated to get more frequent and severe, and in the absence of resilience-building for communities and habitations, the impact could be devastating.
- The public sector must view resilience building as a strategic priority and actively address this matter.
- Climate adaptation must come to be seen as a strategic investment by the public sector, which it must make in order to climate-proof lives, livelihoods, the environment, and the economy.
Mission Adaptation
- Mission Adaptation is a term used in the context of climate change and refers to the need for a strategic, proactive approach to building adaptive capacity in order to climate-proof lives, livelihoods, the environment and the economy.
- It is a proposed initiative for creating a supportive ecosystem for all entities, including the private sector, non-profits, and civil society, to come together and work towards developing and scaling up locally-sound adaptation solutions in India.
- The idea is to view climate adaptation as a strategic investment by the public sector and to bridge complex challenges faced by society today using the idea of public purpose to guide policy and business activity.
Conclusion
Given the increasing frequency at which climate-related stress is occurring and is expected to occur, the public sector will remain a crucial contributor to funding for climate adaptation. The government must work towards developing a more systemic understanding of resilience and support efforts aimed at building such an understanding across the ecosystem to make Mission Adaptation a reality.
Source: The Hindu
Sangita Kalanidhi award
Why in News?
Recently, Carnatic vocalist Bombay Jayashri has been selected for the Sangita Kalanidhi award of the Music Academy for 2023.
About Sangita Kalanidhi award:
- It is considered the highest award in the field of Carnatic music.
- The award is conferred by the Madras Music Academy.
- The award comprises a gold medal and a birudu patra (citation).
- It is a landmark institution in the history of the fine arts. It emerged as an offshoot of the All India Congress Session held in Madras in December 1927.
What is Carnatic music?
- Carnatic music is commonly associated with southern India including the states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu, but also practised in Sri Lanka.
- It is one of two major genres of Indian classical music that evolved from ancient Hindu traditions, the other being Hindustani music, which emerged as a distinct form in northern India as a result of Persian and Islamic influences.
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
HDI: Addressing India’s Subnational Human Development
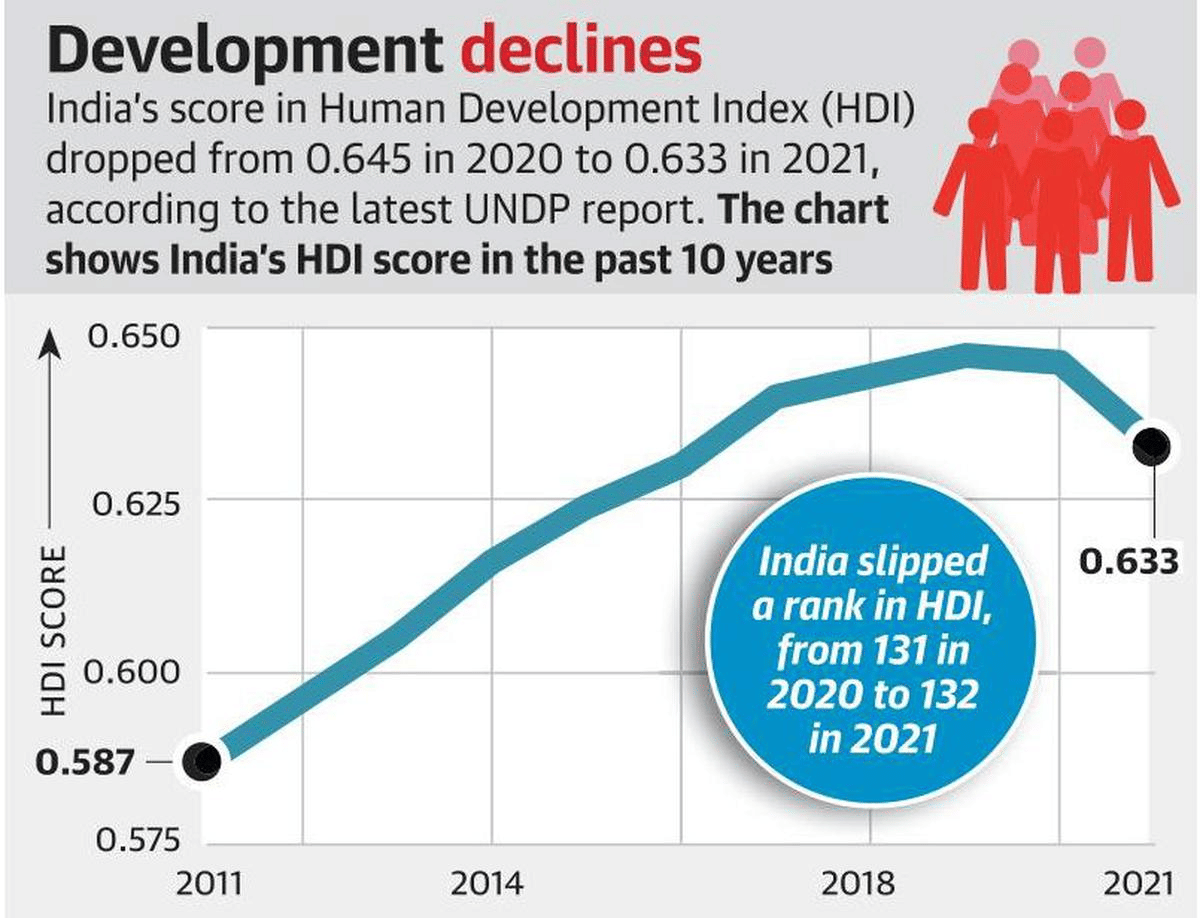
India is now one of the fastest-growing economies globally. However, this growth has not resulted in a corresponding increase in its Human Development Index (HDI). According to the Human Development Report of 2021-22, India ranks 132 out of 191 countries, behind Bangladesh (129) and Sri Lanka (73).
