Doc: How to Use SOHCAHTOA | The Complete SAT Course - Class 10 PDF Download
Trigonometry is not a major focus of the new SAT exam, but a few of the math questions, around six out of 58, deal with additional topics in math, including trigonometry. Trigonometry deals with the relationship between angles and triangle side lengths, specifically right triangles. It involves using mathematical tools to identify missing side lengths and angle measurements. Although some test takers may feel anxious about encountering trigonometry questions on the SAT, the key to answering them correctly is simply knowing which tools to use. The majority of SAT trigonometry questions ask students to apply sine, cosine, and tangent to solve problems involving right triangles. An important acronym to remember when tackling these questions is SOHCAHTOA.
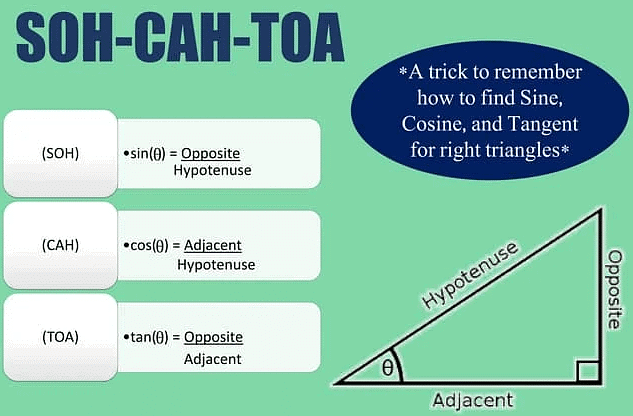
What Is SOHCAHTOA?
SOHCAHTOA is a mnemonic acronym used in trigonometry to help students remember the three primary trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, and tangent. Each letter in the acronym represents a different ratio.
"S" stands for sine, which is equal to the ratio of the length of the side opposite an acute angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The formula for sine is sinθ = Opposite/Hypotenuse.
"C" stands for cosine, which is equal to the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to an acute angle to the length of the hypotenuse. The formula for cosine is cosθ = Adjacent/Hypotenuse.
"T" stands for tangent, which is equal to the ratio of the length of the side opposite an acute angle to the length of the side adjacent to that angle. The formula for tangent is tanθ = Opposite/Adjacent.
By memorizing the SOHCAHTOA acronym and its corresponding formulas, students can easily apply these trigonometric ratios to solve problems related to right triangles.
In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is the side that is opposite the right angle and is also the longest side of the triangle. The opposite side is the side that is opposite to the angle being considered and is the side whose length is being sought. The adjacent side is the side that is adjacent to the angle being considered, and it touches the angle at one of its endpoints. Together, these three sides form the basis for calculating the trigonometric ratios using SOHCAHTOA.
Solving SAT Trigonometry Questions
- The first type of SAT trigonometry question asks students to solve for an angle’s sine, cosine, or tangent. For example, in triangle ABC, where B is the right angle, the question may include the length of the hypotenuse (4) and side BC (3) and ask students to determine the cosine of angle C.
- For some problems, the SAT will provide you with a diagram, and in other cases you’ll have to draw one yourself. If you have to draw your own triangle, start by filling in the information provided. In this case, you would fill in the length of the hypotenuse and side BC. Then assess what information you need to find and choose the correct formula for solving the problems.
For example, if you’re asked to find the cosine of angle C, you can do so with the following equation:
Cos C = The length of the adjacent side of the triangle (BC) / the length of the hypotenuse
So, the cosine of C is equal to 3/4.
When solving the second question type, students will use the sine, cosine, or tangent of an acute angle to determine the sine, cosine, or tangent of another angle.
For example, a problem involving a triangle ABC, where B is the right angle, may provide the cosine of angle C and ask you to come up with the sine of angle A.
To solve this problem, start by using the cosine formula to determine what information should go where in your diagram. So, if the cosine of angle C is 3/4, then the measure of the adjacent side (BC) is 3 and the measure of the hypotenuse is 4.
You can then calculate the sine of angle A using the following formula:
Sine A = length of the side opposite the angle (BC) / length of the hypotenuse.
In other words, Sine A is equal to 3/4.
|
433 videos|220 docs|166 tests
|
















