Science and Technology: April 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Brightest Gamma Ray Burst Detected
Why in News?
- In October 2022, astronomers recorded the brightest gamma-ray radiation (named GRB 221009A) of all time, which could overturn a long-standing theory of GRB jets.
- The observation was conducted jointly by Center for Astrophysics, Harvard and Smithsonian’s Submillimeter Array (SMA) in Hawaii, the MeerKAT Array in South Africa, the US National Science Foundation’s Karl G Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) in New Mexico (USA), the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile and NCRA’s Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope, India.
What is a Gamma-Ray Burst?
- About:
- Gamma-Ray Bursts are the most powerful class of explosions in the universe, and they occur when massive stars die.
- When a massive star collapses, it creates a black hole, and the energy released during this process produces jets of high-energy particles that travel almost at the speed of light.
- These jets pierce through the collapsing star, producing X-rays and gamma rays, which can be detected by observatories on Earth and in space.
- Types of GRBs:
- Long-duration gamma-ray bursts (LGRBs):
- LGRBs last for more than two seconds and are thought to be caused by the collapse of massive stars, known as supernovae.
- These explosions release a tremendous amount of energy and create a black hole at their center.
- LGRBs are the most common type of GRB and can be observed from distant galaxies.
- Long-duration gamma-ray bursts (LGRBs):
- Short-duration gamma-ray bursts (SGRBs):
- SGRBs last for less than two seconds and are thought to be caused by the collision of two compact objects, such as neutron stars or a neutron star and a black hole.
- SGRBs are much rarer than LGRBs, are more difficult to observe and typically located closer to our galaxy.
What is GRB 221009A?
- About:
- GRB 221009A was detected in October 2022, by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, and Wind spacecraft.
- The signal originated from the direction of the constellation Sagitta, and it took approximately 1.9 billion years to reach Earth.
- The 5-minute-long radiation pulse was the brightest GRB ever and nearly 70 times brighter than any other such eruption ever observed.
- Observation from GRB 221009A:
- The pulse of radiation was unusually bright and long-lasting, which made it stand out from other gamma-ray bursts.
- The signal triggered detectors at multiple observatories, indicating its strength and duration.
- Researchers about 221009A:
- "Long-duration" GRBs occur when the core of a massive star collapses under its own weight, giving birth to a black hole.
- This formation produces powerful plasma jets that shoot gamma rays at almost the speed of light. When these jets collide with the gas surrounding the dying star, a bright afterglow is produced across the spectrum.
- Significance:
- Astronomers from the National Centre for Radio Astrophysics in India concluded that the signal was a birth cry of a black hole.
- GRB 221009A provides astronomers with valuable insights into the formation of black holes and the mechanisms that produce gamma-ray bursts.
- The detection of GRB 221009A will help astronomers refine their understanding of the conditions required for the formation of black holes and the production of gamma-ray bursts.
Laser Carbon to Produce Hydrogen
Why in News?
Recently, a few Researchers have developed a novel Carbon-Based Catalyst called Laser Carbon to make water electrolysis more efficient.
What is Laser Carbon and its Significance?
- Laser Carbon can replace expensive metal-based catalysts in the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen.
- The electrolysis of water consumes a lot of energy. The traditional solution is to use a catalyst to induce the water molecules to split at a lower energy.
- Laser carbon is a porous carbon material containing nitrogen that acts as both a catalyst and an anode in electrolysis.
- It reduces the energy required for splitting water by lowering the overpotential of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER).
- Laser carbon is simpler to synthesise, and can be batch-manufactured with a laser in an environmentally friendly process, unlike other carbon-based catalysts.
- Common catalysts are based on iridium and ruthenium, which are expensive and in great demand in other sectors.
- Although its catalytic activity is not as good as metal-based catalysts, it can be improved by using different polymers in the fabrication process.
What is Electrolysis?
- Electrolysis is a process of using an electric current to bring about a chemical reaction.
- In electrolysis, an electric current is passed through an electrolyte (a substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in water or melted) to produce a chemical change.
- The electric current causes the positive and negative ions in the electrolyte to move towards the opposite electrodes, causing the separation of the electrolyte into its constituent elements or the formation of a new compound.
- Electrolysis is used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of metals, cleaning metal surfaces, and the production of hydrogen gas from water.
The Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) mission
In News
NASA’s high-resolution air pollution monitoring instrument TEMPO lifted atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida
About TEMPO
- It is the first funded project of NASA's Earth Venture Instrument program, which includes small, targeted science investigations designed to complement NASA's larger research missions.
- It is part of the agency's Earth System Science Pathfinder program.
- It will measure atmospheric pollution covering most of North America, from Mexico City to the Canadian tar/oil sands, and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at high spatial resolution.
