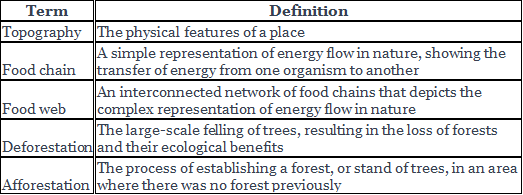
Forests - Our Lifeline Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12
| Table of contents |

|
| The Profile of a Forest |

|
| Interdependence of Plants and Animal |

|
| Conservation of Forests |

|
| Key Words |

|
| Activity |

|
The Profile of a Forest
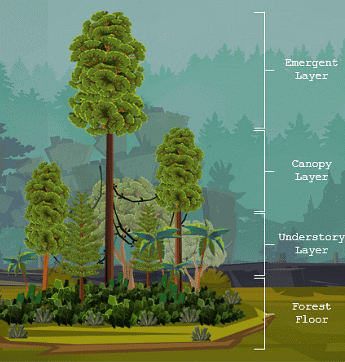
Forests cover about one-third of the world's land surface. Forests vary based on location, climate, topography, and soil type. Four layers of a mature forest: canopy, crown, understorey, and forest floor.
- Canopy: The uppermost layer of branches that forms a dense roof over the forest floor.
- Crown: The layer where tree branches branch off from the trunk.
- Understorey: The shaded layer with low light availability where shrubs, ferns, grasses, and weeds grow.
- Forest Floor: The ground layer consisting of plant litter, dead plants and animals, and decomposers like bacteria and fungi.
India has diverse forests with various uses.
Uses of Forests
Early humans relied on forests for food, clothing, and shelter. Forests have multiple direct and indirect benefits for humans. India is a mega-biodiversity center with numerous plant and animal species. Forests prevent soil erosion and floods by binding soil particles with tree roots. Trees regulate the climate by absorbing water through roots and releasing it as water vapor, leading to cooler air and rainfall. Trees help mitigate global warming by utilizing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Some trees act as windbreakers, protecting coastal areas from strong winds, storms, and tidal waves. Forests provide timber, firewood, nuts, spices, and various medicinal plants. Ayurvedic medicines are derived from plants like neem, eucalyptus, and amla. Cinchona trees produce quinine, essential for treating malaria. Essential oils are obtained from grasses like lemon grass, kewra, and khus, as well as from sandalwood, eucalyptus, and pine. Forests are a source of resins, latex, bamboo, and cane used in various industries.
Forests Help in Purifying Air
Forests release a significant amount of oxygen into the air. Green plants use carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis. Forests act as a sink for carbon dioxide, balancing oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. Forests are often referred to as the 'lungs' of the Earth, especially rainforests.
Interdependence of Plants and Animal
All animals depend on plants for food, directly or indirectly, forming a food chain. Green plants are called producers as they can produce their own food. Animals are called consumers as they cannot produce their own food and depend on plants and other animals for food. When animals die, their bodies are broken down by decomposers such as bacteria and fungi, and they become a part of the soil, making it fertile for plant growth. Several food chains that exist in nature are interconnected, forming a more complex representation of energy flow in nature called a food web.
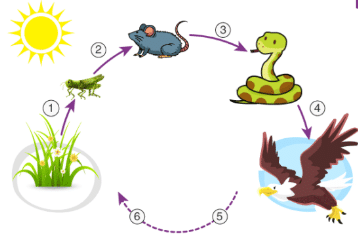
Role of Trees in Forests
- Trees in forests provide shelter to animals such as chimpanzees, monkeys, gorillas, snakes, chipmunks, birds, and squirrels.
- Trees absorb the harmful effects of natural elements such as wind, sunlight, and rainfall, thus protecting animals.
- Several insects and birds become agents that bring about pollination of flowers, thereby assisting in fruit formation.
- Seeds of several plants depend on animals for dispersal, which is important for the survival of those at far off places.
Interdependence of Plants and Animals
All animals depend on plants for food, directly or indirectly. Decomposers break down dead animals and make the soil fertile for the growth of plants. Trees in forests provide shelter to animals and absorb harmful natural elements such as wind, sunlight, and rainfall. Several insects and birds assist in pollination of flowers. Seeds of several plants depend on animals for dispersal.
If Forests Disappear
Deforestation is the large-scale felling of trees that results in permanent destruction of forests and woodlands. Deforestation leads to the loss of habitat for many species of animals and plants, and biological diversity. Deforestation causes the release of large amounts of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane. Deforestation depletes natural resources such as timber, medicinal plants, fruits, and nuts. Deforestation can cause severe flooding, soil erosion, landslide, etc.
Case Study: Decline in the Forest Cover of the North-eastern States of India