Facts for Prelims: Human Development Index (HDI)
- Composite statistical measure by UNDP: The HDI is a composite statistical measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to evaluate and compare the level of human development in different regions around the world.
- As an alternative with broader aspects: It was introduced in 1990 as an alternative to conventional economic measures such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which do not consider the broader aspects of human development.
- Aspects: The HDI assesses a country’s average accomplishment in three aspects 1. A long and healthy life, 2, knowledge, and 3. A decent standard of living.
- India ranks 132 out of 191 countries in the HDI 2021.
The subnational HDI: A new index
- Given India’s large size and population, it’s critical to address subnational or state-wise disparities in human development.
- A new index has developed by using the methodology suggested by the UNDP and the National Statistical Office (NSO), which measures human development on a subnational level for 2019-20.
HDI Calculation
- The HDI is calculated using four indicators: life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, expected years of schooling, and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
- The subnational HDI uses GSDP per capita as a proxy indicator for GNI since GNI per capita estimates are unavailable at the subnational level.
- The methodology involves calculating the geometric mean of the normalised indices for the three dimensions of human development while applying the maximum and minimum values recommended by the UNDP and NSO.
Subnational HDI Findings
- The subnational HDI shows that while some states have made considerable progress, others continue to struggle. Delhi occupies the top spot and Bihar occupies the bottom spot.
- The five states with the highest HDI scores are Delhi, Goa, Kerala, Sikkim, and Chandigarh. Nineteen states, including Kerala, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Punjab, Telangana, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh, have scores ranging between 0.7 and 0.799 and are classified as high human development states.
- The bottom five states are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Assam, with medium levels of human development.
Reasons for Discrepancies
- The economic growth has been unevenly distributed, with the top 10% of the Indian population holding over 77% of the wealth. This has resulted in significant disparities in access to basic amenities, healthcare, and education.
- While India has made significant progress in reducing poverty and increasing access to healthcare and education, the quality of such services remains a concern.
Conclusion
The government needs to prioritize human development alongside economic growth to ensure that the benefits of growth are more evenly distributed, and it requires a multi-faceted approach to address various issues such as income inequality, gender inequality, access to quality social services, environmental challenges, and social infrastructure investment. India must prioritize investments in human development and job creation, particularly for its youth, to realize its demographic dividend.
Source: Indian Express
Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961)
Why in News?
The Indian government lodged a strong protest against the UK government and reminded obligations of the host nation under the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations amid the vandalism incident that occurred at the Indian High Commission in London.
What is the Vienna Convention?
- The treaty being referred to by the MEA in this instance is the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961).
- It provides a complete framework for the establishment, maintenance and termination of diplomatic relations on a basis of consent between independent sovereign States.
FYI: Vienna Convention
Vienna, the capital city of Austria, has a long history of hosting international conventions and conferences.
There are several conventions that are named as “Vienna Convention”. Here is a list of some of the most well-known Vienna Conventions:
- Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961)
- Vienna Convention on Consular Relations (1963)
- Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (1969)
- Vienna Convention on Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage (1977)
- Vienna Convention on Succession of States in respect of Treaties (1978)
- Vienna Convention on the Physical Protection of Nuclear Material (1987)
- Vienna Convention on the Protection of the Ozone Layer (1985)
- Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Stratospheric Ozone Layer (1985)
Note that there may be other treaties or agreements that have been signed in Vienna that may also be referred to as Vienna Conventions, but the above are some of the most commonly recognized ones.
Obligations of a “receiving State” under the Vienna Convention
- As per the Vienna Convention, a “receiving State” refers to the host nation where a diplomatic mission is located.
- Article 22 of the Convention deals with obligations with regards to the premises of the Mission.
