Exercises: Transport of Substances in Animals & Plants | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Objective Type Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Objective Type Questions
A. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
Q.1. In unicellular organisms, every part gets nutrients and oxygen directly through ____ (diffusion/translocation).
In unicellular organisms, every part gets nutrients and oxygen directly through diffusion.
Unicellular organisms are single-celled organisms, and their small size allows for nutrients and oxygen to diffuse directly into the cell through their cell membrane.
Q.2. Blood contains several cells floating in a straw-coloured liquid called the ____ (platelets/plasma).
Blood contains several cells floating in a straw-coloured liquid called the plasma.
Blood is a connective tissue composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets suspended in plasma, a straw-colored liquid that contains various substances such as hormones, proteins, and electrolytes.
Q.3. Diffusion of gases and chemical substances takes place through the walls of the ____ (arteries/capillaries)
Diffusion of gases and chemical substances takes place through the walls of the capillaries.
Capillaries are small, thin-walled blood vessels that connect arteries and veins, and they are the site of exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and tissues through the process of diffusion.
Q.4. ____ (Valves/Auricles) separate the chambers of the heart so that there is no mixing of blood.
Valves separate the chambers of the heart so that there is no mixing of blood.
The heart has four chambers, two atria and two ventricles, and each chamber is separated by a valve that prevents the backflow of blood and ensures that blood flows in one direction through the heart.
Q.5. ____ (Right/Left) ventricle pumps blood to the farthest parts of the body through the aorta.
Left ventricle pumps blood to the farthest parts of the body through the aorta.
The left ventricle is the largest and most muscular chamber of the heart, and it pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs into the aorta, the largest artery in the body, which then distributes blood to the rest of the body.
Q.6. The larger the leaf, the ____ (faster/slower) is the rate of transpiration.
The larger the leaf, the slower is the rate of transpiration.
Transpiration is the loss of water from plants through their leaves, and it occurs through small openings called stomata. The rate of transpiration is affected by various factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind, but larger leaves have a lower surface area-to-volume ratio, which results in a slower rate of transpiration compared to smaller leaves.
B. Write T for the True and F for the False statements. Correct the false statements.
Q.1. The human circulatory system is made up of the heart and blood.
True
The human circulatory system is made up of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps blood through the blood vessels, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells and removing waste products.
Q.2. White blood cells contain haemoglobin that helps to transport oxygen.
False
White blood cells do not contain hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds with oxygen to transport it throughout the body. White blood cells, on the other hand, are a type of blood cell that helps to fight infection and disease.
Q.3. Blood consists of two types of blood cells.
False
Blood consists of three types of blood cells: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infection, and platelets help with blood clotting.
Q.4. Kidneys are always working separately to get rid of wastes.
False
The kidneys are not always working to get rid of wastes. They filter waste products from the blood and produce urine, but they do not do this continuously. The rate at which the kidneys filter blood and produce urine depends on various factors such as hydration, blood pressure, and hormone levels.
Q.5. All arteries always carry oxygenated blood.
False
Arteries do not always carry oxygenated blood. The pulmonary artery, for example, carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated. The pulmonary vein, on the other hand, carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
Q.6. When blood enters the kidney, useful substances are absorbed or filtered back into the blood.
True
When blood enters the kidney, useful substances are absorbed or filtered back into the blood. The kidneys play an important role in regulating the body's fluid balance, electrolyte levels, and acid-base balance. They filter waste products from the blood and excrete them in urine while retaining useful substances and returning them to the bloodstream.
C. Choose the Correct Option.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Give two examples for the following.
Q.1. Organisms that do not require any special transport system inside them ____, ____
Organisms that do not require any special transport system inside them include single-celled organisms like amoeba and paramecium.
Q.2. Wastes formed inside the human body ____, ____
Wastes formed inside the human body include carbon dioxide, urea, and excess salts.
Q.3. Animals that have tubular structures to help them excrete wastes ____, ____
Animals that have tubular structures to help them excrete wastes include earthworms and cockroaches.
Q.4. Toxic wastes of plants ____, ____
Toxic wastes of plants include alkaloids and tannins.
Q.5. Things manufactured using plant secretions ____, ____
Things manufactured using plant secretions include rubber, resins, and essential oils.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. How do substances get transported in Hydra?
In Hydra, substances are transported by diffusion, as it is a simple aquatic animal. The nutrients and gases diffuse in and out of the cells through the body surface, and the waste products are eliminated through the same surface.
Q.2. What is blood? Describe what blood is made up of.
