Work, Force, Energy and Simple Machines - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Which of the following is an example of a simple machine?
(a) Car
(b) Lever
(c) Airplane
(d) Computer
Ans: (b)
A lever is an example of a simple machine because it is a basic mechanical device that helps make work easier.
(ii) What is work?
(a) The force applied to an object
(b) The energy transferred by a force to move an object
(c) The distance an object moves
(d) The speed at which an object moves
Ans: (b)
Work is done when a force is applied to an object, causing it to move a certain distance.
(iii) Which of the following is a unit of force?
(a) Newton (N)
(b) Joule (J)
(c) Watt (W)
(d) Meter (m)
Ans: (a)
The unit of force is the Newton (N), named after the scientist Sir Isaac Newton.
(iv) Which of the following is a unit of energy?
(a) Newton (N)
(b) Joule (J)
(c) Watt (W)
(d) Meter (m)
Ans: (b)
The unit of energy is the Joule (J), named after the scientist James Prescott Joule.
(v) What is the purpose of a simple machine?
(a) To make work harder
(b) To reduce the amount of energy needed
(c) To increase the amount of force needed
(d) To make work easier
Ans: (d)
The purpose of a simple machine is to make work easier by reducing the amount of force needed or changing the direction of the force.
Q2: Fill in the Blanks.
(i) Work is done when _______ is applied to an object, and it moves a certain _______.
Ans: force, distance
Work is defined as the product of force and distance. It occurs when a force is applied to an object, causing it to move a specific distance.
(ii) The unit of measurement for work is _______.
Ans: Newton meter (Nm) or Joule (J)
Work is measured in Newton meters (Nm) or Joules (J), which are standard units in physics.
(iii) _______ force is applied when we push, pull, or lift something with our hand.
Ans: Muscular force
Muscular force is the force applied by our muscles when we engage in activities such as pushing, pulling, or lifting objects.
(iv) Gravitational force is the force that attracts objects towards the _______.
Ans: center of the earth
Gravitational force is responsible for pulling objects toward the center of the Earth, giving weight to objects.
(v) A heated substance possesses _______ energy.
Ans: heat energy
Heat energy is the energy possessed by a substance due to its temperature, reflecting the kinetic energy of its molecules.
Q3: True or False.
(i) Frictional force tries to stop the movement of objects across a surface.
(ii) Potential energy is the energy due to an object's position or motion.
(iii) The law of conservation of energy states that energy can be created or destroyed.
(iv) In a first-class lever, the load is between the fulcrum and the effort.
(v) A pulley used for drawing water from a well is a movable pulley.  (vi) Work is done only when an object moves.
(vi) Work is done only when an object moves.
(vii) Gravity is a force that pushes objects away from the Earth.
(viii) A lever is an example of a simple machine.
(ix) Energy can be created or destroyed.
(x) The pulley is a simple machine that helps lift heavy objects.
Ans:
(i) True: Frictional force is a force of resistance that opposes the movement of objects across a surface.
(ii) False: Potential energy is the energy due to an object's position, while kinetic energy is the energy due to its motion.
(iii) False: The law of conservation of energy states that energy can only be transformed from one form to another; it cannot be created or destroyed.
(iv) False: In a first-class lever, the fulcrum lies between the load and the effort.
(v) False: A pulley used for drawing water from a well is a fixed pulley.
(vi) True: Work is done only when a force moves an object in the direction of the force.
(vii) False: Gravity is a force that pulls objects towards the Earth.
(viii) True: A lever is an example of a simple machine that helps to lift heavy objects or exert a greater force with less effort.
(ix) False: Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. This is known as the conservation of energy.
(x) True: The pulley is a simple machine that helps lift heavy objects by changing the direction of the force and reducing the amount of force needed.
Q4: Match the column.