- It covers not only the continental United States, but also Canada, Mexico, Cuba, the Bahamas, and part of the island of Hispaniola.
- It will take important scientific observations, including that of ozone, nitrogen oxide, sulphur dioxide and formaldehyde levels
Benefits
- TEMPO’s measurements from geostationary orbit (GEO) of tropospheric ozone, ozone precursors, aerosols, and clouds will create a revolutionary dataset that provides understanding and improves prediction of air quality (AQ) and climate forcing.
- TEMPO data will play an important role in the scientific analysis of pollution, including studies of rush hour pollution, the potential for improved air quality alerts, the effects of lightning on ozone, the movement of pollution from forest fires and volcanoes, and even the effects of fertilizer application.
Physicists Discover New Uranium Isotope
In News
- Physicists in Japan discovered a previously unknown isotope of uranium, with atomic number 92 and mass number 241, i.e Uranium-241 and its half-life, according to theoretical calculations, could be 40 minutes.
What is Uranium?
- Uranium is a naturally occurring chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table
- Uranium has several isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons like U-235 and U-238.
- It is a heavy metal that is radioactive and found in small quantities in rocks and soils worldwide.
- Atomic number = No. of Protons = No. of Electrons
- No. of Neutrons = Atomic mass- Atomic No.
Why does a new isotope matter?
- It re-defines the boundaries of models that physicists use to design nuclear power plants and models of exploding stars.
- It gives essential nuclear information to understand the synthesis of such heavy elements in explosive astronomical events.
How was uranium-241 found?
- The researchers accelerated uranium-238 nuclei into plutonium-198 nuclei at the KEK Isotope Separation System (KISS).
- In a process called multinucleon transfer, the two isotopes exchanged protons and neutrons.
- The resulting nuclear fragments contained different isotopes. This is how the researchers identified uranium-241 and measured the mass of its nucleus by using time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
What are Magic numbers?
- In nuclear physics, a magic number is a number of nucleons (either protons or neutrons, separately) such that they are arranged into complete shells within the atomic nucleus.
- As a result, atomic nuclei with a 'magic' number of protons or neutrons are much more stable than other nuclei
- The heaviest known ‘magic’ nucleus is lead (82 protons)
Multiple Sclerosis
Why in News?
Recently, Scientists have fabricated monolayers of pure Myelin Basic Protein (MBP).
- MBP is a major protein component of the myelin sheath, a protective membrane that wraps around the axon of nerve cells and acts as a model protein in studying diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS).
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
- About:
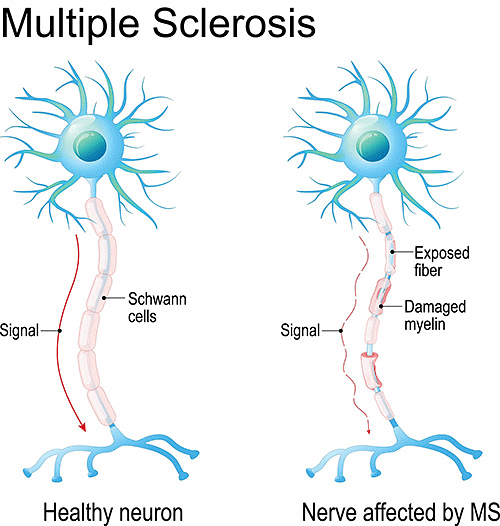
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS).
- In MS, the immune system attacks and damages the myelin sheath, a protective covering that surrounds the nerve fibers in the brain and spinal cord, causing a range of symptoms.
- Symptoms:
- Muscle weakness and Numbness
- Bladder Problems: A person may have difficulty emptying their bladder or need to urinate frequently or suddenly
- Bowel problems, Fatigue, Dizziness, and damaged nerve fibers in the spinal cord.
- Since symptoms are common, people don’t often recognise the disease early and often takes many years for someone to be diagnosed, as it is impossible to determine a specific cause or trigger.
- Causes:
- The exact cause of the disease is unknown, but it could be a combination of:
- Genetic factors: Susceptibility may pass down in the genes
- Smoking and Stress
- Vitamin D and B12 deficiency
 What are the Key Highlights from the Research?
What are the Key Highlights from the Research?
- Understanding the Behaviour of Protein under Variable pH Conditions:
- The researchers studied how the protein behaved in different levels of acidity, by looking at different parts of the layer formed on top of the water.
- They found that the stiffness of the layer was related to the specific patterns formed and the space they occupied on the water surface.
- Fabricated MBP Layer:
- The researchers have created a tightly packed layer of MBP using Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) technique.
- The Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) technique is a process used to create monolayers of molecules, including proteins, at air-water and air-solid interfaces.
- This layer can be used to study the different properties of MBP in 2D and how it interacts with other proteins.