The forests of north-east India are very rich in biodiversity but have been declining in forest cover due to shifting cultivation and development activities. The top five states-Mizoram, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and Meghalaya-have showed a huge decline in forest cover. Extensive deforestation for developmental activities has led to an overall decrease in the forests. The loss of forests is leading to a loss in biodiversity.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Forest: Our Lifeline
|
Download as PDF |
Conservation of Forests
Conservation of forests refers to preventing the further depletion of forests and preserving their biodiversity. Afforestation is an effective measure to conserve forests. It involves planting trees on lands where there were no forests previously. Planned cultivation should be adopted instead of clearing forests for agriculture to prevent soil erosion. Illegal logging has led to the decrease in the number of trees. The Indian government has made it punishable under law to prevent illegal logging. Provision of sufficient pastures should be made in areas adjoining forests to prevent overgrazing and trampling of growing plants by cattle. Forest fires are beneficial for plants but can have devastating effects on animal life and people living nearby. These fires can be prevented by being careful while burning debris. Fire retardants and water bombs are also used to prevent forest fires.
Indian Forests
India has a diverse range of forests that can be classified into five categories: open forests, dry forests, scrublands, mangroves, and dense forests. Open forests are found in the Himalayan region and northeastern parts of India. Dry forests are mainly found in central India and are well-adapted to dealing with long dry seasons. Scrublands are areas covered by grass or thorn scrubs and are commonly found in the Deccan Plateau. Mangroves are well-adapted to salty and swampy habitats and are found in the Gangetic Sunderbans, the largest mangrove area in India. Dense forests have thick vegetation and a dense canopy cover. They are found in the Western Ghats and the Eastern Himalayas, which are tropical forests.
Indian Forests
- Indian forests can be classified into five categories based on their characteristics: Open forests, Dry forests, Scrublands, Mangroves, and Dense forests.
- Open forests are found in the Himalayan region and the North-eastern parts of India.
- Dry forests are mainly found in Central India and are well adapted to long dry seasons.
- Scrublands are covered by grass or thorn scrubs and are found in the Deccan Plateau and the Himalayan region.
- Mangroves are well adapted to salty and swampy habitats and are found in the Gangetic Sunderbans.
- Dense forests are found in the Western Ghats and the Eastern Himalayas and have thick vegetation and a dense canopy cover.
Case Study: Forest Fires in India
Forest fires are a major threat to the environment and cause a lot of damage to forests and wildlife. In May 2018, several hectares of forest cover were lost in Uttarakhand due to massive forest fires. Global warming is one of the prime reasons for forest fires as it leads to a rise in temperature and the release of excessive carbon dioxide. Most forest fires, however, are caused due to human negligence, climate change, and excessive deforestation. Dried pine needles and eucalyptus leaves are highly inflammable and facilitate the propagation of forest fires.
Key Words
Activity
Aim: To explore a local forest and understand its importance
Materials: Notebook, pen/pencil, camera (optional)
Method:
- Choose a nearby forest or wooded area.
- Take notes on the types of trees, plants, and animals you observe.
- Observe and document the interdependence between plants and animals.
- Take pictures (if possible) to create a visual record of your exploration.
- Reflect on the importance of forests in your observations.
- Share your findings with the class and discuss the significance of forests in our lives.
Conservation:
- Forest conservation is the sustainable management and preservation of forests.
- It aims to protect biodiversity, maintain ecological balance, and provide socio-economic benefits.
- Conservation measures include afforestation, reforestation, wildlife protection, and sustainable harvesting practices.
- Active participation and awareness among individuals and communities are crucial for successful forest conservation.
|
140 videos|108 docs|18 tests
|
















