Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 8
| Table of contents |

|
| Asexual Reproduction |

|
| Vegetative Reproduction |

|
| Sexual Reproduction in Plants |

|
| Types of Reproduction |

|
| Key Words |

|
| Activity 1 |

|
| Activity 2: |

|
| Activity 3: |

|
Reproduction is the process of producing young ones from their parents. Plants reproduce through asexual, vegetative, and sexual means.
Asexual Reproduction
The formation of new plants from the cells of a single parent. Three common forms are budding, fragmentation, and spore formation
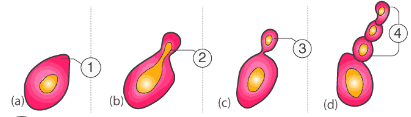
- Budding: microscopic organisms reproduce asexually by forming a bud that grows into an independent organism
- Fragmentation: adult organism breaks up into two or more fragments that grow into new plants
- Spore formation: plants such as ferns and mosses multiply asexually through spores that burst out of a protective wall and grow into new plants
Vegetative Reproduction
Type of asexual reproduction in which a cell, tissue, or part of an organ of a plant develops into a new organism
- Sexual Reproduction
Takes place by the formation of seeds through the fusion of male and female reproductive cells. Involves two parents and the formation of a single cell called the zygote
Vegetative Reproduction
In some plants, vegetative parts such as root, stem, and leaf can be used to produce new plants. This type of reproduction is known as vegetative reproduction. It can be done by natural as well as artificial methods.
- Natural Methods
Most plants reproduce naturally without the involvement of human beings. They do so with the help of stems, roots, and leaves. - Reproduction through Roots
Tuberous roots of sweet potato, Dahlia, and Asparagus can be set aside for multiplication in the next season. These roots have food stored in them. - Reproduction through Stems
Stems are the most common parts involved in vegetative propagation. Vegetative propagation through stems is of the following types: Plants such as Oxalis and grass have horizontal stems growing parallel to the ground, almost touching it. New roots sprout from the nodes, and new shoots also grow upwards forming new plants at frequent intervals. In plants such as mint and Chrysanthemum, horizontal stems arise from the base of the erect shoot, grow horizontally in the soil, and then come out to form new aerial shoots. These shoots become independent plants when stems break away from the parent plants. Some plants have arched stems which cross over small obstacles and develop small plantlets at their nodes, e.g., Vallisneria, wild strawberry. Some plants have stems that grow underground. They are mostly swollen because they have food stored in them. The different types of underground stems are: rhizomes, bulbs, tubers, and corms.
Types of Underground Stems
- Rhizomes: They have buds from which outgrowths are produced which give rise to new plants. This is seen in ginger, turmeric, and banana.
- Bulbs: They are very short underground stems encased in thickened fleshy bulb scales (which are modified leaves). The scales serve as sites of food storage. This is seen in onions. In the spring, when a new plant shoots up from the centre of the scale cluster, it gets its food from the scales.
- Tubers: They have buds in the eyes, which give rise to new plants, e.g., potato.
- Corms: They are lots of rhizomes joined together which develop into new plants, e.g., Gladiolus and Colocasia.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
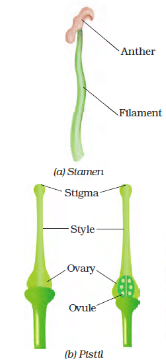
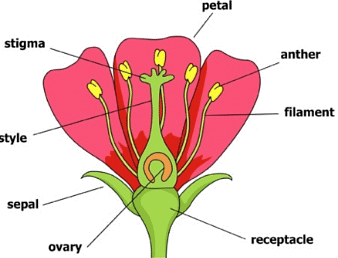
Sexual reproduction is the fusion of male and female gametes. It occurs only in flowering plants. Flowers are the reproductive organs of a plant. Flowers can be complete (having both male and female reproductive cells) or incomplete (having either male or female cells). A complete flower has sepals, petals, stamens, and pistil. Stamens are the male organs that bear the anthers containing pollen grains. Pistil is the female organ that produces female cells in the ovary.
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma. It is the first step in the process of seed formation. Pollination can be self-pollination (transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the same flower) or cross-pollination (transfer of pollen from one flower to another). Pollination can occur through wind, water, or animals.
Fertilization
- Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- It occurs in the ovary of the flower.
- After fertilization, the ovary develops into a fruit.