- The researchers also found that the layer can act as a template for other proteins to crystallize on, which can help in studying their structures.
- Overall, this research helps us better understand the role of MBP in our bodies and how it interacts with other molecules.
Fertiliser Consumption in India
Why in News?
The Indian government has implemented several measures to promote balanced fertilisation. Despite these efforts, the consumption of urea has risen, leading to imbalanced fertilisation, decreased nitrogen use efficiency, and a decline in crop yield response to fertiliser use.
What Measures have been taken to Promote Balanced Fertilisation?
Initiatives:- In 2015, Indian government mandated neem-coating of all urea
- Govt introduced 45kg urea bags in place of 50kg to cut demand in 2018
- Indian Farmers Fertiliser Cooperative Limited (IFFCO) launched liquid 'Nano Urea' in 2021.
- More recently, first Liquid Nano Urea (LNU) plant was inaugurated at Kalol, Gujarat.
- LNU is urea in the form of a nanoparticle and is developed to replace conventional urea and curtail its requirement by at least 50%.
- Impact of the Measures Taken:
- Initially, the use of neem-coated urea led to a dip in consumption, making it difficult for urea to be used for non-agricultural purposes.
- However, this trend reversed from 2018-19. Urea sales in 2022-23 were about 5.1 mt higher than in 2015-16 and over 9 mt higher than in 2009-10, before the introduction of the Nutrient-Based Subsidy (NBS) regime in April 2010.
Why does Urea Continue to be the Dominant Fertiliser?
- Favourable Characteristics: Urea is the most widely used fertilizer because it is a rich source of nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth.
- Urea is a readily available and affordable nitrogen source for farmers, making it a popular choice.
- It can also be easily stored and transported, making it a convenient choice for both farmers and manufacturers.
- Urea is also a versatile fertilizer that can be applied to a wide range of crops and soil types.
- Heavy Subsidy: In India, urea is the most produced, imported, consumed and physically regulated fertiliser of all.
- Urea consumption rose by over a third since 2009-10; this has been largely courtesy of its MRP going up by a mere 16.5% – from Rs 4,830 to Rs 5,628 per tonne.
- This current per-tonne MRP for urea against DAP (Rs 27,000) and MOP (Rs 34,000) is nowhere compatible with a 4:2:1 NPK use ratio generally considered ideal for Indian soils.
What is the Nutrient-based Subsidy (NBS) regime?
- Targeted Beneficiaries:
- The NBS regime is aimed at benefiting farmers across the country, especially small and marginal farmers who may not be able to afford fertilizers at market rates.
- The scheme provides subsidies to farmers based on their fertilizer requirements, and the subsidy amount is directly transferred to their bank accounts.
- Benefits:
- It helps in improving soil fertility and crop productivity.
- Reduces the cost of cultivation for farmers by providing fertilizers at subsidized rates.
- Improves the quality of agricultural produce, which can help farmers get better prices for their crops in the market.
- It helps in conserving soil health and reducing the environmental impact of excessive use of fertilizers.
- Failure of NBS:
- Urea is left out of the scheme and hence it remains under price control. There is technically no price control on other fertilizers.
- The prices of the other fertilizers which were decontrolled have gone up which has led the farmers to use more urea than before.
- This has further worsened fertilizer imbalance.
- Price controls on DAP have been reintroduced, with companies not allowed to charge more than Rs 27,000 per tonne. This has led to the sales of both urea and DAP soaring in 2022-23.
What is the Cost of Imbalanced Fertilisation?
- Reduced Crop Yields and Quality:
- Applying too little or too much fertilizer can lead to reduced crop yields and quality, resulting in financial losses for farmers.
- Soil Degradation:
- Imbalanced fertilization can lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil, leading to soil degradation, erosion, and loss of soil fertility over time.
- Environmental Pollution:
- Overuse of fertilizers can lead to the leaching of excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into water bodies, causing eutrophication, algal blooms, and other environmental problems.
- Health Risks:
- Excessive use of fertilizers can result in the accumulation of nitrates in crops, which can be harmful to human health if consumed in large quantities.
Way Forward
- Expand the NBS Regime to Include Urea:
- The current exclusion of urea from the NBS regime has led to an increase in its consumption, exacerbating the problem of imbalanced fertilisation.
- Including urea in the NBS regime would promote its balanced use and reduce its consumption, which would in turn reduce the cost of cultivation for farmers and improve crop productivity.
- Encourage the use of Alternative Fertilisers:
- The use of alternative fertilisers, such as organic and bio-fertilisers, can help reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilisers, which can lead to imbalanced fertilisation.
- Promoting the use of alternative fertilisers through subsidies, awareness campaigns, and capacity building can help improve soil health and reduce environmental pollution.