- Part 2 of this article states that “The receiving State is under a special duty to take all appropriate steps to protect the premises of the mission against any intrusion or damage and to prevent any disturbance of the peace of the mission or impairment of its dignity”.
Did the UK not fulfil its obligations in this instance?
- The fact that protestors were able to climb the walls of the High Commission premises indicates a breach.
- India finds the UK government’s indifference to the security of Indian diplomatic premises and personnel in the UK unacceptable.
- UK has condemned the event and promised to take the security of the Indian High Commission in London seriously.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Sand Battery
Why in News?
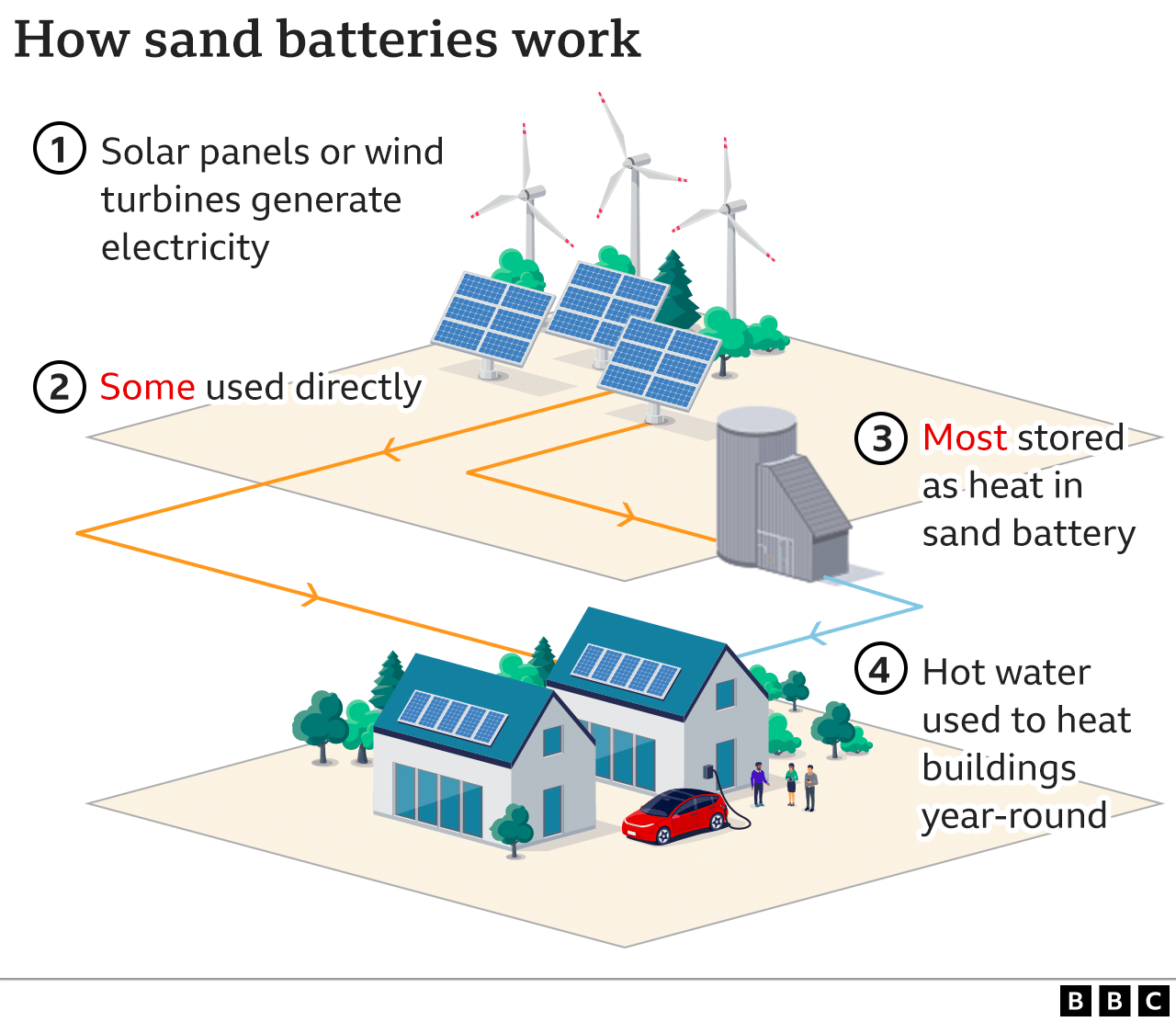
Finland has installed the world’s first sand battery that can store heat from renewable energy sources for months
About Sand Battery:
- The battery, made of sand collected from construction sites, can solve the problem of round-the-year energy supply, a known limitation of renewable energy sources that can be harnessed intermittently.
- Sand can be heated up to 600 degrees Celsius (°C), whereas water starts to boil at 100°C. It also has low heat conductivity, which reduces energy loss.