Blood is a vital fluid that circulates throughout the body and performs various functions such as carrying oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. It is made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma is a yellowish liquid that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products. Red blood cells carry oxygen to different parts of the body. White blood cells protect the body against diseases and infections. Platelets help in blood clotting and prevent excessive bleeding.
Q.3. Define the following:
a. Translocation
b. Excretion
a. Translocation is the process of transport of food substances from the leaves to the other parts of the plant. It occurs through the phloem tissue of the plant and is a vital process for the growth and development of plants.
b. Excretion is the process of elimination of waste products produced by the cells of the body. In animals, it occurs through specialized organs like kidneys, skin, lungs, and liver. In plants, it occurs through the elimination of waste products in the form of gases through stomata, and in the form of leaves or bark shedding.
Q.4. How do plants get rid of toxic wastes produced in them?
Plants get rid of toxic wastes produced in them by the process of excretion. The waste products in plants are mainly in the form of gases like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor, which are eliminated through stomata. Plants also get rid of excess salts, minerals, and other waste products through the shedding of leaves, bark, and other plant parts. Additionally, some plants can also accumulate toxic waste products in their vacuoles, which are later eliminated through the shedding of leaves or other parts of the plant.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. Explain the main differences between arteries, veins and capillaries.
Arteries, veins and capillaries are the three types of blood vessels found in the human body. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to all parts of the body, while veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels that connect arteries and veins.
The main differences between arteries, veins and capillaries are as follows:
Arteries:
Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
Have thick walls with a layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Can withstand high pressure of blood flow
Have no valves
Veins:
Carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart
Have thin walls with a layer of smooth muscle and elastic fibres
Have valves to prevent backflow of blood
Can collapse or expand to regulate blood flow
Capillaries:
Connect arteries and veins
Have thin walls made of a single layer of cells
Allow exchange of substances between blood and tissues
Form networks called capillary beds
Q.2. Describe how the heart acts as the pumping station of the body.
The heart is the pumping station of the body that circulates blood throughout the body. It is a muscular organ located in the thoracic cavity of the chest. The heart has four chambers - two upper chambers called atria and two lower chambers called ventricles.
The heart acts as a pump by contracting and relaxing rhythmically to move blood through the blood vessels. The process of pumping blood is called the cardiac cycle. During the cardiac cycle, the atria and ventricles contract and relax in a coordinated manner to ensure efficient blood flow.
The heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava into the right atrium. The right atrium then contracts to push the blood into the right ventricle. The right ventricle then contracts to pump the deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary artery, which carries it to the lungs for oxygenation.
The oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium through the pulmonary vein. The left atrium then contracts to push the blood into the left ventricle. The left ventricle then contracts to pump the oxygenated blood into the aorta, which carries it to the rest of the body.
Q.3. What is transpiration? Discuss the role that transpiration plays in a plant and the factors that affect the rate of transpiration.
Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water vapour through the stomata on their leaves. It is an important process that helps in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil, and also helps in the cooling of the plant.
The role of transpiration in a plant is as follows:
Absorption of water and minerals from the soil: Transpiration creates a negative pressure in the roots that helps in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
Transport of water and minerals: Transpiration creates a suction force that pulls water and minerals up through the plant's xylem vessels.
Cooling of the plant: Transpiration helps in the cooling of the plant by releasing water vapour into the atmosphere.
The factors that affect the rate of transpiration are as follows:
Humidity: High humidity reduces the rate of transpiration as the air surrounding the plant is already saturated with water vapour.
Temperature: High temperature increases the rate of transpiration as it increases the evaporation of water from the leaves.
Wind: Wind increases the rate of transpiration by carrying away the water vapour from the leaves.
Light intensity: High light intensity increases the rate of transpiration as it increases the opening of stomata on the leaves.
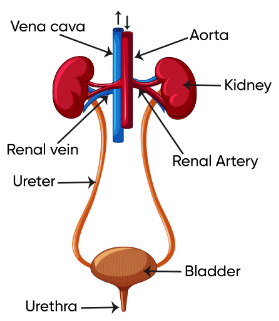
Q.4. With the help of a well-labelled diagram, describe the human excretory system.
The human excretory system is responsible for removing waste products from the body. The major organs of the excretory system are the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra.
The process of excretion in the human body is as follows:
The kidneys filter waste products from the blood and produce urine.
The urine flows from the kidneys to the ureters, which are tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
The bladder stores the urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
The urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
The following is a well-labelled diagram of the human excretory system:
Key:
1. Kidney
2. Ureter
3. Bladder
4. Urethra
|
138 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|