- Promote Soil Testing and Balanced Fertilisation:
- Soil testing can help determine the nutrient requirements of crops, which can help farmers apply fertilisers in a balanced manner.
- Promoting soil testing and providing subsidies for it can encourage farmers to adopt balanced fertilisation practices, which can improve crop yields and soil health.
- Monitor and Regulate the Prices of Decontrolled Fertilisers:
- Regulating the prices of decontrolled fertilisers, such as DAP, can help prevent their excessive use and promote the use of balanced fertilisers.
- The government can consider reintroducing price controls on decontrolled fertilisers to ensure their affordability and prevent their excessive use.
- R&D of Sustainable Fertilisers:
- Investing in R&D of sustainable fertilisers can help develop fertilisers that are environmentally friendly, promote balanced fertilisation, and improve crop productivity.
- The government shall provide funding for R&D of sustainable fertilisers besides encouraging private sector participation.
- Improving NUE (Nitrogen Use Efficiency):
- NUE refers to the proportion of Nitrogen applied mainly through urea that is actually utilized by crops to produce harvested yields.
- It will enable farmers to harvest the same or more grain yields with fewer bags.
LockBit Ransomware
Context
LockBit ransomware was found to be targeting Mac devices, in a first.
What is LockBit ransomware?
- First reported in September 2019 and dubbed the “abcd” virus, due to the file extension used when encrypting victim’s files, the LockBit ransomware is designed to infiltrate victims’ systems and encrypt important files.
- The virus is categorised as a “crypto virus” due to its requests for payment in cryptocurrency to decrypt the files on the victim’s device.
- The ransomware is therefore typically deployed against victims who feel hindered enough by the disruption to pay heavy sums in exchange for access and can afford to do so.
- In the past, LockBit ransomware has been used to target enterprises and organisations in the U.S., China, India, Ukraine, and Indonesia. Attacks have also been recorded throughout Europe, including in France, Germany, and the U.K.
How does LockBit ransomware work?
- It works as a self-spreading malware, not requiring additional instructions once it has successfully infiltrated a single device with access to an organizational intranet. It is also known to hide executable encryption files by disguising them in the .PNG format, thereby avoiding detection by system defences.
- Attackers use phishing tactics and other social engineering methods to impersonate trusted personnel or authorities to lure victims into sharing credentials.
- Sometimes, the ransomware has also used brute force to gain access to the intranet server and network of an organization.
- Once it has gained access, the ransomware prepares the system to release its encryption payload across as many devices as possible.
- It then disables security programs and other infrastructures that could permit system data recovery. The goal is to ensure that data recovery without assistance from the LockBit gang is impossible.
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) C-55
Context
ISRO, is scheduled to launch the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C55 (PSLV-C55) mission on April 22 with Singapore’s TeLEOS-2 as primary satellite and Lumelite-4 as a co-passenger satellite.
Backdrop PSLV
- Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is the third generation launch vehicle of India. It is the first Indian launch vehicle to be equipped with liquid stages.
- It is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle.
- It was developed to allow India to launch its Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites into sun-synchronous orbits – a service that until the advent of the PSLV in 1993, was commercially available only from Russia.
- PSLV can also launch small size satellites into Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- Some notable payloads launched by PSLV include India's first lunar probe Chandrayaan-1, India's first interplanetary mission, Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan) and India's first space observatory, Astrosat.
About PSLV C-55
- The PSLV-C55 mission will be the 57th flight of PSLV and the 16th mission using the PSLV Core Alone configuration.
- The PSLV C55 rocket has four stages; each one was self-contained, with its own propulsion system, thereby capable of functioning independently.
- The first and third stages used composite solid propellants.
- The second and fourth stage use earth-storable liquid propellant.
What all is PSLV-C55 launching with?
- The PSLV-C55 mission will lift off with two big satellites with the
- TeLEOS-2, a Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite as the primary mission and
- Lumelite-4 a technology demonstration nano-satellite, will be a co-passenger satellite.
- The two satellites combined weigh around 757 kilograms.
- The two satellites are intended to be launched into an Eastward low-inclination orbit.
The satellites
- TeLEOS-2 spacecraft
- The TeLEOS-2 spacecraft will provide imagery that could be used for hotspot monitoring and haze management, air crash search and rescue operations, and much more.
- It will provide all-weather day and night coverage and is capable of imaging at 1m full-polarimetric resolution.
- LUMELITE-4
- It has also been developed by Singapore and is an advanced 12U satellite designed for the technology demonstration of the High-Performance Space-borne VHF Data Exchange System (VDES).
- Using the VDES communication payload Lumelite-4 aims to augment Singapore’s e-navigation maritime safety and benefit the global shipping community.
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|
