- The storage system has three main components: the sand silo, an electrical air heater and an air-to-water heat exchanger.
- For charging the sand silo, the air is heated to 600°C in the electric air heater.
- The hot air is then circulated inside the silo using a heat-exchange pipe and blowers to raise the temperature of the sand at the silo’s core to 600°C.
- When the storage enters the discharging stage, the blowers are used to pump air into the pipe inside the sand silo.
- Once the air reaches 200°C, it is transferred to the air-to-water heat exchanger, where it is used to boil water. It is then sent to the heating network.
- The storage system requires electricity at all times.
- It is needed to charge the battery, monitor the temperature during standby and run the blowers when the battery is used.
- 1,000 times more power is discharged as heat than is used as electricity.
Source: DownToEarth
Long-Term Repo Operations (LTRO) and Tri-party Repo (TREPS)
Why in News?
Banks expect overnight rates to edge higher at the end of the month as advance tax and goods and services tax (GST) payments should cause liquidity shrinkage.
What are Long term repo operations?
- LTRO is a tool that allows banks to borrow one to three years of funds from the Central Bank at the Repo rate.
- It is called ‘Targeted’ LTRO if the Central Bank wants banks opting for funds under this option to be specifically invested in investment-grade corporate debt.
- LTRO was first introduced by the European Central Bank (ECB) during its sovereign debt crisis that began in 2008.
What is Tri-party repo or TREPS?
- Tri-party repo is a type of repo contract where a third entity (apart from the borrower or lender), called a Tri-Party Agent, acts as an intermediary between the two parties to the repo to facilitate services like collateral selection, payment and settlement, custody and management during the life of the transaction.”
- The triparty repo is a financial market instrument like the market repo and not like the Central Bank repo (RBI’s repo).
Eligible Tri-Party Agents are
- All tri-party agents need authorization from RBI to act in that capacity before they commence operations.
- Scheduled commercial banks are eligible to be tri-party agents.
- Eligible collateral: Government Securities and Corporate securities.
Source: Economic Times
What is Generative AI?
Google and Microsoft have added generative AI to their search engines and browsers, as well as to consumer products such as Gmail, Docs, Copilot 365, Teams, Outlook, Word, Excel, and more.What is Generative AI?
- Like other forms of artificial intelligence, generative AI learns how to take actions from past data.
- It creates brand new content – a text, an image, even computer code – based on that training, instead of simply categorizing or identifying data like other AI.
- The most famous generative AI application is ChatGPT, a chatbot that Microsoft-backed OpenAI released late last year.
- The AI powering it is known as a large language model because it takes in a text prompt and from that writes a human-like response.
- Google and Microsoft have added generative AI to their search engines and browsers, as well as to consumer products such as Gmail, Docs, Copilot 365, Teams, Outlook, Word, Excel, and more.
- In Google’s Gmail and Docs, generative AI can help users write documents automatically, such as a welcome email for employees.
- Copilot 365, a feature of Microsoft 365 apps, can generate spreadsheets on command or even write an entire article on Word, depending on the topic.
- Both companies are making generative AI platforms and models a part of their cloud offerings, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
- In Google’s Gmail and Docs, generative AI will help users write documents automatically.
- For instance, an HR executive can simply ask the AI app to write a welcome email for employees, instead of typing out the document.
- Similarly, Microsoft has ‘Copilot 365’ for its Microsoft 365 apps, which includes Teams, Outlook, Word and Excel.
- Here, AI could generate a spreadsheet on command, or even write down an entire article on Word (depending on the topic).
- Copilot can also match entries on Calendar with emails, and generate quick, helpful pointers that a person should focus on in their meetings.
- The technology is currently not very accurate and often provides incorrect responses, despite being popular.
- During the initial demonstrations of these products, Google and Microsoft were found to give inaccurate responses.
- While these products may have utility, they are not yet capable of replacing humans in the workplace.
- Humans are better suited to check information generated by AI.
- Bias: The data that is used to train generative AI systems can be biased, leading to biased outputs.
- Misinformation: Since generative AI systems learn from the internet or training data which itself may have been inaccurate, they could increase the spread of misinformation online.
- Security: Generative AI systems could be used to create deepfakes or other forms of digital manipulation that could be used to spread disinformation or commit fraud.
- Ethics: There are ethical concerns around the use of generative AI, particularly when it comes to issues like privacy, accountability, and transparency.
- Regulation: There is a need for regulatory frameworks to ensure that generative AI is used responsibly and ethically, and that it does not have any negative impacts on society.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 21st March 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the eligibility criteria for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. How many papers are there in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. Can I write the UPSC exam in any language? |  |
| 4. How is the UPSC exam conducted? |  |
| 5. What is the syllabus for the General Studies Paper III in the UPSC exam? |  |