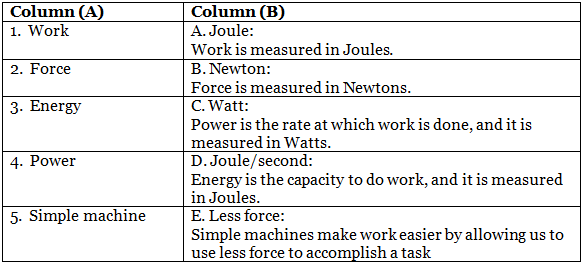 Ans:
Ans: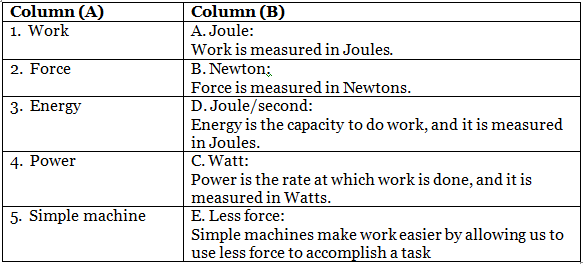
Q5: Short Answer Questions.
(i) Explain the formula for calculating work.
Ans: The formula for work is Work = Force × Distance. It means that work is the product of the force applied to an object and the distance the object moves.
(ii) Give an example of each type of force mentioned in the text.
Ans:
- Muscular force: Lifting a heavy box using your muscles.
- Gravitational force: Objects falling to the ground due to gravity.
- Frictional force: Walking on a rough surface.
- Elastic force: Stretching a rubber band.
- Mechanical force: Using a wedge to separate two objects.
- Buoyant force: A piece of wood floating on water.
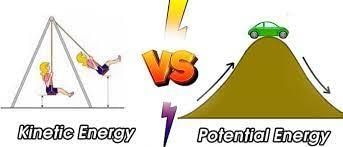
(iii) Define potential energy and kinetic energy with examples.
Ans:
- Potential energy: Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position. For example, a book on a table has potential energy because of its height above the ground.
- Kinetic energy: Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. For example, a moving car has kinetic energy.
(iv) What are the six different types of simple machines?
Ans: The six different types of simple machines are:
- Lever
- Wheel and axle
- Pulley
- Inclined plane
- Wedge
- Screw
(v) Explain how a pulley works.
Ans: A pulley works by changing the direction of the force applied to an object. It consists of a wheel with a groove around its edge, through which a rope or cable is threaded. When the rope is pulled, the pulley rotates, lifting or moving the object attached to the other end of the rope.
(vi) What is the principle of conservation of energy?
Ans: The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. In a closed system, the total amount of energy remains constant.
Q6: Long Answer Questions.
(i) Explain the three types of levers with examples.
Ans: Levers are simple machines that help lift or move loads. There are three types of levers, each defined by the relative positions of the fulcrum, load, and effort.
- First-class lever: The fulcrum is positioned between the load and the effort. Examples: A seesaw and scissors.
- Second-class lever: The load is located between the fulcrum and the effort. Examples: A wheelbarrow and a bottle opener.
- Third-class lever: The effort is applied between the fulcrum and the load. Examples: A stapler and a pair of tongs.
(ii) Describe the different forms of energy mentioned in the text and their applications in daily life.
Ans:
- Mechanical energy: Mechanical energy is the energy due to an object's position or motion. It is used in various everyday activities like pushing a cart or riding a bicycle.
- Heat energy: Heat energy is possessed by heated substances and is used in various applications such as cooking, heating water, and running steam engines.
- Chemical energy: Chemical energy is released or absorbed during chemical reactions and is used in batteries to power electronic devices.
- Sound energy: Sound energy is possessed by sound waves and is used in devices like music players and speakers to produce sound.
- Muscular energy: Muscular energy is the energy possessed by muscles and is used when we perform physical activities like lifting weights or playing sports.
(iii) Explain the working principle of a wheel and axle with real-life examples.
Ans: The wheel and axle is a simple machine consisting of a wheel attached to a rod, known as the axle. When force is applied to the wheel, it rotates around the axle, thereby making work easier. This arrangement is commonly found in various everyday applications, including:
- Vehicles (e.g., car wheels)
- Sewing machines (e.g., spool and needle)
- Bicycles (e.g., pedals and wheels)
|
42 videos|377 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Work, Force, Energy and Simple Machines - 1 Class 5 Worksheet Science
| 1. What is the relationship between work, force, and energy in physics? |  |
| 2. How do simple machines help in reducing the amount of work done? |  |
| 3. What is mechanical advantage and how is it calculated? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the concept of potential and kinetic energy in relation to simple machines? |  |
| 5. How does friction affect the efficiency of simple machines? |  |
