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction is the process by which new plants are produced from vegetative parts of the plant such as roots, stems, and leaves. This method is commonly used in plants like potato, onion, ginger, and banana.
- Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the process by which new plants are produced from the fusion of male and female reproductive cells. In plants, sexual reproduction occurs through flower formation and pollination. - Flower Formation
Flower formation is the process by which the reproductive structure of the plant is formed. It consists of four main parts: sepals, petals, stamen, and pistil. - Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organ to the female reproductive organ. This can occur through self-pollination or cross-pollination. - Fruit and Seed Formation
After fertilization, the ovary enlarges to form the fruit. The ovules become the seeds. A fruit may have one or more seeds. Petals, sepals, and other parts of the flower usually dry up and fall off. - Germination
The process by which the embryo in the seed becomes active and begins to grow into a new plant is called germination. When a seed has matured and suitable conditions of air, water, and temperature are available, it germinates. - Know Your Scientist
Jagadish Chandra Bose was the first Indian who did a detailed study on plants and their responses. He invented a special machine called the crescograph that could measure the growth in plants. His plant experiments had direct connections with an ancient text on plants called Vrikshayurveda'.
Types of Reproduction
- Plants can reproduce through sexual and asexual reproduction.
- Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
- Asexual reproduction involves the production of new plants without the involvement of gametes.
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
- Male reproductive organs in plants are called stamens, which produce pollen.
- Female reproductive organs in plants are called pistils, which contain the ovules.
- Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the pistil.
- Fertilization occurs when the pollen grain reaches the ovule and forms a zygote.
- The zygote develops into an embryo, which grows into a seed.
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Asexual reproduction in plants can occur through various methods such as fragmentation, budding, and vegetative propagation. Fragmentation is the breaking of a plant into pieces, which grow into new plants. Budding is the formation of a new plant from a bud on the parent plant. Vegetative propagation involves the use of plant parts such as stems, leaves, or roots to produce new plants.
Seed Dispersal
Seed dispersal is the process by which seeds or fruits are scattered to reduce competition and enter new habitats. Dispersal can occur through mechanisms such as wind, water, explosion, and animals. Wind dispersal involves seeds with wings or threads that can be carried long distances. Water dispersal involves seeds with a spongy outer coat that can float on water. Explosion dispersal involves seeds that are automatically set free by opening of the fruit. Animal dispersal involves fruits that are eaten by birds and mammals, which pass the seeds through their digestive tract or carry them on their fur or feet.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Reproduction in Plants
|
Download as PDF |
Key Words
Activity 1
Aim: To observe asexual reproduction in Spirogyra
Materials needed: Spirogyra, microscope, slide, cover slip, water dropper
Method:
1. Take a piece of Spirogyra and place it on a slide
2. Add a drop of water and cover it with a cover slip
3. Observe the Spirogyra under a microscope
4. Look for any signs of fragmentation
Observation: If fragmentation has occurred, there will be two or more pieces of Spirogyra growing on the slide.
Conclusion: Spirogyra reproduces asexually through fragmentation.
Activity 2:
Aim: To observe vegetative reproduction in plants.
Materials needed: A potato, knife, potting soil, and a pot.
Observation: Cut the potato into small pieces, each containing an eye. Plant the pieces in the potting soil in the pot. Water it regularly. Observe the growth of new potato plants from the pieces.
Activity 3:
Aim: The aim of the activity is to observe the process of pollination and fertilization in plants.
Method: Choose a flower and observe the different parts of the flower. Use a magnifying glass to observe the pollen and ovary.
Use a brush to collect pollen from the stamen and transfer it to the stigma.
Observe the growth of the ovary and the formation of a seed.
|
140 videos|108 docs|18 tests
|




























