Chemical Reactions & Equations - keshav Chapter Notes - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Chemical Reaction ? |

|
| What is Chemical Equations and Its Types ? |

|
| Oxidation and Reduction |

|
| Effects of Oxidation Reaction on Everyday Life |

|
Most of the substance around us undergoes various changes. Some of these changes are temporary with no new substance being formed. They are called physical changes.
Chemical equations are a simple but powerful way to represent chemical reactions, and are essential for understanding and predicting the behavior of chemicals in a variety of settings.
 Chemical equations are important because they allow us to understand the process of a chemical reaction and to predict the products that will be formed. They also help us to balance the equation, which means making sure that the same number of atoms of each element is present on both sides of the equation.
Chemical equations are important because they allow us to understand the process of a chemical reaction and to predict the products that will be formed. They also help us to balance the equation, which means making sure that the same number of atoms of each element is present on both sides of the equation.
What is Chemical Reaction ?
Chemical reaction , a process in which one or more substances, the Reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the Products.
For example , Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
( Reactants ) ( Products )
The substances that undergo chemical change in the reaction , Magnesium and 0xygen, are the Reactants. The new substance, Magnesium Oxide, formed during the reaction, is the Product.
- These are the following changes to determine that the chemical reaction has taken place:
- Change in state
- Change in colour
- Evolution of gas
- Change in temperature
What is Chemical Equations and Its Types ?
Chemical Equation is representation of chemical reaction using symbols and formulae of the substances. A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction.
Chemical equations can be made more concise and useful if we use chemical formulae instead of words. For example , the chemical formula for water is H2O, which indicates that it is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Is a Chemical Equation is balanced or Unbalanced ?
The Chemical Equation is said to be balanced when the number of atoms on both sides of the equation is same . If not, then the equation is unbalanced because the mass is not the same on both side of the equation.
Here are the steps to write a balanced chemical equation:
(i) Write the reactants on the left side of the equation and the products on the right side, separated by an arrow.
(ii)Write the chemical formulas for each reactant and product. If you don't know the formula for a compound, you'll need to look it up.
(iii)Balance the equation by adjusting the coefficients (the numbers in front of each compound or element) until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. Start with the most complex molecule or the molecule that appears in multiple places in the equation.
(iv)Check that the equation is balanced by counting the atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
Finally, make sure that the chemical equation represents a feasible chemical reaction, i.e., it obeys the laws of chemistry and makes sense in terms of the reactants and products.
For example: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
3Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Types of chemical reaction
(1.)Combination reaction: It occurs when two or more reactants combine to form a single product. or we say , such a reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is known as a combination reaction.
For examples:
(i) Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) releasing a large amount of heat.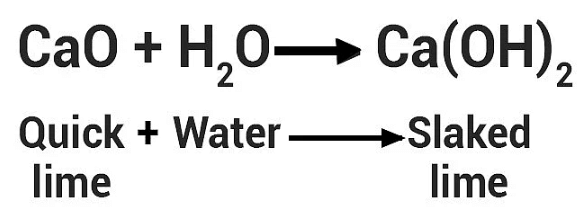
(ii) A solution of slaked lime produced by the reaction is used for white washing walls. Calcium hydroxide reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide in air to form a thin layer of calcium carbonate on the walls. Calcium carbonate is formed after two to three days of white washing and gives a shiny finish to the walls. It is interesting to note that the chemical formula for marble is also CaCO3.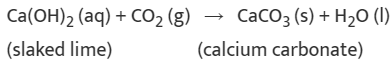
Some More Reactions:
(i)Exothermic reaction: An endothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which energy is absorbed from the surroundings in the form of heat, light, or electricity.
For Example : Endothermic reaction is the process of photosynthesis, in which plants use energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen gas.
Reaction as: C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2(aq) → 6CO2 + 6H2O (l) + energy (glucose)
(ii)Endothermic reaction: An exothermic reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which energy is released from the reaction system into the surroundings, usually in the form of heat, light, or sound.
(2.)Decomposition reaction:
A decomposition reaction occurs when one reactant breaks down into two or more products. This can be represented by the general equation: AB → A + B.For example: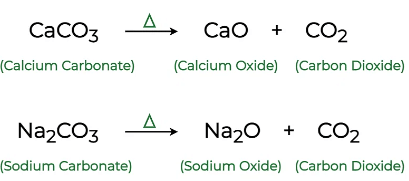
Another example of it as , White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight. This is due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light.
NOTE: The above reactions are used in black and white photography.
(3) Displacement reaction:
Displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. Both metals and non-metals take part in displacement reactions.
Some Important Reaction as:
(i) Reaction of iron nails with copper sulphate solution.
(ii)Reaction of lead with copper chloride solution.
Pb (s) + CuCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu (s)
NOTE: Zinc and lead are more reactive elements than copper. They displace copper from its compounds.
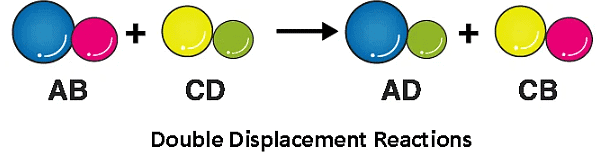
(4) Double Displacement reaction:
A double displacement reaction, is a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react, and the positive ions (cation) and the negative ions (anion) of the two reactants switch places, forming two new compounds or products.For example: Na2(SO)4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq)
Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation and reduction are two important chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or molecules.
(i)Oxidation is the process in which an atom, ion, or molecule loses one or more electrons. During oxidation, the oxidation state of the atom or molecule increases, since it becomes more positive or less negative.
Some examples of oxidation include the reaction of iron with oxygen to form rust, and the reaction of glucose with oxygen in cellular respiration.
(ii)Reduction is the opposite process of oxidation, in which an atom, ion, or molecule gains one or more electrons.
Some examples of reduction include the reaction of silver ions with electrons to form silver metal, and the reaction of hydrogen ions with electrons to form hydrogen gas.
Redox Reaction , Oxidized Agent , Reducing Agent:
- Oxidation and reduction always occur together in a chemical reaction, and are often referred to as redox reactions.
- In a redox reaction, one substance is oxidized while another substance is reduced. The substance that is oxidized is called the reducing agent.
- It causes the reduction of another substance by donating electrons. The substance that is reduced is called the oxidizing agent. It causes the oxidation of another substance by accepting electrons.
- For example, in the reaction between zinc metal and hydrochloric acid, zinc is oxidized to form zinc ions, while hydrogen ions are reduced to form hydrogen gas:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
NOTE: In this reaction, zinc is the reducing agent and hydrogen ions are the oxidizing agent.
Effects of Oxidation Reaction on Everyday Life
(i)Corrosion:
The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to their reaction with oxygen, water, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is called corrosion.
Rusting – Iron when reacts with oxygen and moisture forms red substance called rust.
(ii)Rancidity:
- The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are left exposed to air for long time. This is called rancidity. It is caused due to oxidation of fat and oil present in food material.
- It can be prevented by using various methods such as by adding antioxidants to the food materials, Storing food in air tight container and by flushing out air with nitrogen.